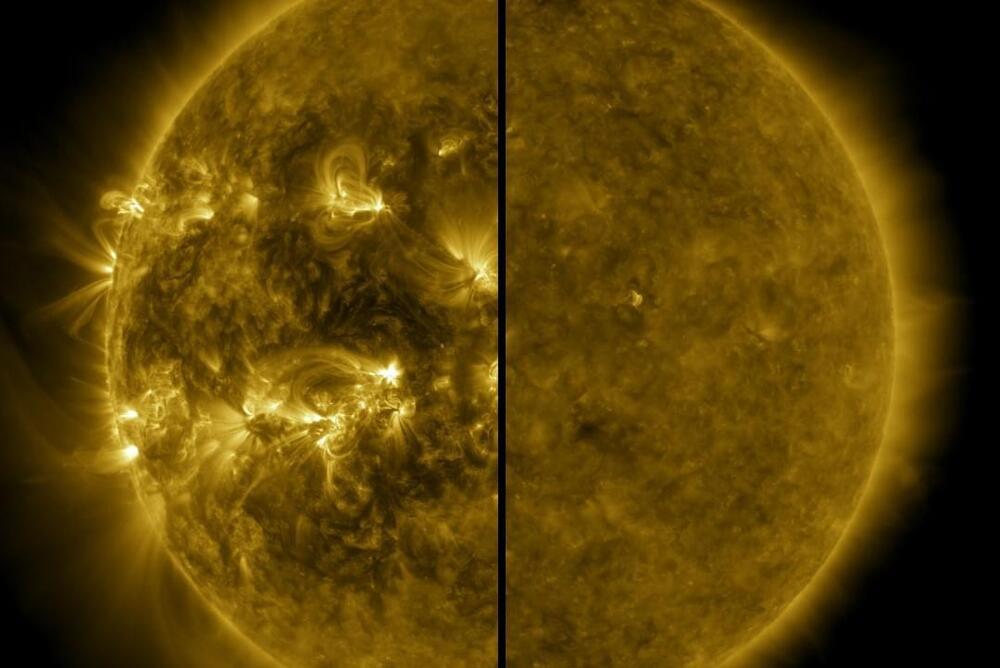
Experts believe that the sun will likely reach a peak in its solar cycle by the end of the year, signaling potential consequences for Earth.
Category: futurism – Page 307
Florida Atlantic University.
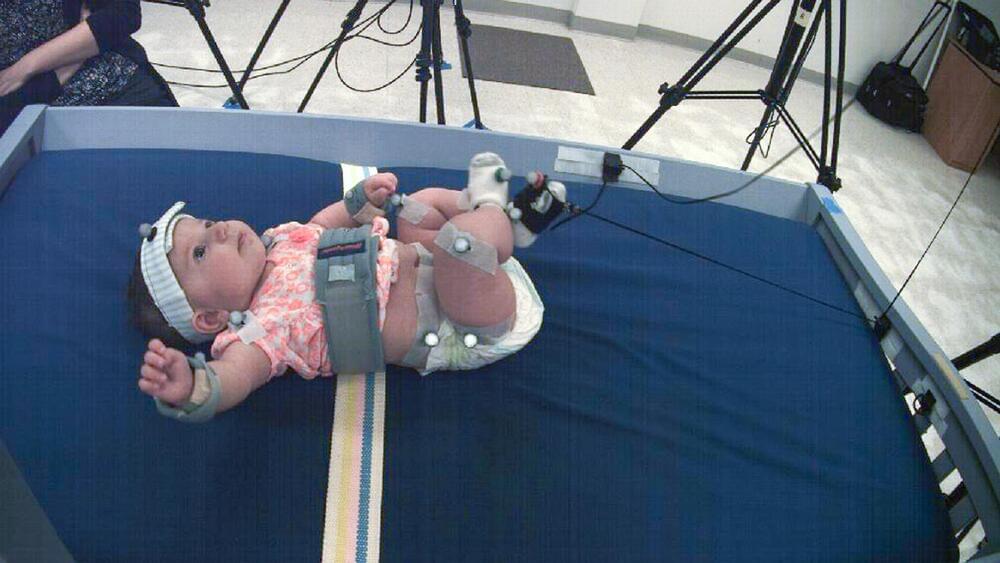
In psychology, agency is also defined as a person’s capability to act freely and control their actions. However, what’s interesting is that nobody knows how humans develop this sense of agency.
