Category: cybercrime/malcode – Page 103
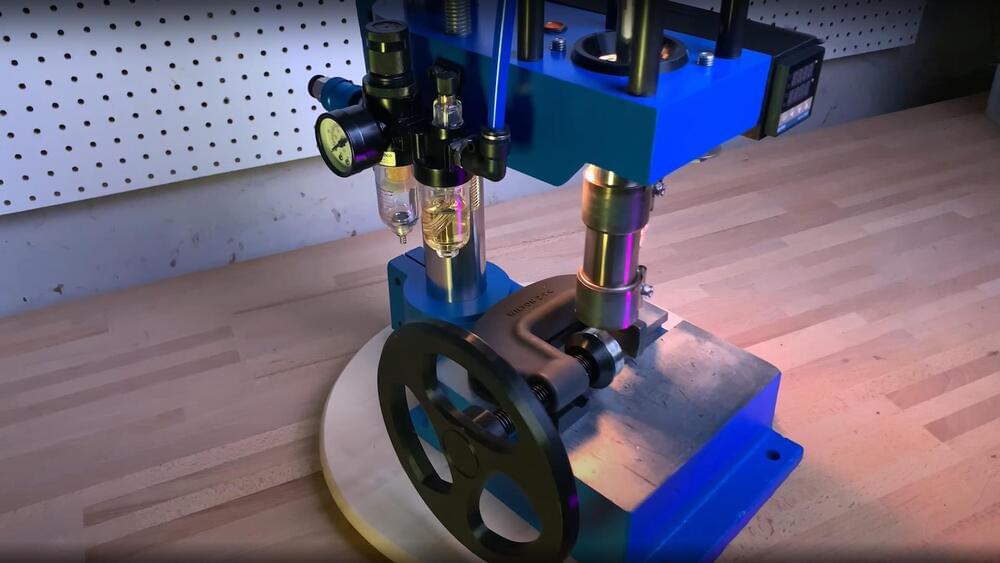
[Kurt Schaefer] was watching YouTube videos of people making molds for injection molding purposes using what he considered to be the toy 3,018 CNC machines, and looking at the results, decided he needed a piece of the action. However, once you have molds, the next obvious issue to address is lack of access to an injection molding machine. But these things are expensive. As luck would have it, you can get a nice-looking pneumatic press for less than $350, and with a little more money spent, [Kurt] found he could convert it into a functional injection molding machine (video, embedded below), and get some half-decent results out of it.
After ordering the press on eBay, what eventually arrived was quite a mess, having clearly been inadequately packed for its weight, and had sustained some damage in transit. Despite this, it seemed the functional bits were fine, so [Kurt] decided to press on with the build. The first obvious change is the requirement of a heated chamber to deal with the feedstock material. Using an off-the-shelf injection molding chamber by buster beagle 3D, only a few standoffs and a support bracket needed machining in order to complete the mechanics. A common PID controller available from the usual suppliers, with some heat bands wrapped around the chamber, dealt with the injection temperature requirements, and some 3D printed enclosures wrapped it all up neatly.
After some initial wobbles, and a couple of hacks to the design, [Kurt] got some pretty good results out of this simple setup, and it appears to be pretty tune-able and repeatable, which will help maintain the quality of those results. In short, a neat hack of easy to get parts, and perhaps a welcome addition to a hackerspace near you?
Musk and SpaceX sent Starlink terminals to Ukraine at the request of a government official after internet service was disrupted across the country by the Russian invasion. A shipment of Starlink ground terminals, which use an antenna and terminal to access the satellite broadband service, arrived in Ukraine by Monday Feb. 28). With the terminals in use, SpaceX is working to keep them online, Musk said.
“Some Starlink terminals near conflict areas were being jammed for several hours at a time,” Musk wrote in a Twitter statement Friday (March 1). “Our latest software update bypasses the jamming.”
I wonder how many of the satellites are damaged?
Starship and Starlink V2 progress will be delayed, Musk said.
Yet the United States lacks an organized response. The weekly reports of ransomware attacks and data breaches make it clear that we’re losing this battle. That’s why America’s leaders must rethink the current cyberdefense system and rally around a centralized regulator to defend both citizens and the private sector against current and future attacks.
The decentralized nature of the American government does not lend itself to fighting foreign cyberthreats. Government agencies handle cyberregulation and threats in the sectors they oversee — an inefficient and ineffective way to address an issue that cuts across our entire economy. In just the past few months, the D.H.S.’s Transportation Security Agency announced new cybersecurity requirements for pipelines and railroads; the Federal Communications Commission put out its own proposal for telecommunication companies; the Securities and Exchange Commission voted on rules for investment advisers and funds; and the Federal Trade Commission threatened to legally pursue companies that fail to fix a newly detected software vulnerability found in many business applications. And on Capitol Hill, there are approximately 80 committees and subcommittees that claim jurisdiction over various aspects of cyberregulation.
These scattered efforts are unlikely to reduce, let alone stop, cybercrime.
Log4Shell is still a threat but it’s mostly being used for crypto mining and knocking out websites.
Guest contributor, Brian Wallace writes about the rising threat from cyber attackers who in 2021 have cost organizations over $20 billion.
The hackers who struck Nvidia last week have released source code related to DLSS into the wild.
But no other genuine details have so far made it out of the stolen data folder.
The reported Nvidia hack has allegedly thrown up the codenames of a bunch of next-gen GPUs, which have now been leaked out to the press. The most pertinent ones for us would be the Lovelace GeForce GPUs, of which there are six listed, but here are also listings for the server-based Hopper and Blackwell GPUs. This looks to have come from an initial leak of some of the stolen documents, supplied to Videocardz.
The green team is allegedly being held to ransom over the Ethereum hash rate limiter attached to its most recent graphics card release after hacking group, Lapsus$, made off with around 1TB of sensitive data.
A new, third, data wiper malware — dubbed “IsaacWiper” — is now targeting Ukrainian governmental systems.
Teabot android banking malware spreads again through google play store apps.