Kawasaki Unveils Japan’s Future of Transport | #breakingnews #Robotics.
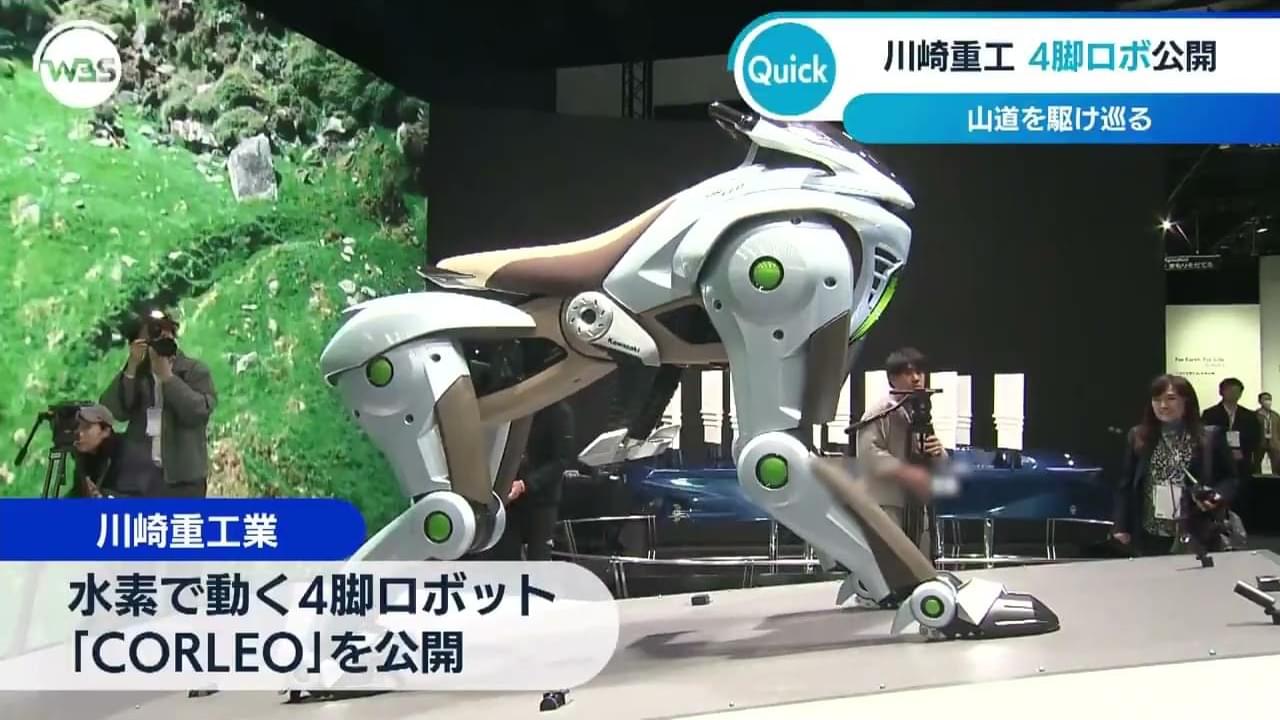
🚨 Japan’s Kawasaki has unveiled a groundbreaking concept robot called CORLEO that could revolutionize future transport.
🔹 Designed to resemble a lion for navigating rough and mountainous terrains.
🔹 Powered by a hydrogen engine—eco-friendly innovation.
🔹 Controlled by shifting body weight, similar to horseback riding.
🔹 A bold step into the future of personal robotic transport.
📢 Keywords:
Kawasaki CORLEO robot, Japan transport robot, hydrogen-powered robot, robotic lion vehicle, futuristic mobility, mountain transport robot, robotics innovation Japan.
📢 Hashtags:
#ThriveNews #Japan #Robotics #Kawasaki #CORLEO #FutureTransport #Innovation #TechNews #HydrogenPower