Archive for the ‘engineering’ category: Page 114
Sep 10, 2021
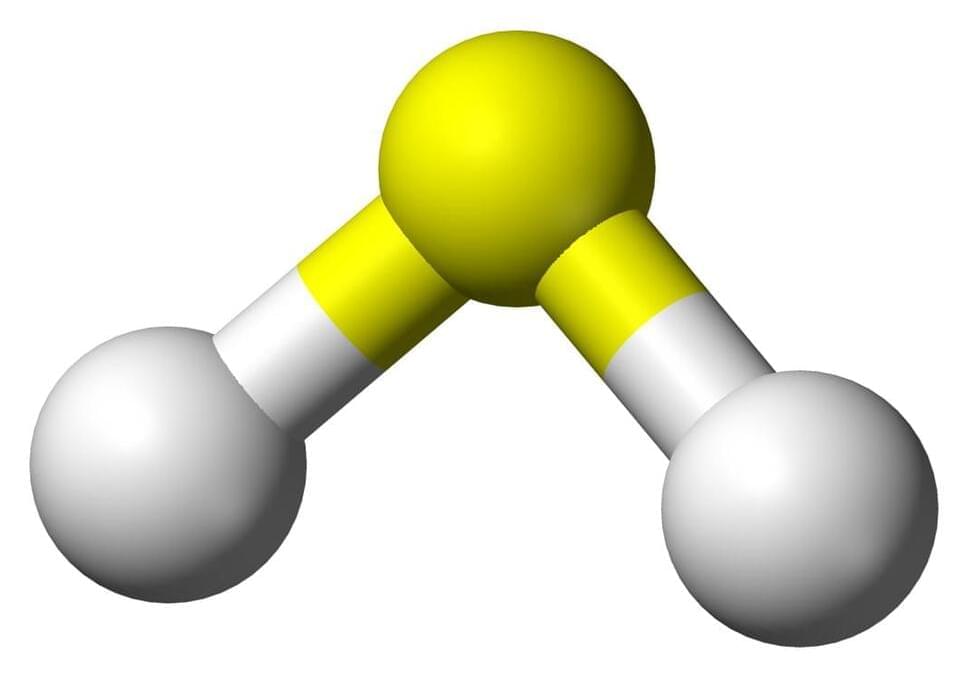
Transforming ‘sewer gas’ into clean hydrogen fuel
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: chemistry, energy, engineering, sustainability
Scientists have found a new chemical process to turn a stinky, toxic gas into a clean-burning fuel.
The process, detailed recently in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Sustainable Chemical Engineering, turns hydrogen sulfide —more commonly called “sewer gas”—into hydrogen fuel. Hydrogen sulfide is emitted from manure piles and sewer pipes and is a key byproduct of industrial activities including refining oil and gas, producing paper and mining.
The process detailed in this study uses relatively little energy and a relatively cheap material—the chemical iron sulfide with a trace amount of molybdenum as an additive.
Sep 7, 2021
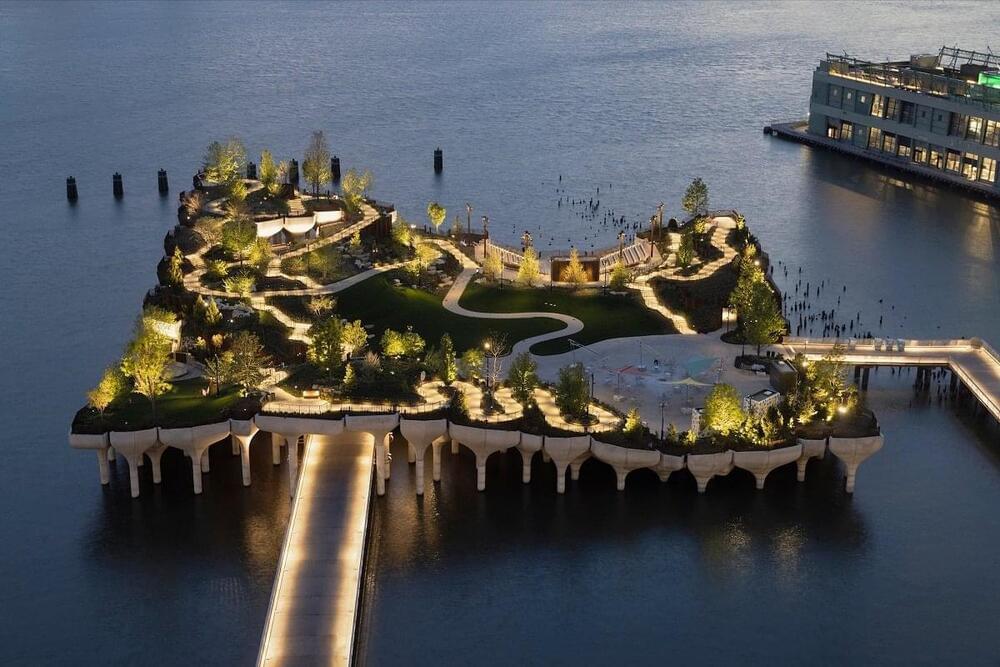
New York City Opens A $335 Million Park Island On Hudson River
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: engineering, space travel
The long-awaited $355 million development of Little Island New York has finally been made reality, offering the Big Apple a unique new space.