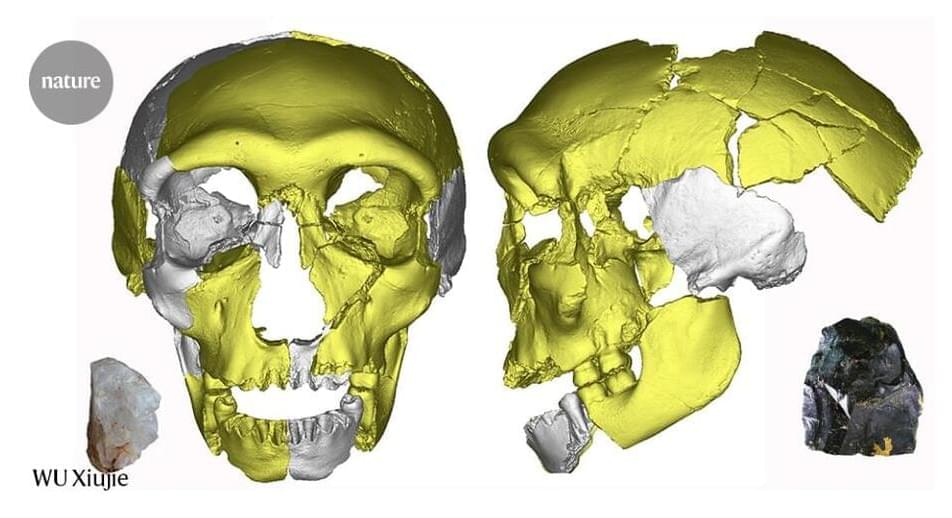
A chinless jawbone from eastern China that displays both modern and archaic features could represent a new branch of the human family tree.
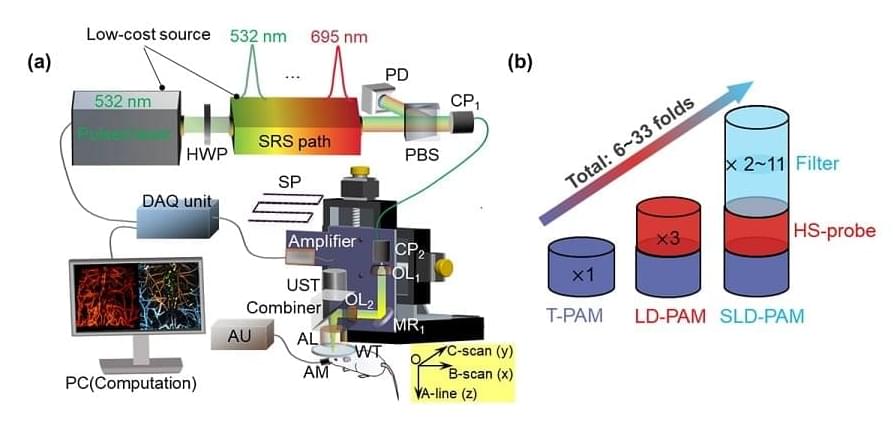
A multispectral, super-low-dose photoacoustic microscopy (SLD-PAM) system developed by City University of Hong Kong (CUHK) achieves significantly higher sensitivity than traditional optical resolution photoacoustic imaging.
By providing an exceptionally high level of sensitivity, SLD-PAM could help broaden the use of photoacoustic microscopy in biomedical applications. In the future, it could translate to clinical settings; for example, it could be used for ophthalmic exams where a low-power laser is preferred for the patient’s safety and comfort. Long-term monitoring of pharmacokinetics or blood flow also requires low-dose imaging to alleviate perturbation to tissue function.
