What are the potential health risks from airborne dust pollution, especially in the growing threat of climate change? This is what a recent study published | Earth And The Environment
Category: sustainability
Reports of extraterrestrial beings, particularly the iconic “grey aliens,” have permeated modern folklore and ufology since the mid-20th century. These beings — typically described as small-statured humanoids with large, black almond-shaped eyes, diminutive noses and mouths, and grey skin — have become embedded in our cultural consciousness (Sagan, 1995). But what if these entities are not visitors from distant stars, but rather glimpses of our own evolutionary future? This essay explores a compelling hypothesis: that the grey aliens reported in countless encounters might be evolved or bio-engineered humans from our future, adapted specifically for subterranean existence following a global catastrophe.
Humanity stands at a crossroads of existential risk. Climate change, nuclear proliferation, biological warfare capabilities, and ecological collapse represent just a few of the potential calamities that could force a dramatic reshaping of human civilization (Bostrom, 2013). If surface conditions on Earth became inhospitable — whether through nuclear winter, extreme solar radiation following ozone depletion, or uninhabitable surface temperatures — surviving populations might be driven underground, initiating a profound evolutionary divergence.
“When faced with extinction-level threats, species often undergo rapid adaptation to secure their survival,” notes evolutionary biologist Dr. Elena Rodriguez (2022, p. 87). “Humans, with their capacity for technological intervention in their own biology, could potentially accelerate this process by orders of magnitude.”
Scientists unveil MacGyver-like energy breakthrough with unexpected materials: ‘Materials … have garnered considerable attention’
Posted in chemistry, energy, sustainability | Leave a Comment on Scientists unveil MacGyver-like energy breakthrough with unexpected materials: ‘Materials … have garnered considerable attention’
In answer, the team needed to develop an affordable catalyst that could improve the salty electrode. For reference, when batteries operate, ions move between the anode and cathode through the electrolyte, per a U.S. Department of Energy description.
This is where wood waste and urine enter the lab, replacing platinum as a catalyst. The UNIST creation facilitates effective electrochemical reactions and quick discharges. The experts used lignin, abundant in wood and used to make paper and biofuels, in combination with urea. Urea is a nitrogen-rich substance found in wastewater, UNIST reported.
“Conventional electrocatalysts, primarily noble metals, are scarce and expensive. In this context, carbon materials derived from biowaste have garnered considerable attention,” according to the abstract.
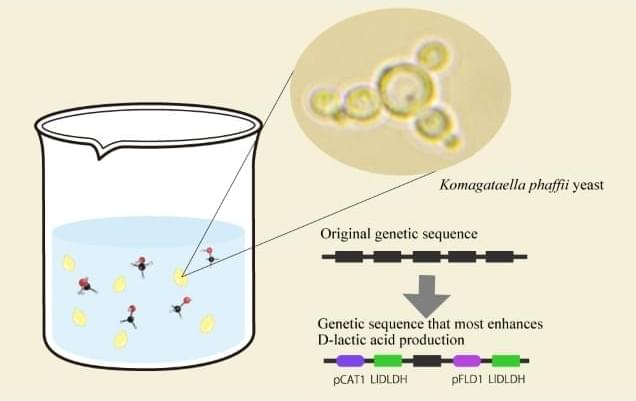
Constructed strain achieves record-high yield from methanol, advancing ecofriendly biomanufacturing. Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University have discovered the ideal genetic “recipe” to turn yeast into a tiny yet powerful eco-friendly factory that converts methanol into D-lactic acid, a key compound used in biodegradable plastics and pharmaceuticals.
This approach could help reduce reliance on petroleum-based processes and contribute to more sustainable chemical production.
Lactic acid is widely used in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and bioplastics.
Scientists have discovered a new phylum of microbes in Earth’s Critical Zone, an area of deep soil that restores water quality. Ground water, which becomes drinking water, passes through where these microbes live, and they consume the remaining pollutants. The paper, “Diversification, niche adaptation and evolution of a candidate phylum thriving in the deep Critical Zone,” is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Leonardo da Vinci once said, “We know more about the movement of celestial bodies than about the soil underfoot.” James Tiedje, an expert in microbiology at Michigan State University, agrees with da Vinci. But he aims to change this through his work on the Critical Zone, part of the dynamic “living skin” of Earth.
