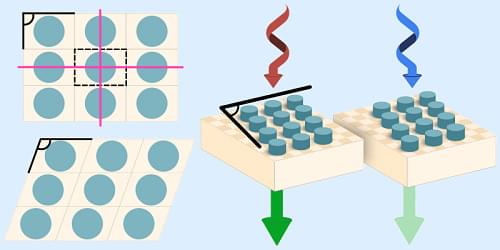
Contrary to conventional wisdom, a lattice of engineered nanoparticles called meta-atoms can have a chiral optical response even when each meta-atom is not chiral.
Category: particle physics – Page 56
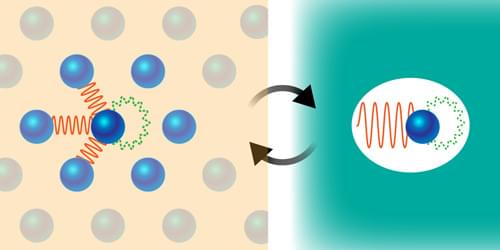
A new framework that embeds electrons in a surrounding bath captures nonlocal correlation effects that are relevant to metals, semiconductors, and correlated insulators.
Searching for new types of superconductors, magnets, and other useful materials is a bit like weaving a tapestry with threads of many different colors. The weaver selects a short-range (local) pattern for how the individual threads intertwine and at the same time chooses colors that will give an overall (nonlocal) mood. A materials scientist works in a similar way, mixing atoms instead of threads, trying to match the motion of their electrons—their correlations—on both local and nonlocal scales. Doing so by trial-and-error synthesis is time intensive and costly, and therefore numerical simulations can be of huge help. To contribute to bridging computations to material discovery, Jiachen Li and Tianyu Zhu from Yale University have developed a new approach that treats local and nonlocal electronic correlations on an equal footing [1] (Fig. 1). They demonstrated their method by accurately predicting the photoemission spectra of several representative materials.
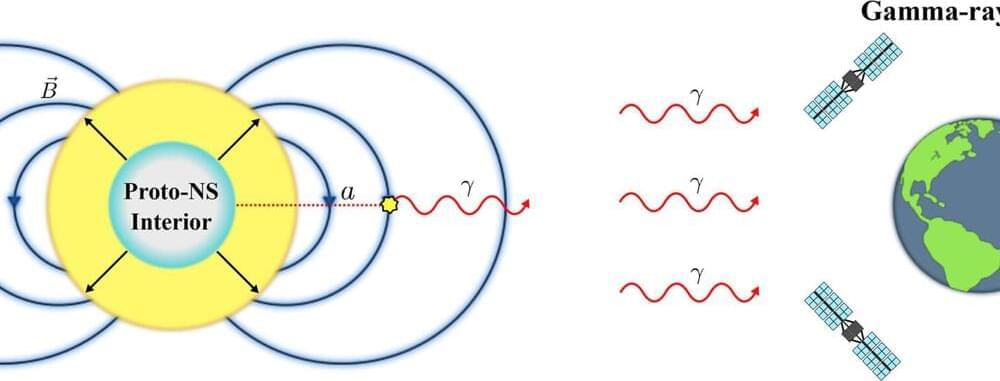
The search for the universe’s dark matter could end tomorrow—given a nearby supernova and a little luck. The nature of dark matter has eluded astronomers for 90 years, since the realization that 85% of the matter in the universe is not visible through our telescopes. The most likely dark matter candidate today is the axion, a lightweight particle that researchers around the world are desperately trying to find.
Astrophysicists at the University of California, Berkeley, now argue that the axion could be discovered within seconds of the detection of gamma rays from a nearby supernova explosion. Axions, if they exist, would be produced in copious quantities during the first 10 seconds after the core collapse of a massive star into a neutron star, and those axions would escape and be transformed into high-energy gamma rays in the star’s intense magnetic field.
Such a detection is possible today only if the lone gamma-ray telescope in orbit, the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, is pointing in the direction of the supernova at the time it explodes. Given the telescope’s field of view, that is about one chance in 10.
