Researchers have simulated what would happen if the greenhouse effect snowballed, causing a dramatic rise in the Earth’s temperature.
Category: futurism – Page 276
The ‘Leaksmus’ event on the Dark Web exposed some 50 million records containing sensitive information from people all around the world.
This track by multi-instrumentalist and vocalist, Prof Steve Nichols, is inspired by Utterance 437 from the Old Kingdom Egyptian Pyramid Texts.\
Consciousness is a Big Suitcase
Posted in futurism, robotics/AI
“[People] like themselves just as they are,” says Marvin Minsky. “Perhaps they are not selfish enough, or imaginative, or ambitious. Myself, I don’t much like how people are now. We’re too shallow, slow, and ignorant. I hope that our future will lead us to ideas that we can use to improve ourselves.”
Marvin believes that it is important that we “understand how our minds are built, and how they support the modes of thought that we like to call emotions. Then we’ll be better able to decide what we like about them, and what we don’t—and bit by bit we’ll rebuild ourselves.”
Marvin Minsky is the leading light of AI—artificial intelligence, that is. He sees the brain as a myriad of structures. Scientists who, like Minsky, take the strong AI view believe that a computer model of the brain will be able to explain what we know of the brain’s cognitive abilities. Minsky identifies consciousness with high-level, abstract thought, and believes that in principle machines can do everything a conscious human being can do.
Scientists have spent decades trying to unravel the intricate mysteries of the human appetite. Are they on the verge of finally determining how this basic drive functions?
The first ever “True” Killscreen was just reached in NES Tetris. Can this record ever be broken?
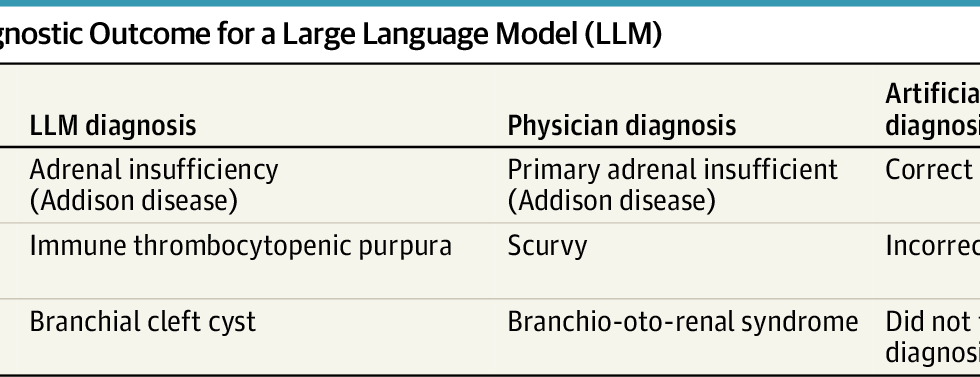
This diagnostic/prognostic study evaluates the accuracy of a large language model against physician diagnoses in pediatric cases.