Archive for the ‘solar power’ category: Page 50
Jul 13, 2022
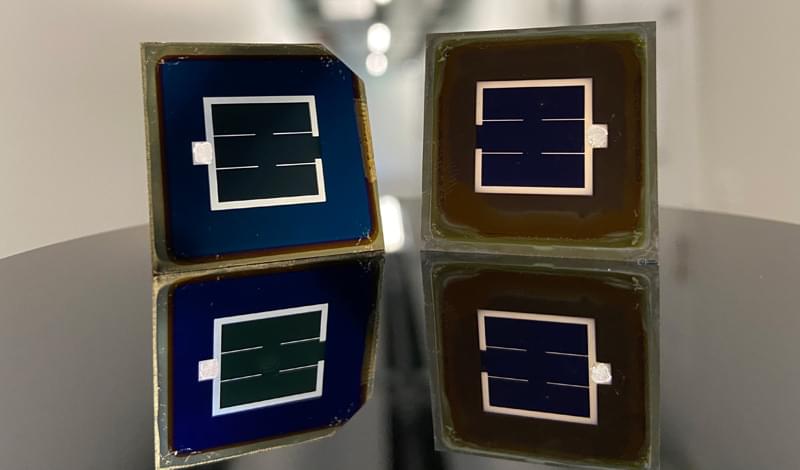
New perovskite-silicon solar cells smash through the 30 efficiency barrier
Posted by Gemechu Taye in categories: solar power, sustainability
Jul 11, 2022
Video reveals China’s first solar-powered car without a wheel
Posted by Gemechu Taye in categories: solar power, sustainability, transportation
Jul 8, 2022
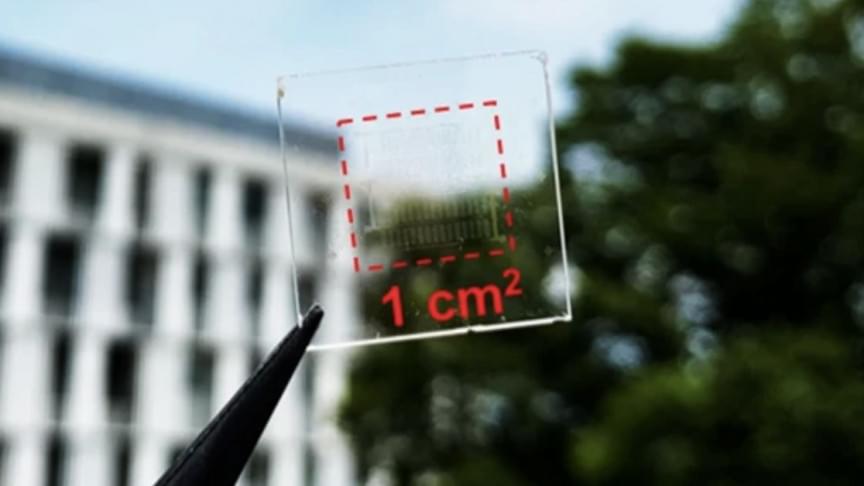
New record solar cell efficiency
Posted by Future Timeline in categories: solar power, sustainability
The first tandem perovskite-silicon solar cells to exceed 30% efficiency have been independently certified.