Although it’s unlikely travel to the US will be on the cards for Aussies anytime soon, it’s good to keep track of the developments that await us when we eventually graduate from tiny travel bubbles to full-scale international adventure once again. The latest development: the ambitious new US$260 million (AU$335 million) Little Island New York, an offshore public park in the Hudson River that has been one of the city’s most anticipated openings for a couple of years now.
Located at Pier 55 the fascinating public park has been designed to resemble a supersized leaf drifting on the Hudson, buoyed by a base of 280 concrete piles and precast columns driven down as far as 60 metres below water, as well as 132 tulip-shaped concrete pots positioned at various elevations from 4 metres to 18 metres above water, designed specifically by Heatherwick Studio, and developed by engineering firm Arup, to hold the soil, overlooks, and trees. This support base allows for the two-acre park to stay securely afloat so its 687-seat amphitheatre, smaller stage, and plaza don’t suddenly drop to the depths of the Hudson.
Continue reading “New York City Opens A $335 Million Park Island On Hudson River” »
Sep 5, 2021
Chinese Scientists Say Quantum Radar Could End Stealth Advantage
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: climatology, education, engineering, quantum physics
A new quantum radar technology developed by a team of Chinese researchers would be able to detect stealth planes, the South China Morning Post is reporting.
The news service reports that the radar technology generates a mini electromagnetic storm to detect objects. Professor Zhang Chao and his team at Tsinghua University’s aerospace engineering school, reported their findings in a paper in Journal of Radars.
A quantum radar is different from traditional radars in several ways, according to the paper. While traditional radars have on a fixed or rotating dish, the quantum design features a gun-shaped instrument that accelerates electrons. The electrons pass through a winding tube of a strong magnetic fields, producing what is described as a tornado-shaped microwave vortex.
Sep 4, 2021
A high-pressure jet of water can cut through anything
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: engineering
Sep 3, 2021
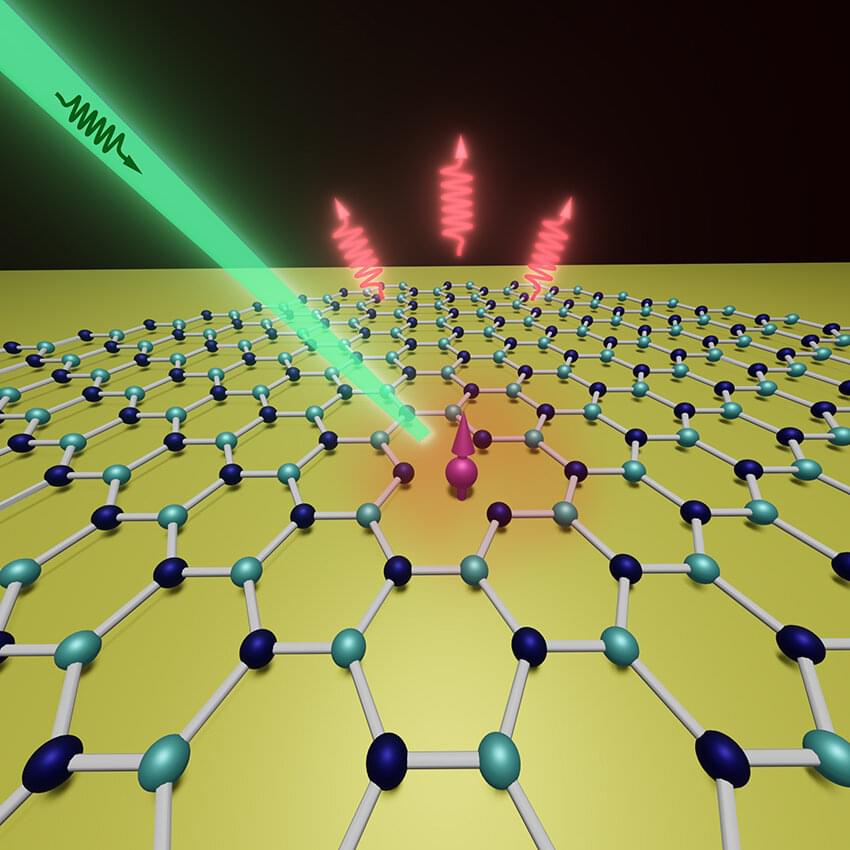
Researchers use gold film to enhance quantum sensing with qubits in a 2D material
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: biological, engineering, quantum physics
Quantum sensing is being used to outpace modern sensing processes by applying quantum mechanics to design and engineering. These optimized processes will help beat the current limits in processes like studying magnetic materials or studying biological samples. In short, quantum is the next frontier in sensing technology.