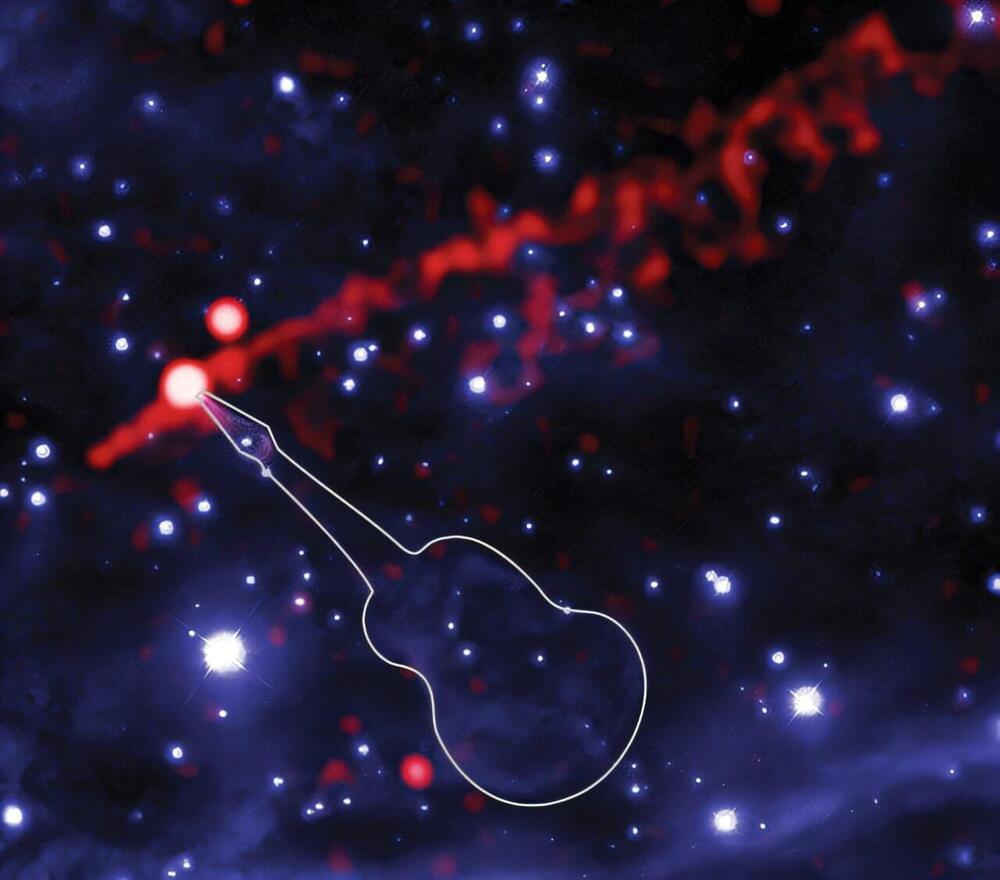
Normally found only in heavy metal bands or certain post-apocalyptic films, a “flame-throwing guitar” has now been spotted moving through space. Astronomers have captured movies of this extreme cosmic object using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope.
The new movie of Chandra (red) and Palomar (blue) data helps break down what is playing out in the Guitar Nebula. X-rays from Chandra show a filament of energetic matter and antimatter particles, about two light-years or 12 trillion miles long, blasting away from the pulsar (seen as the bright white dot connected to the filament).
Astronomers have nicknamed the structure connected to the pulsar PSR B2224+65 as the “Guitar Nebula” because of its distinct resemblance to the instrument in glowing hydrogen light. The guitar shape comes from bubbles blown by particles ejected from the pulsar through a steady wind. Because the pulsar is moving from the lower right to the upper left, most of the bubbles were created in the past as the pulsar moved through a medium with variations in density.
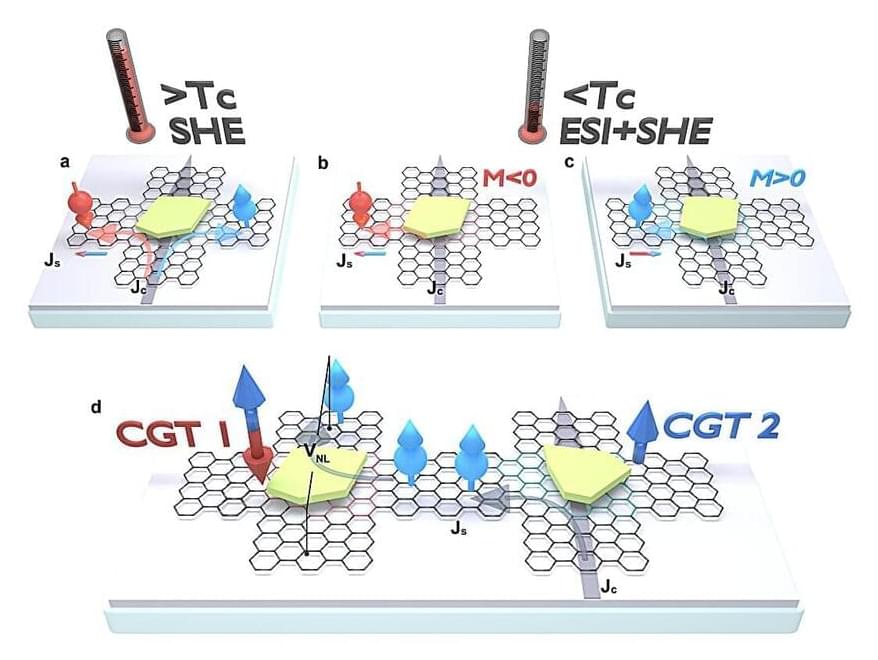
Graphene, particularly in its purest form, has long been considered a promising material for developing spintronic devices. These devices leverage the intrinsic angular momentum (i.e., spin), as opposed to the charge, of electrons to transmit and process data.