Jul 6, 2022
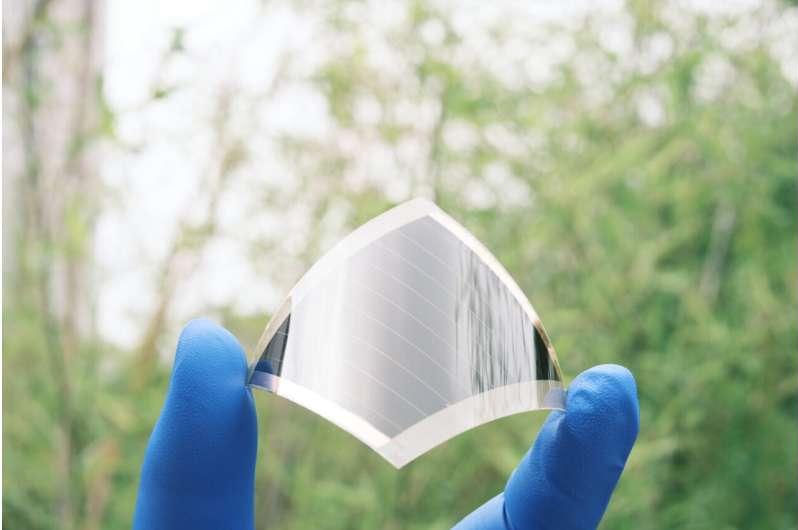
Flexible all-perovskite tandem solar cells with a 24.7% efficiency
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: solar power, sustainability, wearables
Lightweight and flexible perovskites are highly promising materials for the fabrication of photovoltaics. So far, however, their highest reported efficiencies have been around 20%, which is considerably lower than those of rigid perovskites (25.7%).
Researchers at Nanjing University, Jilin University, Shanghai Tech University, and East China Normal University have recently introduced a new strategy to develop more efficient solar cells based on flexible perovskites. This strategy, introduced in a paper published in Nature Energy, entails the use of two hole-selective molecules based on carbazole cores and phosphonic acid anchoring groups to bridge the perovskite with a low temperature-processed NiO nanocrystal film.
“We believe that lightweight flexible perovskite solar cells are promising for building integrated photovoltaics, wearable electronics, portable energy systems and aerospace applications,” Hairen Tan, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told TechXplore. “However, their highest certified efficiency of 19.9% lags behind their rigid counterparts (highest 25.7%), mainly due to defective interfaces at charge-selective contacts with perovskites atop.”
Jul 4, 2022
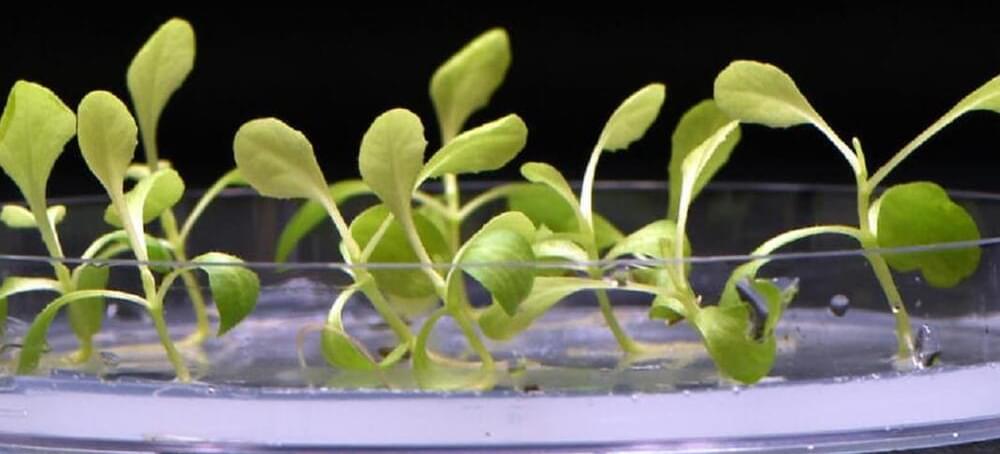
New Artificial Photosynthesis Method Grows Food With No Sunshine
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: chemistry, food, solar power, sustainability
Photosynthesis uses a series of chemical reactions to convert carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight into glucose and oxygen. The light-dependent stage comes first, and relies on sunlight to transfer energy to plants, which convert it to chemical energy. The light-independent stage (also called the Calvin Cycle) follows, when this chemical energy and carbon dioxide are used to form carbohydrate molecules (like glucose).
A research team from UC Riverside and the University of Delaware found a way to leapfrog over the light-dependent stage entirely, providing plants with the chemical energy they need to complete the Calvin Cycle in total darkness. They used an electrolysis to convert carbon dioxide and water into acetate, a salt or ester form of acetic acid and a common building block for biosynthesis (it’s also the main component of vinegar). The team fed the acetate to plants in the dark, finding they were able to use it as they would have used the chemical energy they’d get from sunlight.
