Pix has spiced up Brazil’s fusty banking sector, but it gives the central bank a worrying amount of power
Category: finance
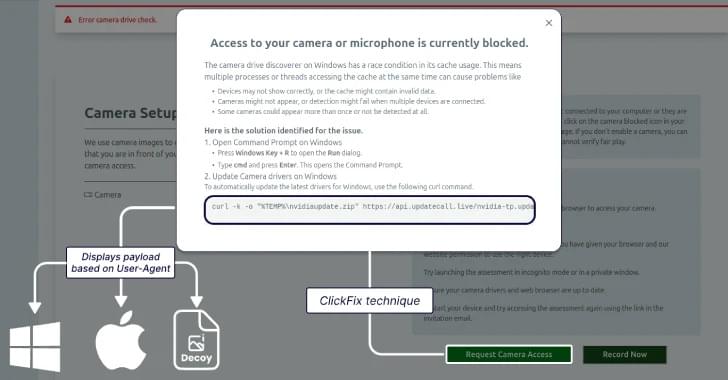
Lazarus Group deploys GolangGhost via fake job interviews using ClickFix, targeting Windows/macOS users with finance roles.
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, shares the groundbreaking potential of AI Copilot — a powerful tool that’s transforming how we work. From streamlining everyday tasks to revolutionizing healthcare workflows, AI Copilot is designed to seamlessly integrate with the tools we already use, like Teams, Word, and Excel.
Satya Nadella explains how AI Copilot is helping doctors prepare for high-stakes meetings, automatically generating agendas, summaries, and even PowerPoint presentations. Plus, see how it empowers professionals to gather the latest insights, collaborate with teams, and create smarter workflows with ease.
Thank You for watching! Do not forget to Like | Comment | Share.
About the channel.
Watch us for the best news and views on business, stock markets, crypto currencies, consumer technology, the world of real estate, bullion, automobiles, start-ups and unicorns and personal finance. Business Today TV will also bring you all you need to know about mutual funds, insurance, loans and pension plans among others.
Follow us at:
An Arlington-based venture capital firm has announced it will pour $32 million in funding into cybersecurity startups.
Runtime Ventures, based out of Arlington and Austin, Texas, officially announced the capital commitment today (Wednesday).
It has already made 11 investments from the fund so far, supporting seed-stage cybersecurity companies focused on domains including code analysis, fraud protection, threat detection and browser security.
Lilly’s lepodisiran reduced levels of genetically inherited heart disease risk factor, lipoprotein(a), by nearly 94% from baseline at the highest tested dose in adults with elevated levels
Posted in biotech/medical, business, finance, genetics | Leave a Comment on Lilly’s lepodisiran reduced levels of genetically inherited heart disease risk factor, lipoprotein(a), by nearly 94% from baseline at the highest tested dose in adults with elevated levels
The Investor Relations website contains information about Eli Lilly and Company’s business for stockholders, potential investors, and financial analysts.
494,000 Americans Affected As Massive Data Breach Exposes Names, Financial Records, Medical Data, Social Security Numbers and More: Report
Posted in biotech/medical, cybercrime/malcode, finance | Leave a Comment on 494,000 Americans Affected As Massive Data Breach Exposes Names, Financial Records, Medical Data, Social Security Numbers and More: Report
A cybersecurity incident affecting nearly half a million people has exposed personal, financial and medical information.
The mobility and assistive solutions provider Numotion says 494,000 customers are affected by a data breach witnessed between September 2nd, 2024, and November 18th, 2024, reports Security Week.
Numotion says an unknown entity managed to access the email accounts of the firm’s employees without authorization several times.
Tesla is preparing to launch its robo taxi in June, leveraging its unique autonomy and data advantages to navigate challenges such as new tariffs and production shifts, while positioning itself for significant growth amid declining competitor viability ## Questions to inspire discussion ## Tesla’s Robo Taxi Service.
🚕 Q: When and where is Tesla launching its robo taxi service? A: Tesla’s robo taxi service is set to launch in Austin, Texas in June 2025, with plans for a nationwide rollout in the US later that year.
🏎️ Q: What vehicles will be eligible for Tesla’s robo taxi service? A: The service will be available on all vehicles equipped with Full Self-Driving (FSD) capability, including existing Model 3 and Model Y, not just the upcoming Cybertruck.
💰 Q: How will Tesla’s robo taxi network economics work? A: The economics will be based on cost per mile, factoring in low capital costs of Tesla EVs and low power consumption of their onboard autonomy systems.
📊 Q: What competitive advantage does Tesla have in the robo taxi market? A: Tesla’s existing fleet of billions of miles of deployed vehicles and hundreds of thousands of users provide a massive data advantage for improving and assessing the service. ## Tariffs and Supply Chain.
🏭 Q: What is Tesla’s supply chain strategy? A: Tesla aims to build cars where sold for environmental reasons, which is considered best practice in network design but extremely difficult to implement.
Law enforcement authorities in seven African countries have arrested 306 suspects and confiscated 1,842 devices as part of an international operation codenamed Red Card that took place between November 2024 and February 2025.
The coordinated effort “aims to disrupt and dismantle cross-border criminal networks which cause significant harm to individuals and businesses,” INTERPOL said, adding it focused on targeted mobile banking, investment, and messaging app scams.
The cyber-enabled scams involved more than 5,000 victims. The countries that participated in the operation include Benin, Côte d’Ivoire, Nigeria, Rwanda, South Africa, Togo, and Zambia.
African law enforcement authorities have arrested 306 suspects as part of ‘Operation Red Card,’ an INTERPOL-led international crackdown targeting cross-border cybercriminal networks.
Between November 2024 and February 2025, authorities seized 1,842 devices allegedly used in mobile banking, investment, and messaging app scams linked to over 5,000 victims.
“Ahead of the operation, countries exchanged criminal intelligence on key targets. This intelligence was enriched by INTERPOL with insights into criminal modus operandi using data from its private sector partners—Group-IB, Kaspersky and Trend Micro,” the international police organization said.
A team of computer scientists and financial specialists at University College London has developed a tool to track the coordination efforts of pump-and-dump crypto coin scheme manipulators. They have published a paper on the arXiv preprint server describing their tool called Perseus, its purpose and how it works.