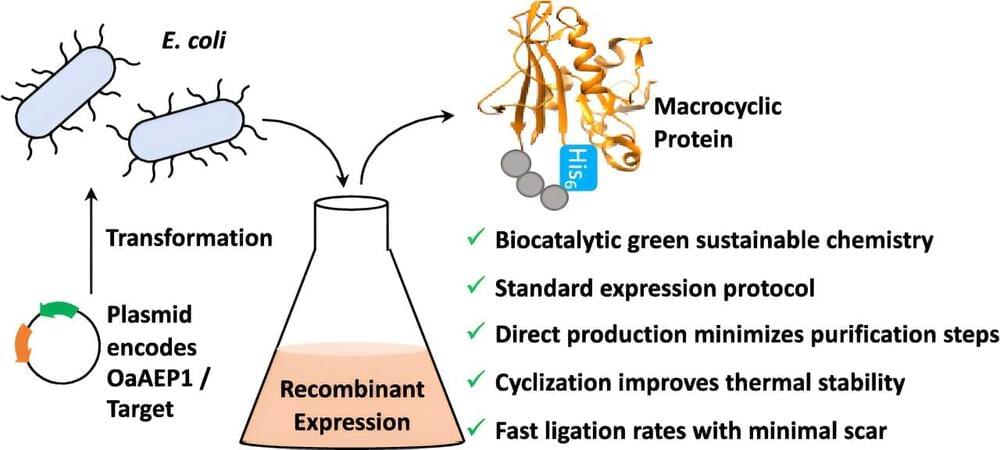
Scientists at the University of Bath have used nature as inspiration in developing a new tool that will help researchers develop new pharmaceutical treatments in a cleaner, greener, and less expensive way.
Drug treatments often work by binding to proteins involved in disease and blocking their activity, which either reduces symptoms or treats the disease.
Rather than using conventional small molecules as drugs, which are not well suited to blocking interactions between proteins, the pharmaceutical industry is now investigating the potential of making drugs using small proteins known as ‘peptides,’ which work in a similar way.