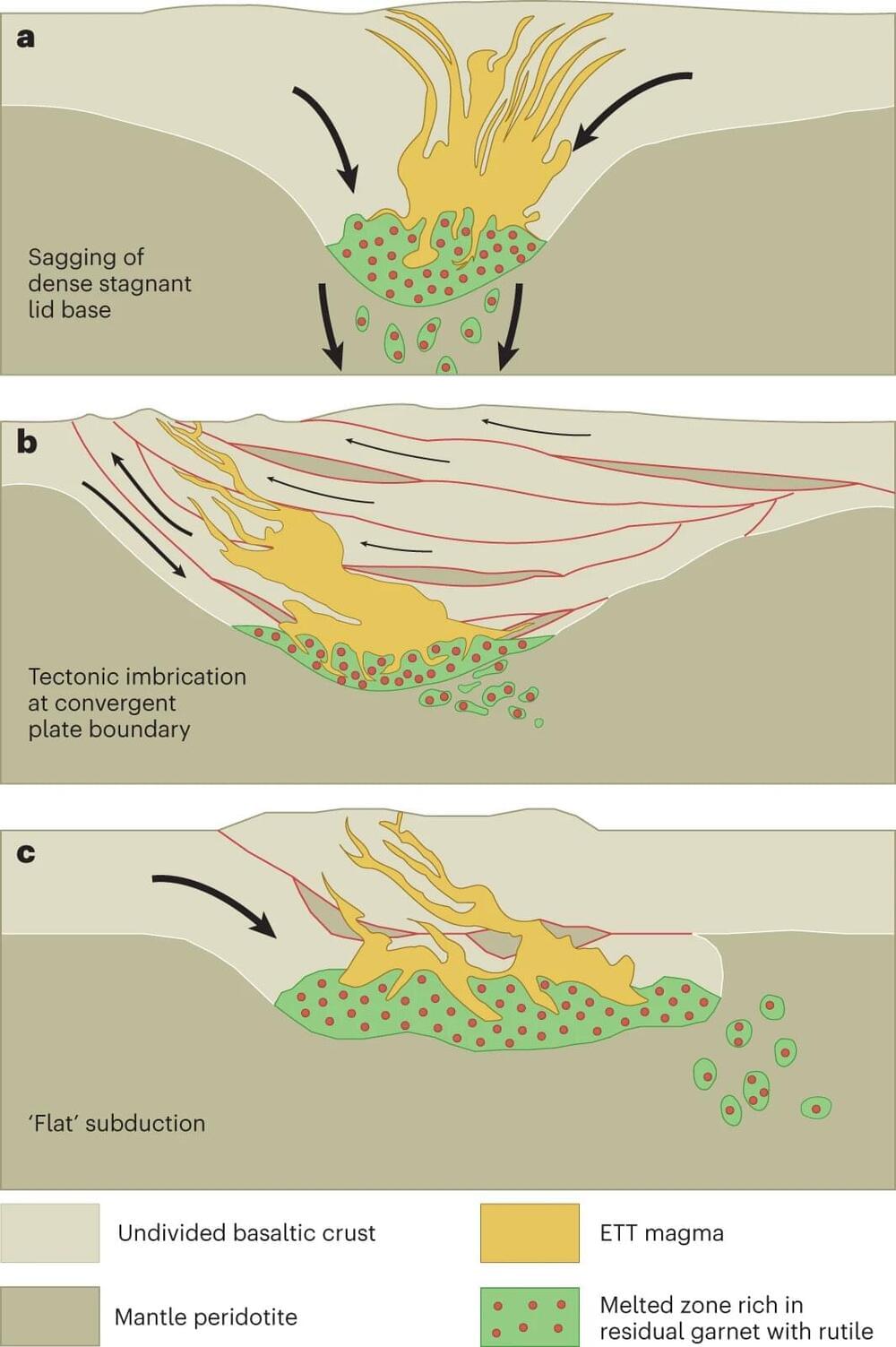
The Earth’s oldest surface layer forming continents, termed its crust, is approximately 4 billion years old and is comprised of 25–50km-thick volcanic rocks known as basalts. Originally, scientists thought that one complete lithospheric crust covered the entire planet, compared to the individual plates we see today which were believed to have only begun formation 1 billion years later. However, attitudes towards this hypothesis are being challenged.
The formation mechanism of this continental crust is somewhat enigmatic, with academics now suggesting it may have been driven by plate tectonics, the movement of Earth’s major surface plates across the globe over billions of years, forming the landmasses and topographic features which we see today.
