For instance, continuous-variable (CV) QKD has its own distinct advantages at a metropolitan distance36,37 due to the use of common components of coherent optical communication technology. In addition, the homodyne38 or heterodyne39 measurements used by CV-QKD have inherent extraordinary spectral filtering capabilities, which allows the crosstalk in wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) channels to be effectively suppressed. Therefore, hundreds of QKD channels may be integrated into a single optical fiber and can be cotransmitted with classic data channels. This allows QKD channels to be more effectively integrated into existing communication networks. In CV-QKD, discrete modulation technology has attracted much attention31,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50 because of its ability to reduce the requirements for modulation devices. However, due to the lack of symmetry, the security proof of discrete modulation CV-QKD also mainly relies on numerical methods43,44,45,46,47,48,51.
Unfortunately, calculating a secure key rate by numerical methods requires minimizing a convex function over all eavesdropping attacks related with the experimental data52,53. The efficiency of this optimization depends on the number of parameters of the QKD protocol. For example, in discrete modulation CV-QKD, the number of parameters is generally \(1000–3000\) depending on the different choices of cutoff photon numbers44. This leads to the corresponding optimization possibly taking minutes or even hours51. Therefore, it is especially important to develop tools for calculating the key rate that are more efficient than numerical methods.
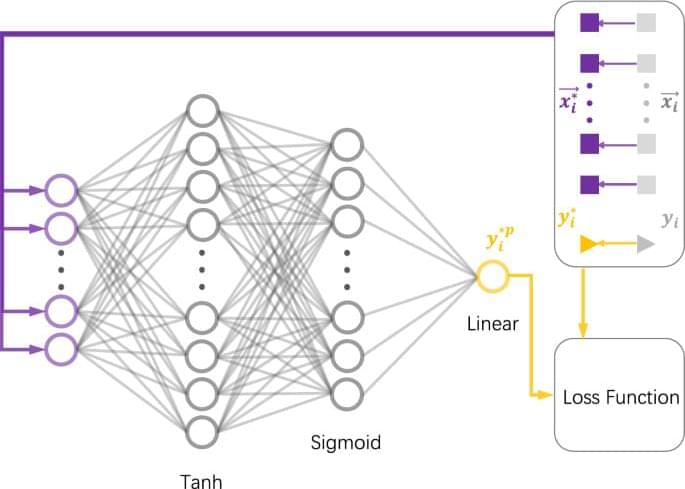
In this work, we take the homodyne detection discrete-modulated CV-QKD44 as an example to construct a neural network capable of predicting the secure key rate for the purpose of saving time and resource consumption. We apply our neural network to a test set obtained at different excess noises and distances. Excellent accuracy and time savings are observed after adjusting the hyperparameters. Importantly, the predicted key rates are highly likely to be secure. Note that our method is versatile and can be extended to quickly calculate the complex secure key rates of various other unstructured quantum key distribution protocols. Through some open source deep learning frameworks for on-device inference, such as TensorFlow Lite54, our model can also be easily deployed on devices at the edge of the network, such as mobile devices, embedded Linux or microcontrollers.