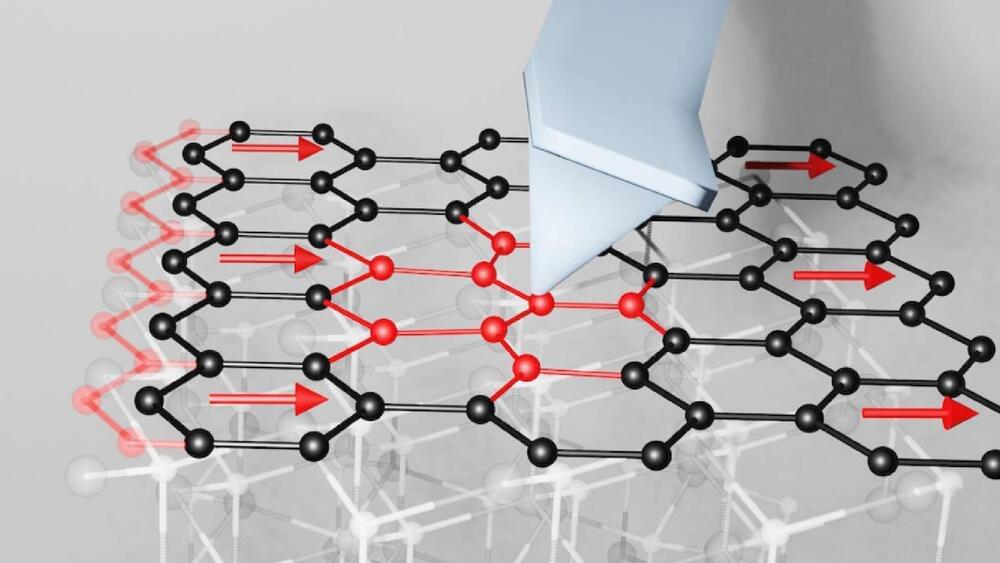
The fundamental laws of friction remain a mystery to this day.
Researchers at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering have discovered a fundamental friction law that is leading to the design of two-dimensional materials capable of minimizing energy loss, according to a press release from the institution published on Thursday.
Friction lies behind the invention and development of many of today’s most advanced technologies, however, its fundamental laws remain obscure to this day despite many developments in the field.
NYU Tandon School of Engineering professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Elisa Riedo and postdoctoral researcher Martin Rejhon have found evidence of a new law of friction.