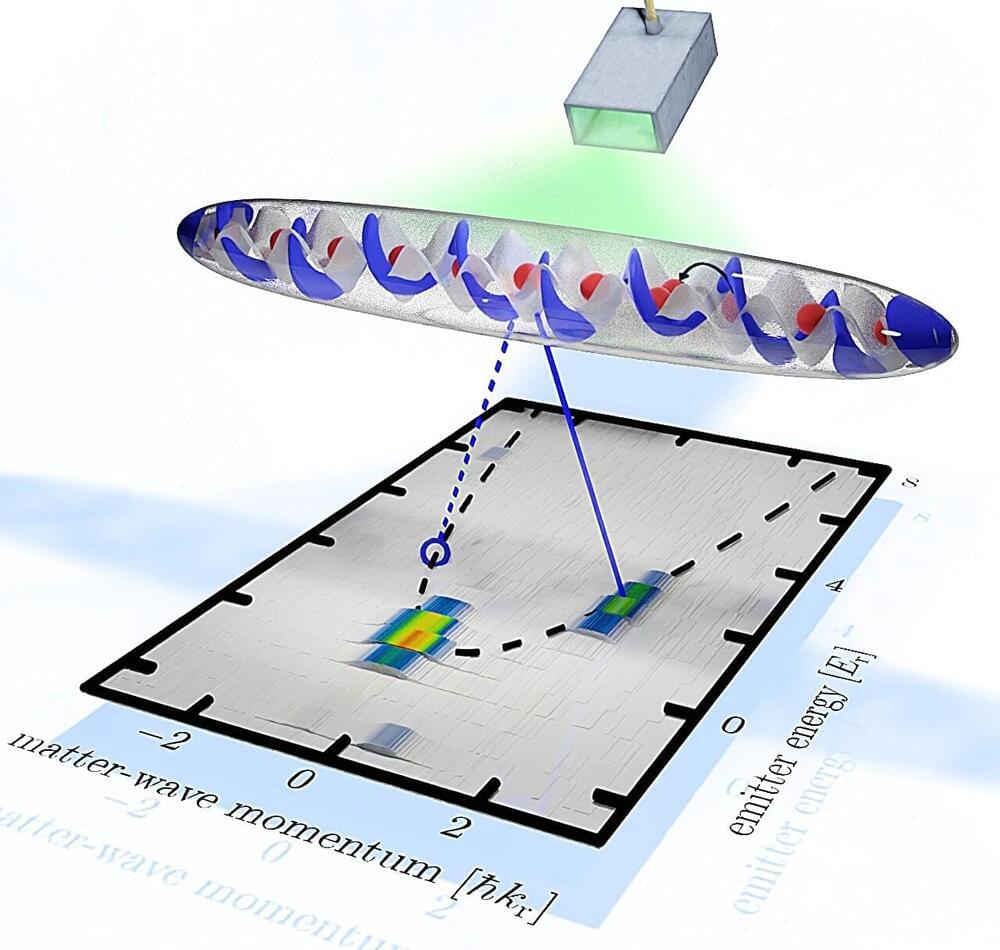
A research team led by Dominik Schneble, Ph.D., Professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy, has uncovered a novel regime, or set of conditions within a system, for cooperative radiative phenomena, casting new light on a 70-year-old problem in quantum optics.
Their findings on previously unseen collective spontaneous emission effects, in an array of synthetic (artificial) atoms, are published in Nature Physics, accompanied by a theoretical paper in Physical Review Research.
Spontaneous emission is a phenomenon in which an excited atom falls to a lower-energy state and spontaneously emits a quantum of electromagnetic radiation in the form of a single photon. When a single excited atom decays and emits a photon, the probability of finding the atom in its excited state falls exponentially to zero as time progresses.
Imagine a thread so thin it’s invisible to the naked eye but packed with the mass of thousands of stars. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the theoretical description of cosmic strings, structures that may hold answers to the Universe’s greatest mysteries. If confirmed, researchers believe these theoretical strings could unlock the key to time travel.
