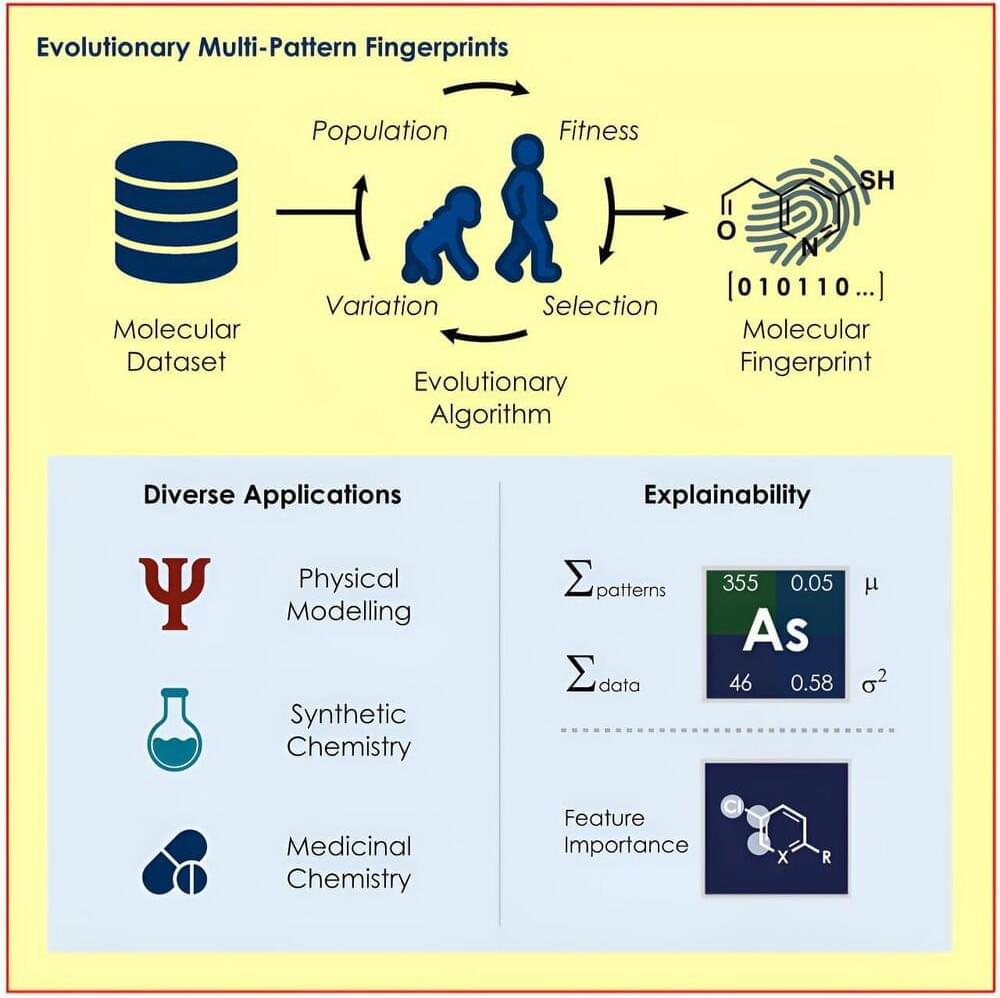
Perovskites are among the most researched topics in materials science. Recently, a research team led by Prof. LOH Kian Ping, Chair Professor of Materials Physics and Chemistry and Global STEM Professor of the Department of Applied Physics of The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU), Dr Kathy LENG, Assistant Professor of the same department, together with Dr Hwa Seob CHOI, Postdoctoral Research Fellow and the first author of the research paper, has solved an age-old challenge to synthesise all-organic two-dimensional perovskites, extending the field into the exciting realm of materials. This breakthrough opens up a new field of 2D all-organic perovskites, which holds promise for both fundamental science and potential applications.
This research was published in the journal Science (“Molecularly thin, two-dimensional all-organic perovskites”).
Perovskites are named after their structural resemblance to the mineral calcium titanate perovskite, and are well known for their fascinating properties that can be applied in wide-ranging fields such as solar cells, lighting and catalysis. With a fundamental chemical formula of ABX 3, perovskites possess the ability to be finely tuned by adjusting the A and B cations as well as the X anion, paving the way for the development of high-performance materials.