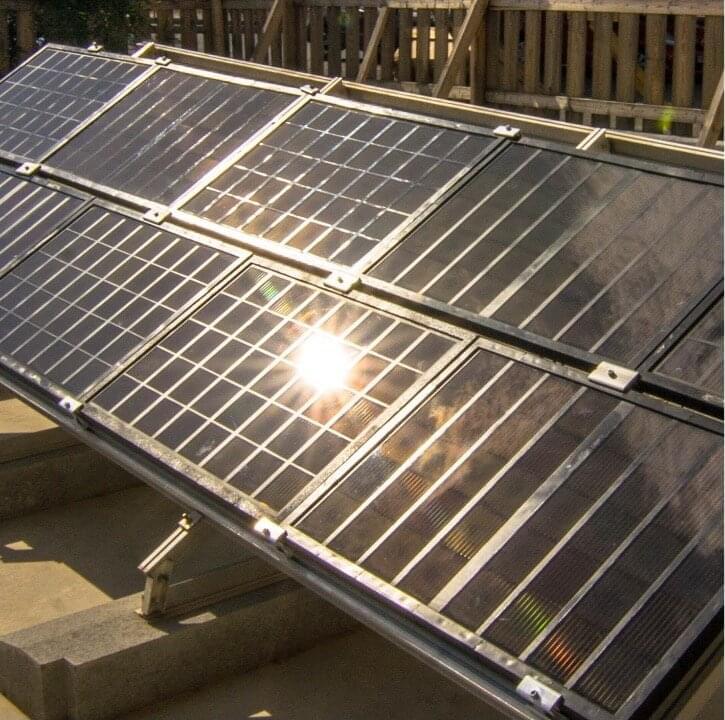
Perovskites, mineral materials composed of calcium titanate, have been found to be valuable for the fabrication of high-performance solar cells. While teams of scientists and engineers worldwide have been developing and testing perovskite solar cells in laboratory settings, large-scale outdoor evaluations of these cells are still lacking.
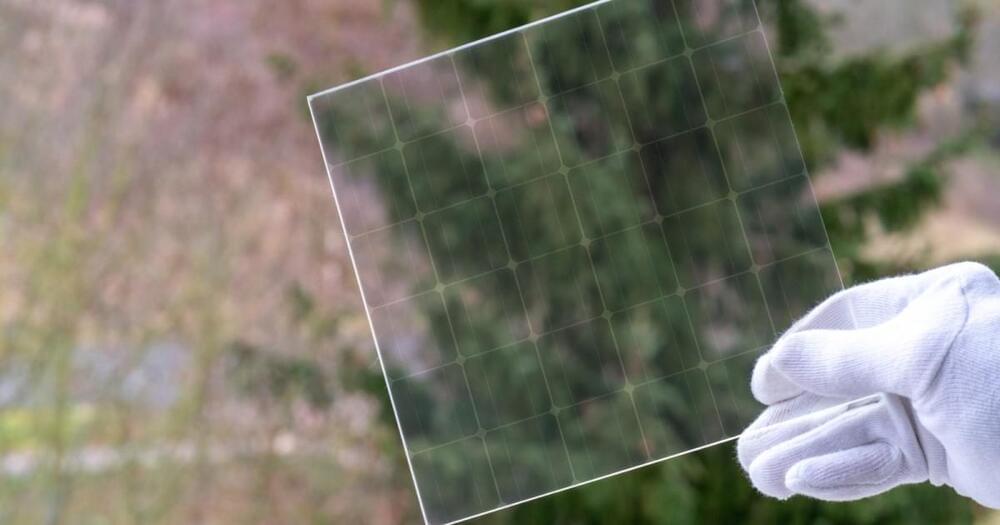
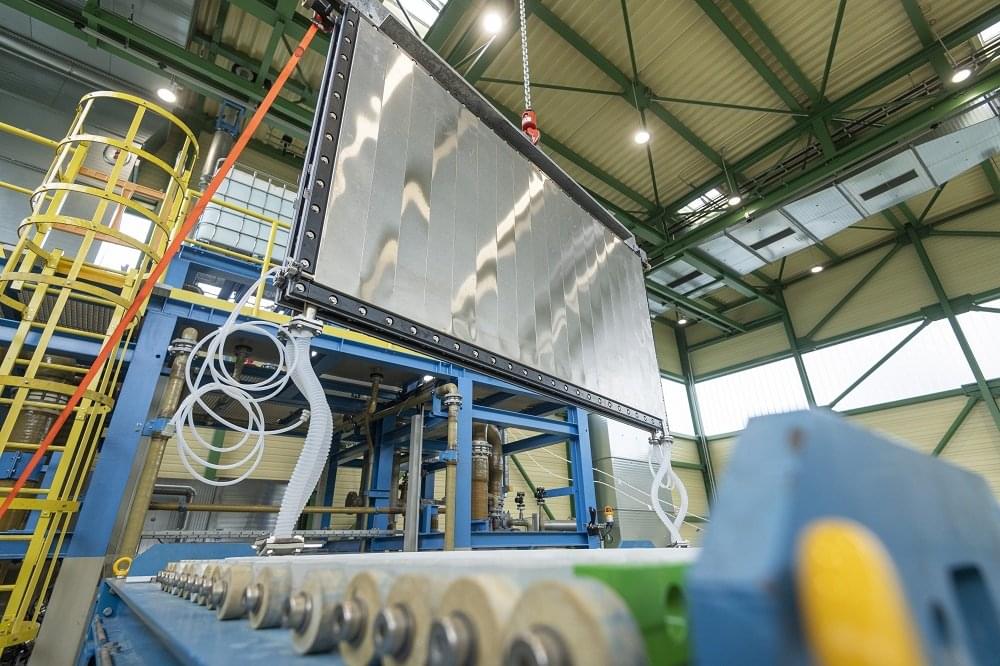
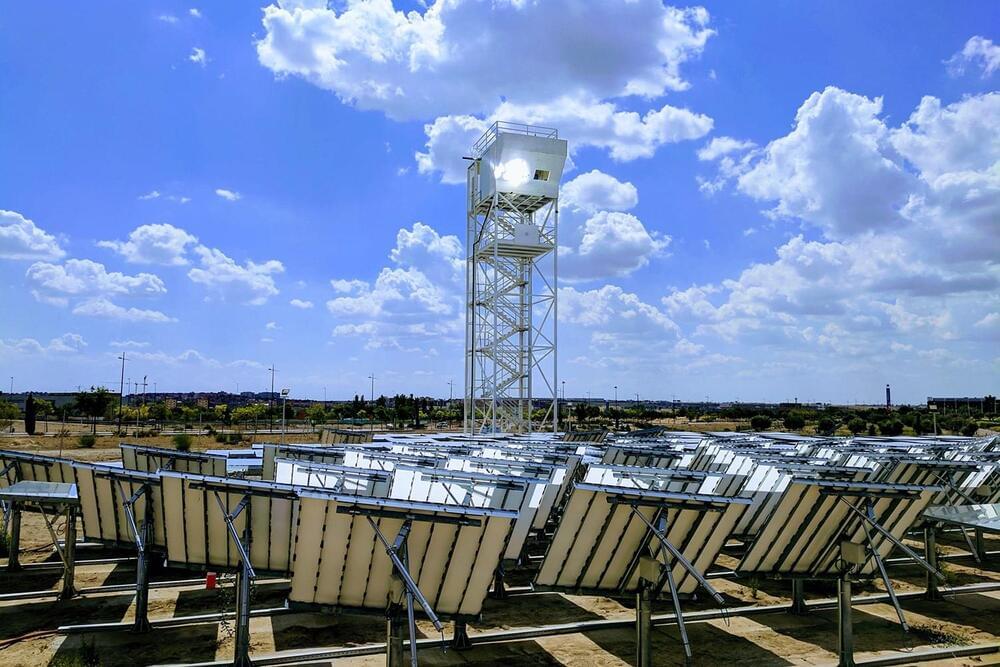
Researchers at University of Rome Tor Vergata, the Hellenic Mediterranean University in Crete, BeDimensional S.p. A., Great Cell, the Italian Institute of Technology (IIT) and University of Siena have recently manufactured large-area perovskite solar panels engineered using two-dimensional (2D) materials. They then successfully integrated 9 of these solar panels into a stand-alone solar farm, located on the Greek island of Crete. This team’s findings, presented in a paper published in Nature Energy, could facilitate and inform the future large-scale implementation of perovskite solar cells.
“Our recent paper highlights our joint research efforts for the last 5 years in the upscaling of perovskite PVs, starting from lab cells to modules, panels and finally to a solar farm infrastructure,” Francesco Bonaccorso, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told to Tech Xplore. “This project was specifically developed in the context of the European Graphene Flagship initiative, which established a close collaboration between University Tor Vergata, BeDimensional S.p. A., GreatCell and Hellenic Mediterranean University, having both complementary and widely different skillsets.”