One theory focuses on when the plates converge, often causing one to subduct beneath the other, resulting in partial melting to change magma composition, while another studies mechanisms occurring within the crust itself (at less than 50km depth) that are entirely separate from plate boundaries but also cause partial melting.
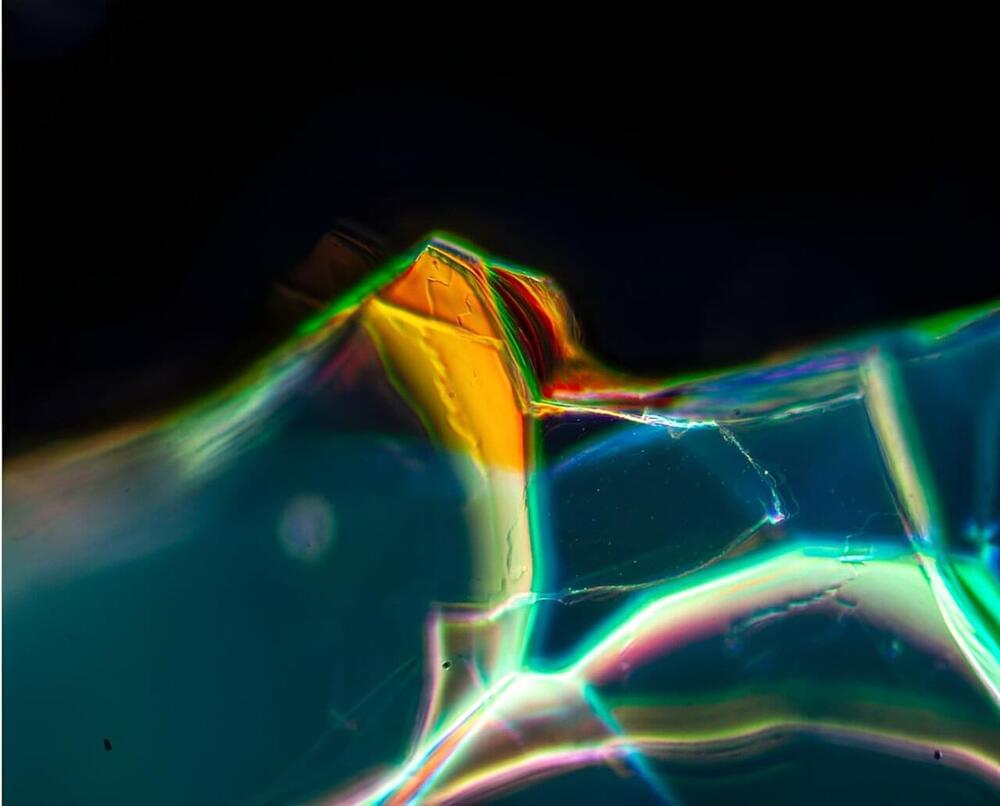
Some 2,000 years ago in ancient Rome, glass vessels carrying wine or water, or perhaps an exotic perfumes, tumble from a table in a marketplace, and shatter to pieces on the street. As centuries passed, the fragments were covered by layers of dust and soil and exposed to a continuous cycle of changes in temperature, moisture, and surrounding minerals.
Now these tiny pieces of glass are being uncovered from construction sites and archaeological digs and reveal themselves to be something extraordinary. On their surface is a mosaic of iridescent colors of blue, green and orange, with some displaying shimmering gold-colored mirrors.
These beautiful glass artifacts are often set in jewelry as pendants or earrings, while larger, more complete objects are displayed in museums.
