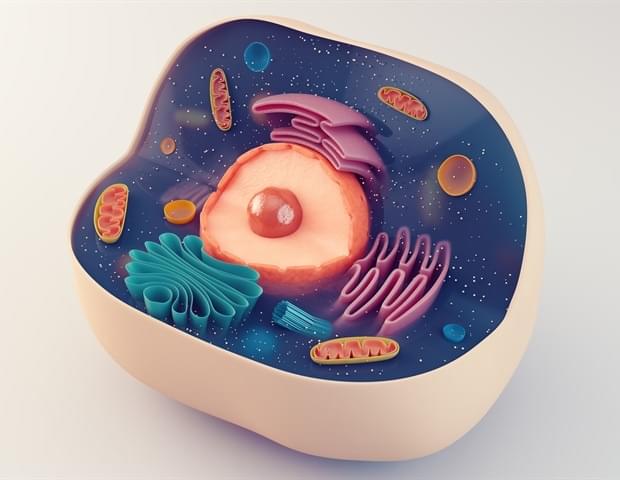
The ongoing AI revolution, set to reshape lifestyles and workplaces, has seen deep neural networks (DNNs) play a pivotal role, notably with the emergence of foundation models and generative AI. Yet, the conventional digital computing frameworks that host these models hinder their potential performance and energy efficiency. While AI-specific hardware has emerged, many designs separate memory and processing units, resulting in data shuffling and reduced efficiency.
IBM Research has pursued innovative ways to reimagine AI computation, leading to the concept of analog in-memory computing, or analog AI. This approach draws inspiration from neural networks in biological brains, where synapse strength governs neuron communication. Analog AI employs nanoscale resistive devices like Phase-change memory (PCM) to store synaptic weights as conductance values. PCM devices transition between amorphous and crystalline states, encoding a range of values and enabling local storage of weights with non-volatility.
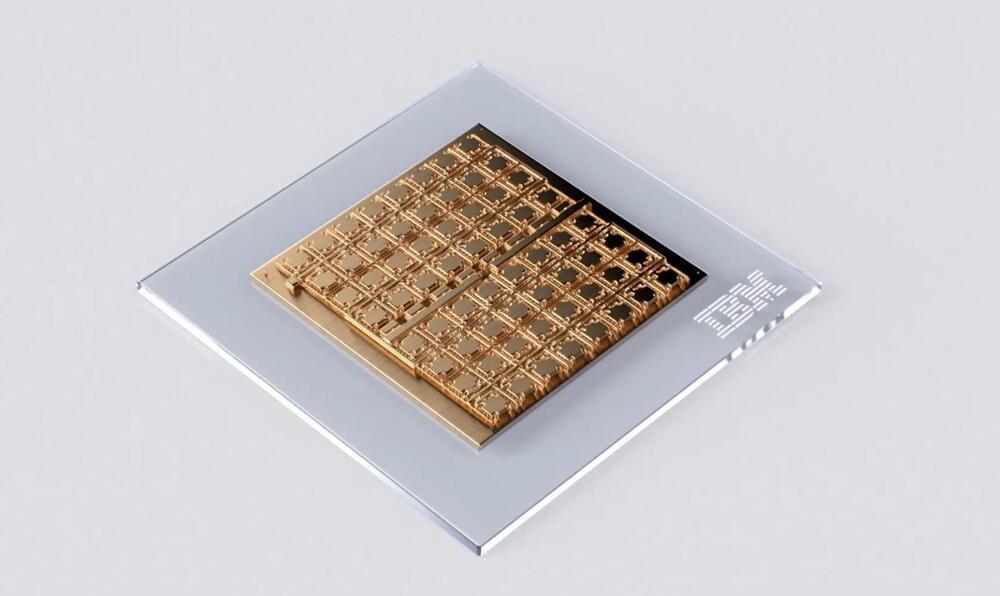
A significant stride towards making analog AI a reality has been achieved by IBM Research in a recent Nature Electronics publication. They introduced a cutting-edge mixed-signal analog AI chip tailored for various DNN inference tasks. This chip, fabricated at IBM’s Albany NanoTech Complex, features 64 analog in-memory compute cores, each housing a 256-by-256 crossbar array of synaptic unit cells. Integrated compact, time-based analog-to-digital converters facilitate seamless transitions between analog and digital domains. Moreover, digital processing units within each core handle basic neuronal activation functions and scaling operations.