Cosmic strings, if they exist, are thought to be incredibly slender. Some say they’d be long tubes, either stretching infinitely or looping back on themselves. Despite their thinness, a cosmic string’s mass could rival tens of thousands of stars, and it would gradually shrink over time, radiating gravitational waves as it “wiggles.”
Physicists have proposed two types of cosmic strings thus far. The first, “cosmic superstrings,” stems from string theory, a framework suggesting the Universe’s fundamental particles are vibrating strings. Superstrings could be stretched across the cosmos, providing clues about the fabric of reality and possibly holding the key to time travel, too.
Researchers propose that time is a result of quantum entanglement, the mysterious connection between particles separated by vast distances. Their findings, published in the journal Physical Review A, could offer a clue to solving the problem of time.
“There exists a way to introduce time which is consistent with both classical laws and quantum laws, and is a manifestation of entanglement,” explained Alessandro Coppo, a physicist at the National Research Council of Italy and the study’s lead author. “The correlation between the clock and the system creates the emergence of time, a fundamental ingredient in our lives.”
In quantum mechanics, time is a fixed phenomenon, an unchanging flow from past to present. It remains external to the ever-changing quantum systems it measures and can only be observed through changes in external entities, like the hands of a clock.
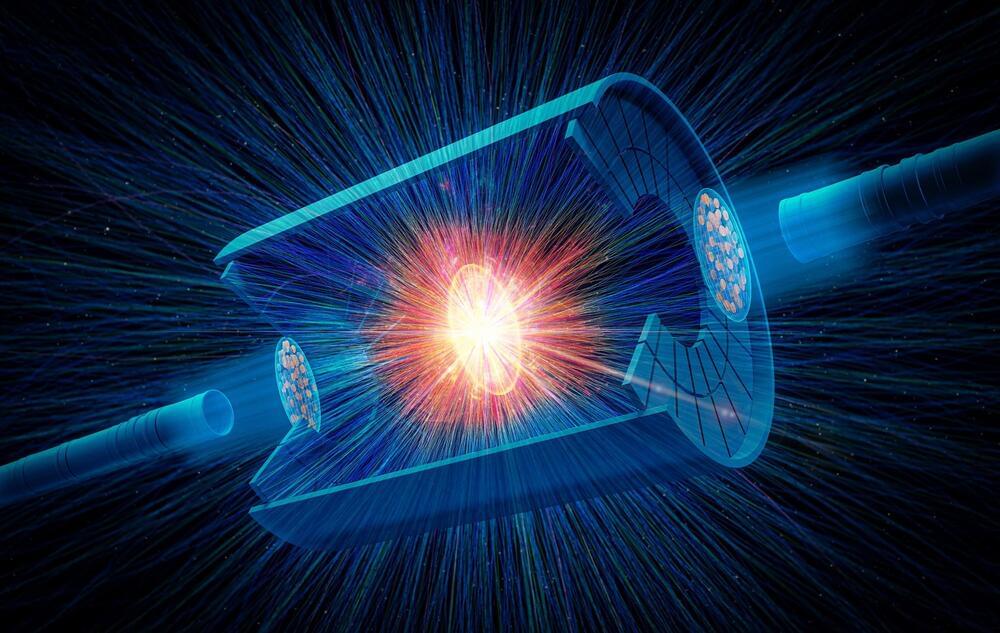
Scientists have developed a novel technique using high-energy particle collisions at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC), a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science user facility for nuclear physics research located at DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory. Detailed in a newly published paper in Nature, this method complements lower-energy approaches for studying nuclear structure. It offers deeper insights into the shapes of atomic nuclei, enhancing our understanding of the building blocks of visible matter.
“In this new measurement, we not only quantify the overall shape of the nucleus — whether it’s elongated like a football or squashed down like a tangerine — but also the subtle triaxiality, the relative differences among its three principle axes that characterize a shape in between the ‘football’ and ‘tangerine,’” said Jiangyong Jia, a professor at Stony Brook University (SBU) who has a joint appointment at Brookhaven Lab and is one of the principal authors on the STAR Collaboration publication.
Deciphering nuclear shapes has relevance to a wide range of physics questions, including which atoms are most likely to split in nuclear fission, how heavy atomic elements form in collisions of neutron stars, and which nuclei could point the way to exotic particle decay discoveries. Leveraging improved knowledge of nuclear shapes will also deepen scientists’ understanding of the initial conditions of a particle soup that mimics the early universe, which is created in RHIC’s energetic particle smashups. The method can be applied to analyzing additional data from RHIC as well as data collected from nuclear collisions at Europe’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC). It will also have relevance to future explorations of nuclei at the Electron-Ion Collider, a nuclear physics facility in the design stage at Brookhaven Lab.