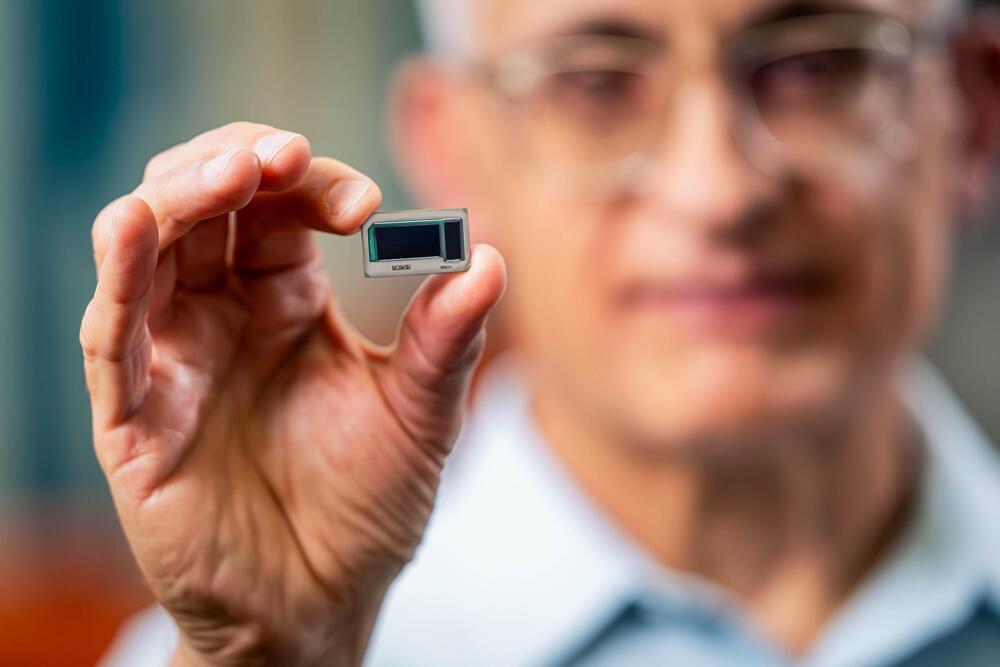
While semiconductor lithography gets the bulk of the attention in chipmaking, other processes are equally important in producing working integrated circuits (ICs). Case in point: packaging. An IC package provides the electrical, thermal, and mechanical transition from the semiconductor die or chip to the circuit board, which is often called a motherboard. One key element of the IC package is the substrate, which is essentially a miniature circuit board with copper traces that bonds to the input/output (I/O), power and ground pads on the chip and electrically connects these pads to the circuit board. The substrate provides a solid mechanical home for the chip and is also thermally matched to… More.
The release also quotes Babak Sabi, Intel senior vice president and general manager of Assembly and Test Development, who said: “After a decade of research, Intel has achieved industry-leading glass substrates for advanced packaging. We look forward to delivering these cutting-edge technologies that will benefit our key players and foundry customers for decades to come.”
Research into using glass substrates for chipmaking is nothing new. As Intel’s release says, the company has been working on this technology for at least a decade, as have other organizations such as the 3D Systems Packaging Research Center located at Georgia Tech, which was founded in 1994 – nearly 30 years ago. Last year, the Georgia Tech PRC launched an industry advisory board with Intel Fellow Ravi Mahajan as one of the initial board members. Intel has already spent more than a billion dollars to develop a glass-substrate manufacturing facility at its site in Chandler, Arizona.
So, if glass IC substrates are nothing new, why would Intel announce this particular development now, after ten years of corporate development and several years before these substrates find their way into products? On the technical side, it’s because existing ceramic and organic substrates are reaching the end of their ability to provide the electrical, thermal, and mechanical transitions for today’s most advanced semiconductors, which is doubly true as the industry adopts chiplets as an increasingly common way to put more transistors into a package.