They tried their method on several varieties of plants and measured the differences in growth efficiency as compared to regular photosynthesis. Green algae grew four times more efficiently, while yeast saw an 18-fold improvement.
Jul 4, 2022
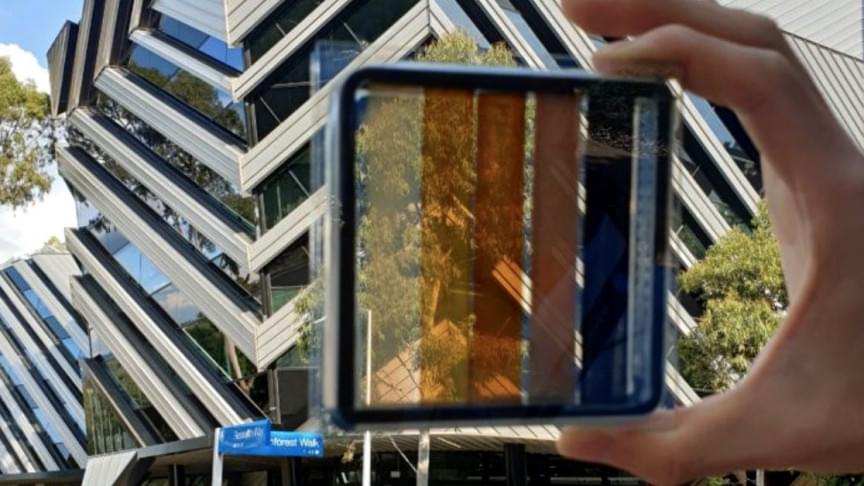
A new breakthrough could turn windows into active solar panels
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: solar power, sustainability
The dream of transforming windows into active power generators has just edged one step closer to realization.
A team of researchers from ARC Centre of Excellence in Exciton Science led by Professor Jacek Jasieniak from Monash University’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering has created perovskite cells with a conversion efficiency of 15.5 percent that allows more than 20 percent of visible light through, a press release states.
This improves the stability of solar windows while allowing more natural light in, which means the amount of visible light passing through the cells is remarkably now reaching glazing levels, increasing their potential for usage in a wide range of real-world applications.
Jul 3, 2022
Soof Azani and Lir Braverman propose collapsible solar-powered bike for last-mile deliveries
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: business, solar power, sustainability, transportation
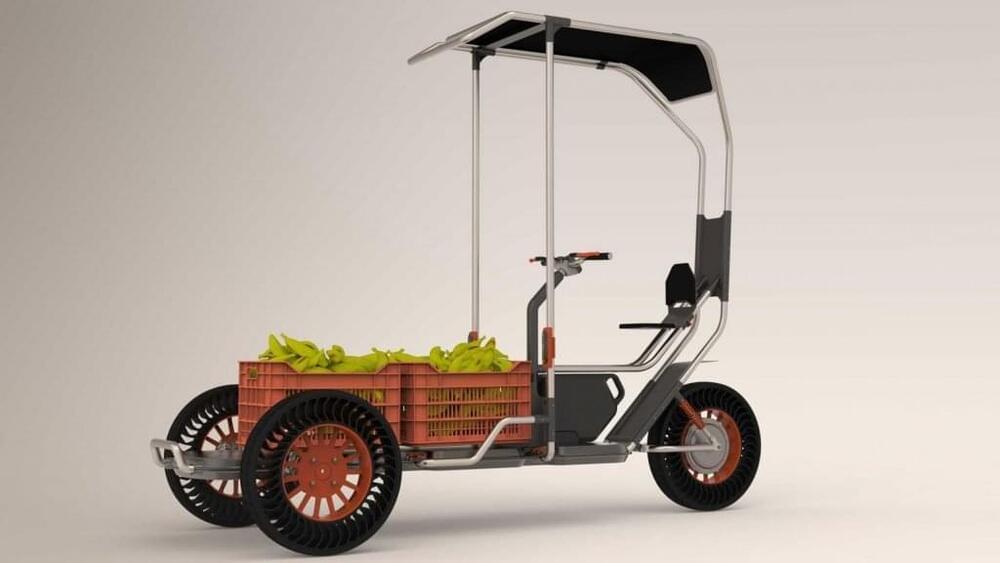

Soof Azani and Lir Braverman’s proposal for a solar-powered cargo bike that aims to facilitate local deliveries is the latest of 10 visionary transportation projects selected for Dezeen’s Future Mobility Competition powered by Arrival.