“The Critical Zone extends from the tops of trees down through the soil to depths up to 700 feet,” Tiedje said. “This zone supports most life on the planet as it regulates essential processes like soil formation, water cycling and nutrient cycling, which are vital for food production, water quality and ecosystem health. Despite its importance, the deep Critical Zone is a new frontier because it’s a major part of Earth that is relatively unexplored.”
Copper is the mineral most fundamental to the human future because it is essential to electricity generation, distribution, and storage. Copper availability and demand determine the rate of electrification, which is the foundation of current climate policy. Many studies have raised concerns that copper supply cannot meet the copper demands of both the green energy transition and equitable global development, but the seemingly universal presumption persists that the copper needed for the green transition will somehow be available. This need not be the case for even the first step of vehicle electrification.
This paper addresses this issue by projecting copper supply and demand from 2018 to 2050 and placing both in the historical context of copper mine output. Discussion is focused on a single diagram that illustrates the unprecedented nature of the copper mining challenge and ways to reduce copper demand.
Just to meet business-as-usual trends, 115% more copper must be mined in the next 30 years than has been mined historically until now. To electrify the global vehicle fleet requires bringing into production 55% more new mines than would otherwise be needed. On the other hand, hybrid electric vehicle manufacture would require negligible extra copper mining.
A race is on in solar engineering to create almost impossibly-thin, flexible solar panels. Engineers imagine them used in mobile applications, from self-powered wearable devices and sensors to lightweight aircraft and electric vehicles. Against that backdrop, researchers at Stanford University have achieved record efficiencies in a promising group of photovoltaic materials.
Chief among the benefits of these transition metal dichalcogenides – or TMDs – is that they absorb ultrahigh levels of the sunlight that strikes their surface compared to other solar materials.
“Imagine an autonomous drone that powers itself with a solar array atop its wing that is 15 times thinner than a piece of paper,” said Koosha Nassiri Nazif, a doctoral scholar in electrical engineering at Stanford and co-lead author of a study published in the Dec. 9 edition of Nature Communications. “That is the promise of TMDs.”
The search for new materials is necessary because the reigning king of solar materials, silicon, is much too heavy, bulky and rigid for applications where flexibility, lightweight and high power are preeminent, such as wearable devices and sensors or aerospace and electric vehicles.