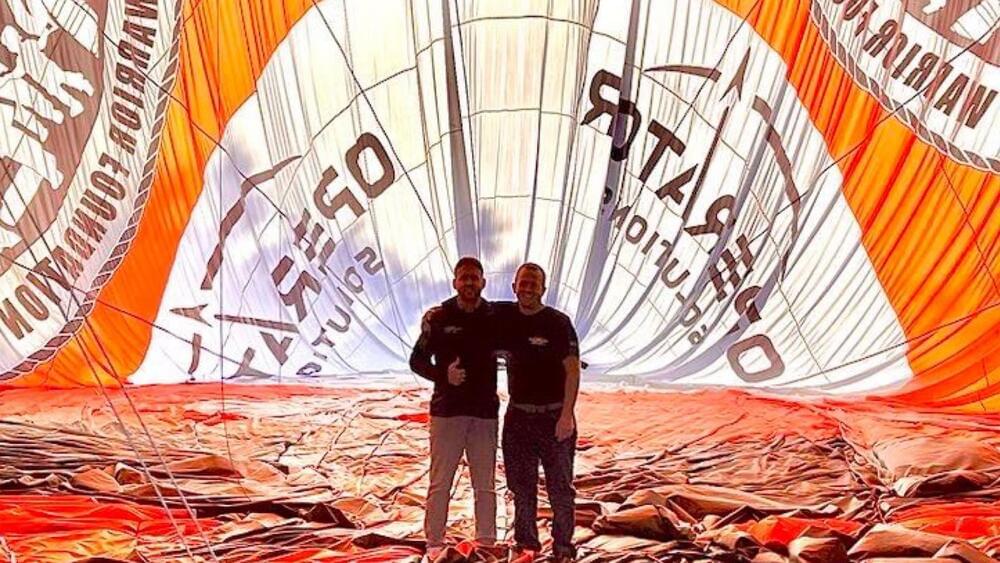
Built to support the US veteran charity Special Operations Warrior Foundation, Cameron Balloons US’ A-560 is the biggest hot air balloon yet seen in the states.
The most gigantic hot air balloon ever designed and built is set to soar to altitudes of 35,000 feet (10,668 meters) or more in support of the US veteran charity Special Operations Warrior Foundation. The balloon will carry seven people within its rattan basket before five plan to skydive out of it. The balloon, built by Cameron Balloons US, will attempt this potential world record-breaking event over New Mexico this month (September 2023).
Operator Solutions/X
Jumping for charity.
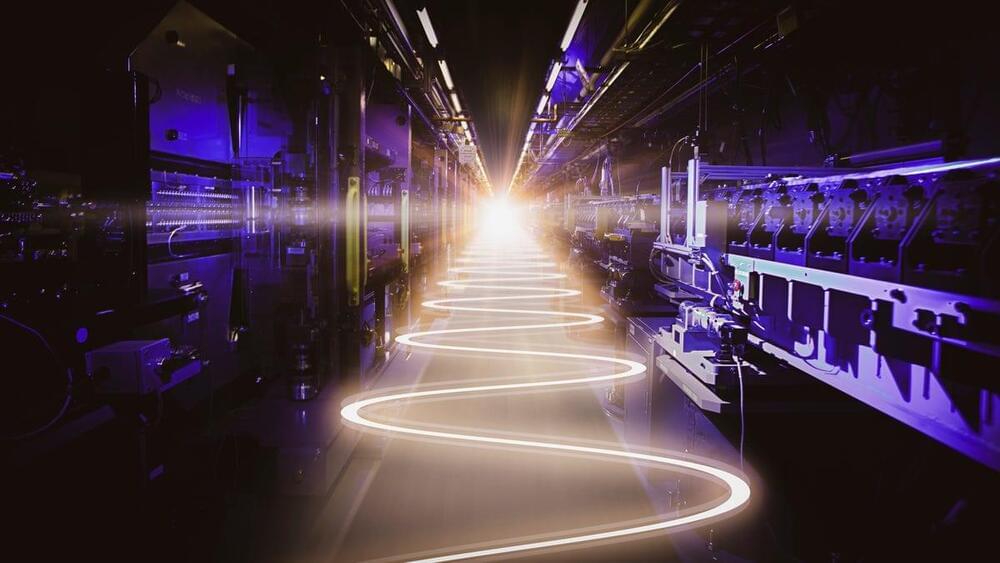
LCLS-II will produce up to one million X-ray pulses per second and will be 10,000 times brighter than its predecessor.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Posted in futurism, robotics/AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to complex software that performs tasks in a way similar to human brains, often by sensing and responding to a feature of their environment. This could mean learning to solve problems in unexpected ways, recognising the nuances of speech, or exhibiting some form of human-like creativity.
Just as no single quality defines human thinking, no clear line differentiates more basic computer programs from AI. It can be thought of more as an ideal than a category — using our own penchant for learning and problem solving to inspire new technology and answers to some of our biggest and most complex questions.
There are many different fields of AI, including ’robotics’, but one of the most commonly known forms is referred to as ‘machine learning’. This involves a program applying known information to new experiences and ‘learning’ how to take this historical information and its experiences into account in future actions.