Called D50, Azani and Braverman’s concept aims to combine solar power with micro-mobility in a bid to improve the distribution of goods while reducing carbon emissions.
Jul 3, 2022
IKEA will now sell solar panels
Posted by Raphael Ramos in categories: government, habitats, solar power, space, sustainability
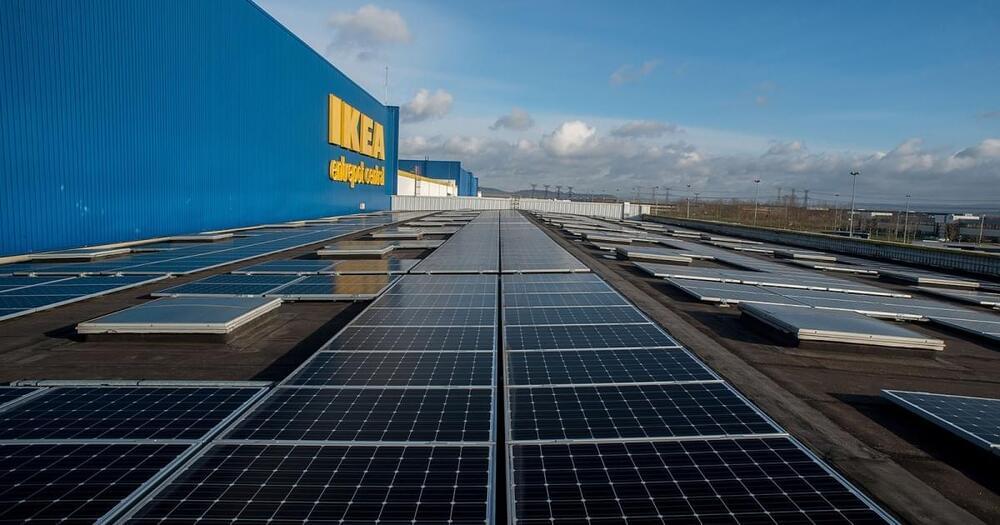

IKEA, the world’s largest furniture retailer, has announced plans to sell home solar panels in the US — a move that could democratize and demystify access to solar.
Solar hesitancy: The benefits of solar go beyond protecting the environment — solar panels are cheaper than ever, and between the lower energy bills and government subsidies, a home solar system could pay for itself before the panels need to be replaced.
Jul 1, 2022
Nextracker & BCI Steel Renovate Abandoned Pittsburgh Steel Factory to Serve Growing U.S. Utility-Scale Solar Market
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: solar power, sustainability
This is Nextracker’s third new factory, adding to the company’s new Texas and Arizona factories announced in April and May, towards building 10 GW of annual domestic solar tracker capacity. Courtesy of Nextracker — by Pallavi Singla.
Nextracker LLC, the global market leader in utility-scale solar trackers, and BCI Steel, a Pittsburgh-based steel fabricator, this week announced the reopening of the historic Bethlehem Steel manufacturing factory in nearby Leetsdale to produce solar tracker equipment for large-scale solar power plants.
The steel processing plant will incorporate both BCI Steel’s new and reshored equipment shipped to the U.S. from factories in Malaysia and Brazil. Solar tracker products produced at the factory will serve rapidly growing solar markets in Pennsylvania, Indiana, New York, and Ohio.