New, ultrathin photovoltaic materials could eventually be used in mobile applications, from self-powered wearable devices and sensors to lightweight aircraft and electric vehicles.
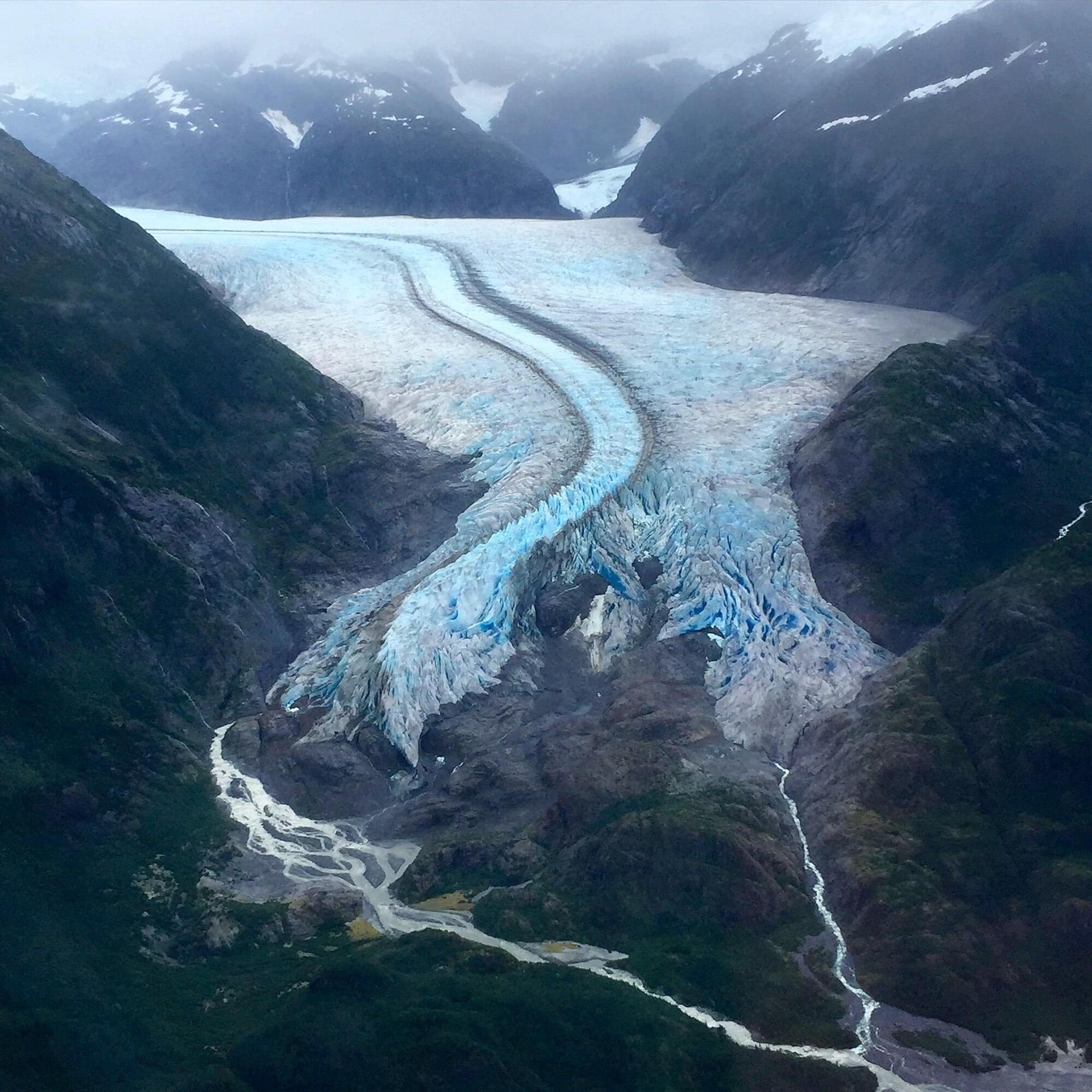
Among the mountains of evidence that climate change is warming Earth faster than any other point in recorded history is the fact that most glaciers around the world are shrinking or disappearing. Melting glaciers and ice sheets are already the biggest contributors to global sea level rise, and according to the World Glacier Monitoring Service, ice loss rates have increased each decade since 1970. Yet, of the approximately 200,000 glaciers in the world currently, no database exists to identify which glaciers have disappeared, and when. The Global Land Ice Measurements from Space (GLIMS) initiative, an international project designed to monitor the world’s glaciers primarily using data from optical satellite instruments, aims to change that.
“Glaciers are indicators of climate change because they grow and shrink on longer timescales than rapidly changing weather, so they give a clearer signal about climate,” said Bruce Raup, a senior associate scientist at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and director of the GLIMS initiative. “We know that glaciers are disappearing, but we’ve had no way to show that to people. So, we are making an effort to document glaciers that have disappeared and approximately when they disappeared.”
When the International Maritime Organization enacted a mandatory cap on the sulfur content of marine fuels in 2020, with an eye toward reducing harmful environmental and health impacts, it left shipping companies with several main options.
They could burn low-sulfur fossil fuels, like marine gas oil, or install cleaning systems to remove sulfur from the exhaust gas produced by burning heavy fuel oil. Biofuels with lower sulfur content offer another alternative, though their limited availability makes them a less feasible option.
While installing exhaust gas cleaning systems, known as scrubbers, is the most feasible and cost-effective option, there has been a great deal of uncertainty among firms, policymakers, and scientists as to how “green” these scrubbers are.
Researchers at EPFL have found a way to dramatically reduce energy loss and boost efficiency in perovskite solar cells by incorporating rubidium using lattice strain—a slight deformation in the atomic structure that helps keep rubidium in place.
Solar energy is one of the most promising solutions for reducing our dependence on fossil fuels. But making solar panels more efficient is a constant challenge. Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have been a game-changer, offering rapid improvements in efficiency and potential for low-cost manufacturing. However, they still suffer from energy losses and operational stability issues.