Imagine shrinking light down to the size of a tiny water molecule, unlocking a world of quantum possibilities. This has been a long-held dream in the realms of light science and technology. Recent advancements have brought us closer to achieving this incredible feat, as researchers from Zhejiang University have made groundbreaking progress in confining light to subnanometer scales.
Traditionally, there have been two approaches to localize light beyond its typical diffraction limit: dielectric confinement and plasmonic confinement. However, challenges such as precision fabrication and optical loss have hindered the confinement of optical fields to sub-10 nanometer (nm) or even 1-nm levels. But now, a new waveguiding scheme reported in Advanced Photonics promises to unlock the potential of subnanometer optical fields.
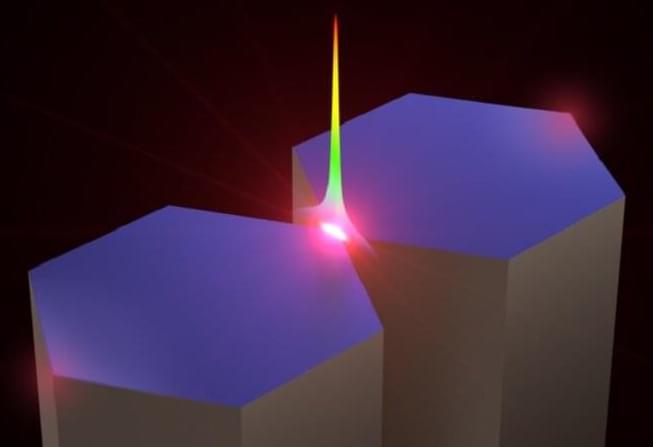
Picture this: Light travels from a regular optical fiber, embarking on a transformative journey through a fiber taper, and finds its destination in a coupled-nanowire-pair (CNP). Within the CNP, the light morphs into a remarkable nano-slit mode, generating a confined optical field that can be as tiny as a mere fraction of a nanometer (approximately 0.3 nm). With an astonishing efficiency of up to 95% and a high peak-to-background ratio, this novel approach offers a whole new world of possibilities.









Comments are closed.