As recently as 2,019 spin defects known as qubits were discovered in 2D materials (hexagonal boron nitride) which could amplify the field of ultrathin quantum sensing. These scientists hit a snag in their discovery which has unleashed a scientific race to resolve the issues. Their sensitivity was limited by their low brightness and the low contrast of their magnetic resonance signal. As recently as two weeks ago on August 9 2021, Nature Physics published an article titled “quantum sensors go flat,” where they highlighted the benefits and also outlined current shortfalls of this new and exciting means of sensing via qubits in 2D materials.
A team of researchers at Purdue took on this challenge of overcoming qubit signal shortcomings in their work to develop ultrathin quantum sensors with 2D materials. Their publication in Nano Letters was published today, September 2 2021, and they have solved some of the critical issues and yielded much better results through experimentation.
Sep 1, 2021
Researchers discover way to switch on and speed up tendon healing
Posted by Jason Blain in categories: biotech/medical, engineering, health
The study investigated whether electrical therapy, coupled with exercise, would show promise in treating tendon disease or ruptures. It showed that tendon cell function and repair can be controlled through electrical stimulation from an implantable device which is powered by body movement.
Researchers at CÚRAM, the SFI Research Centre for Medical Devices based at NUI Galway, have shown how the simple act of walking can power an implantable stimulator device to speed up treatment of musculoskeletal diseases.
The results of have been published in the prestigious journal Advanced Materials.
Continue reading “Researchers discover way to switch on and speed up tendon healing” »
Sep 1, 2021
Using liquid metal to turn motion into electricity, even underwater
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: chemistry, energy, engineering
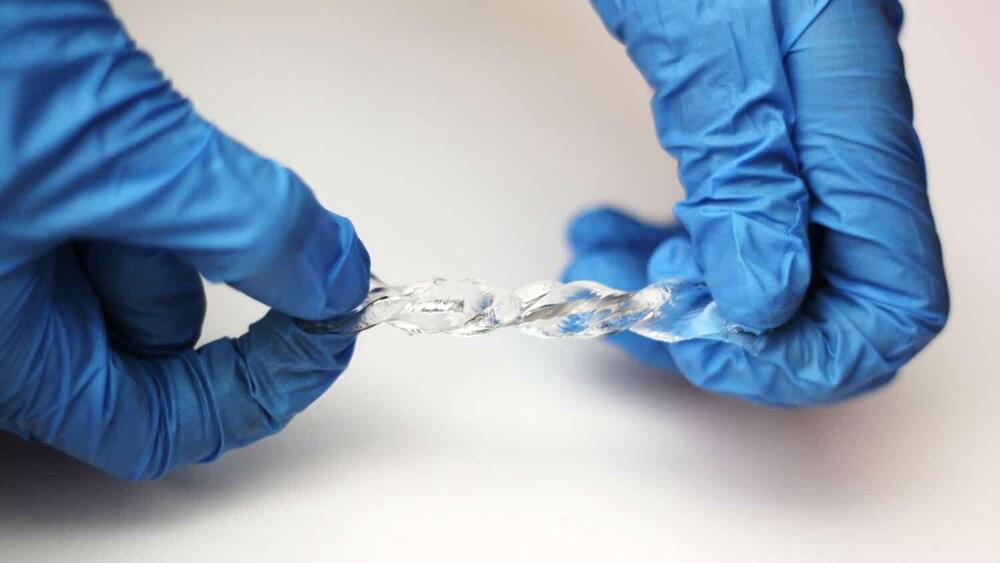

Researchers at North Carolina State University have created a soft and stretchable device that converts movement into electricity and can work in wet environments.
