Aug 8, 2019
Manipulating brain cells
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biotech/medical, engineering, mobile phones, nanotechnology, neuroscience
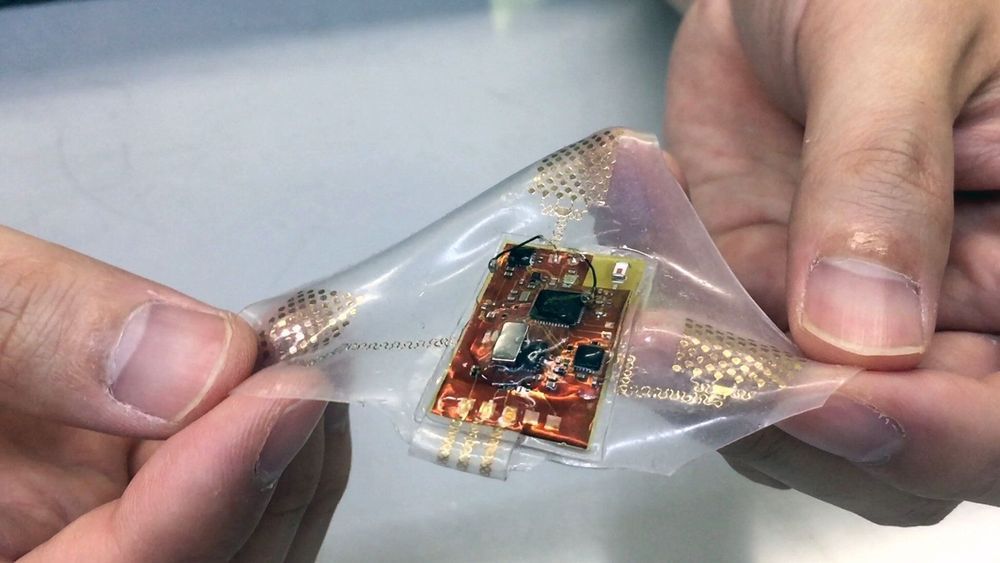
Researchers have developed a soft neural implant that can be wirelessly controlled using a smartphone. It is the first wireless neural device capable of indefinitely delivering multiple drugs and multiple colour lights, which neuroscientists believe can speed up efforts to uncover brain diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, addiction, depression, and pain. A team under Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and his collaborators have invented a device that can control neural circuits using a tiny brain implant controlled by a smartphone. The device, using Lego-like replaceable drug cartridges and powerful, low-energy Bluetooth, can target specific neurons of interest using drugs and light for prolonged periods. This study was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“This novel device is the fruit of advanced electronics design and powerful micro and nanoscale engineering,” explained Professor Jeong. “We are interested in further developing this technology to make a brain implant for clinical applications.”