When you think of empty space, you almost certainly imagine a vacuum in which nothing interesting can ever happen. However, if we zoom in to tiny length scales where quantum effects start to become important, it turns out that what you thought was empty is actually filled at all times with a seething mass of electromagnetic activity, as virtual photons flicker in and out of existence. This unexpected phenomenon is known as the vacuum fluctuation field. However, because these fluctuations of light energy are so small and fleeting in time, it is difficult to find ways for matter to interact with them, especially within a single, integrated device.
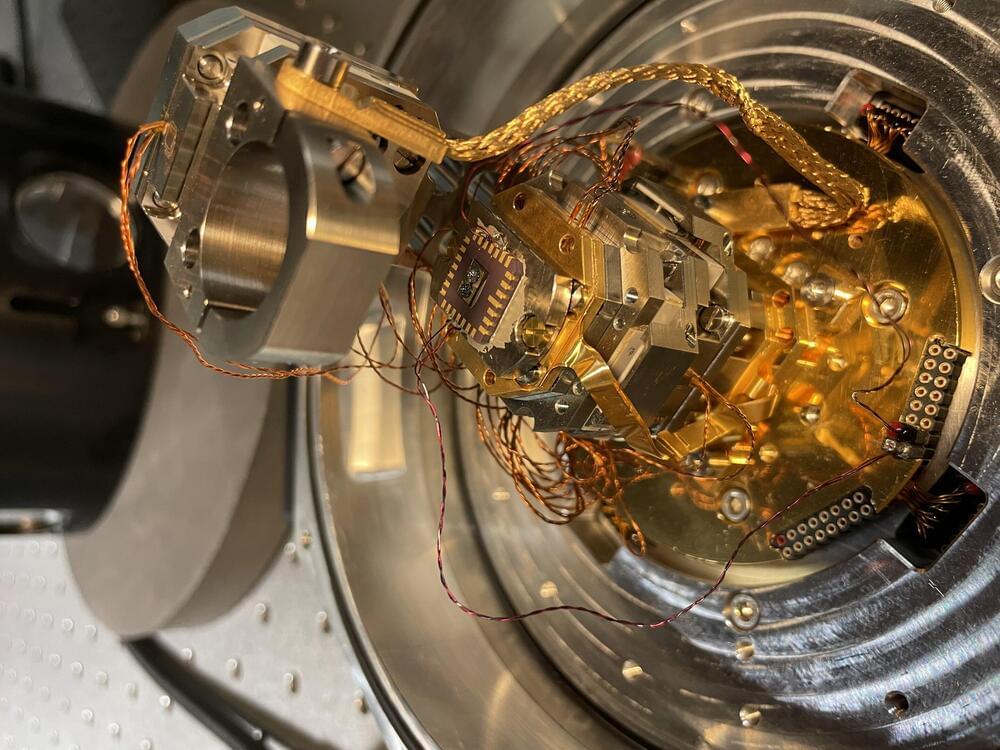
In a study published this month in Nano Letters (“Electrical Detection of Ultrastrong Coherent Interaction between Terahertz Fields and Electrons Using Quantum Point Contacts”), researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science, The University of Tokyo succeeded in fabricating a single nanoscale hybrid system for doing exactly this. In their design, a quantum point contact connects a single on-chip split-ring resonator with a two-dimensional electron system.
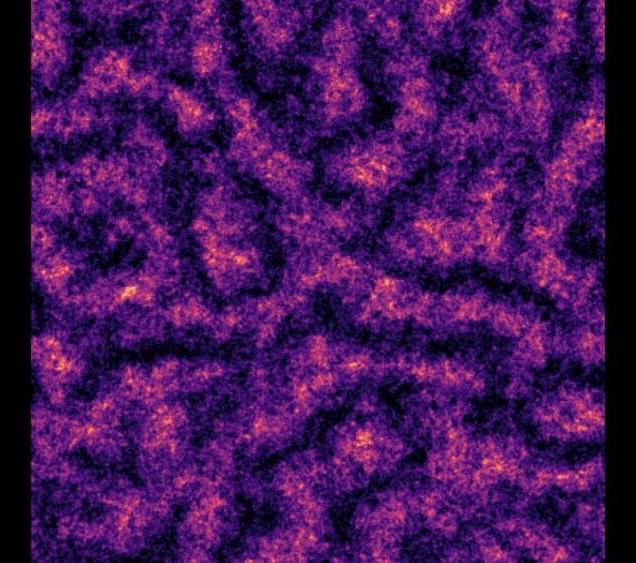
Quantum Hall edge channels at the quantum point contact. (Image: University of Tokyo)