“Mechanical energy—such as the kinetic energy of wind, waves, body movement and vibrations from motors—is abundant,” says Michael Dickey, corresponding author of a paper on the work and Camille & Henry Dreyfus Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at NC State. “We have created a device that can turn this type of mechanical motion into electricity. And one of its remarkable attributes is that it works perfectly well underwater.”
Continue reading “Using liquid metal to turn motion into electricity, even underwater” »
Aug 31, 2021
Genes can respond to coded information in signals —or filter them out entirely
Posted by Dan Kummer in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, engineering
Genes can respond to coded information in signals—or filter them out entirely.
New research from North Carolina State University demonstrates that genes are capable of identifying and responding to coded information in light signals, as well as filtering out some signals entirely. The study shows how a single mechanism can trigger different behaviors from the same gene—and has applications in the biotechnology sector.
“The fundamental idea here is that you can encode information in the dynamics of a signal that a gene is receiving,” says Albert Keung, corresponding author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering at NC State. “So, rather than a signal simply being present or absent, the way in which the signal is being presented matters.”
Continue reading “Genes can respond to coded information in signals —or filter them out entirely” »
Aug 31, 2021
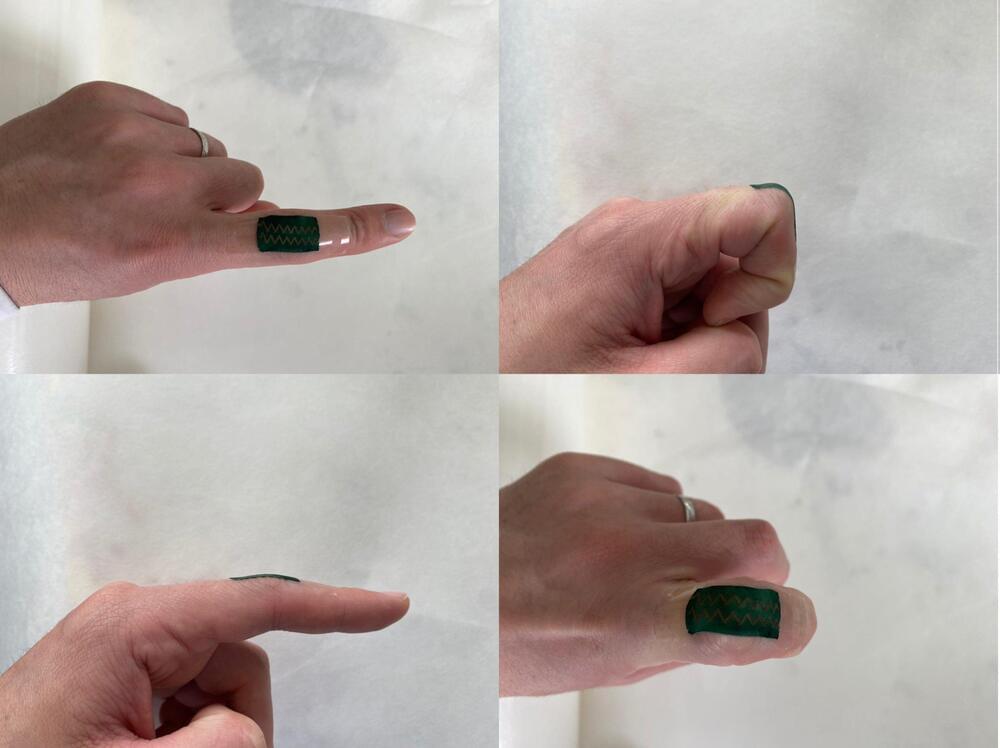
Smart ‘E-Skin’ Identifies Your Movements
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in categories: chemistry, engineering, nanotechnology, wearables
Technion scientists have created a wearable motion sensor capable of identifying movements such as bending and twisting. This smart ‘e-skin’ was produced using a highly stretchable electronic material, which essentially forms an electronic skin capable of recognizing the range of movement human joints normally make, with up to half a degree precision.
This breakthrough is the result of collaborative work between researchers from different fields in the Laboratory for Nanomaterial-Based Devices, headed by Professor Hossam Haick from the Technion Wolfson Faculty of Chemical Engineering. It was recently published in Advanced Materials and was featured on the journal’s cover.
This wearable motion sensor, which senses bending and twisting, can be applied in healthcare and manufacturing.