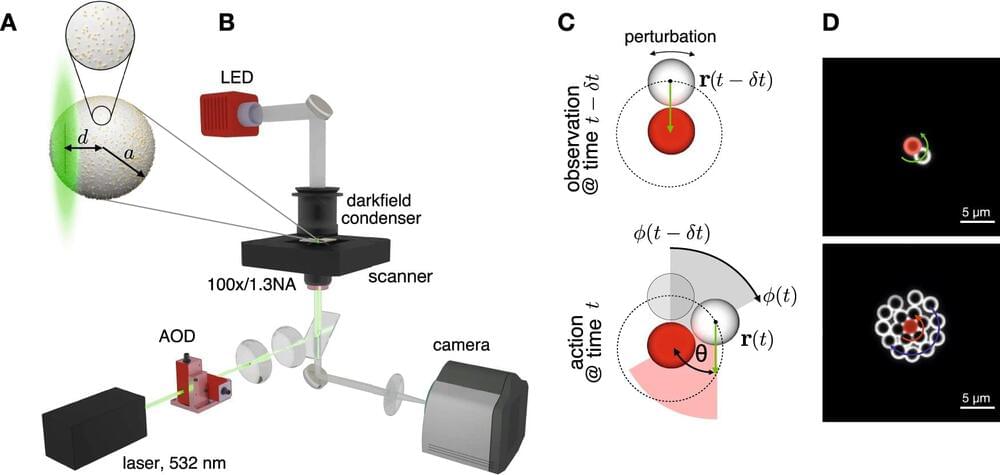
Seemingly spontaneously coordinated swarm behavior exhibited by large groups of animals is a fascinating and striking collective phenomenon. Experiments conducted by researchers at Leipzig University on laser-controlled synthetic microswimmers now show that supposed swarm intelligence can sometimes also be the result of simple and generic physical mechanisms.
A team of physicists led by Professor Frank Cichos and Professor Klaus Kroy found that swarms of synthetically produced Brownian microswimmers appear to spontaneously decide to orbit their target point instead of heading for it directly. They have just published their findings in the renowned journal Nature Communications.
“Scientific research on herd and flock behavior is usually based on field observations. In such cases, it is usually difficult to reliably record the internal states of the herd animals,” Kroy said. As a result, the interpretation of observations frequently relies on plausible assumptions as to which individual behavioral rules are necessary for the complex collective groups under observation.








Comments are closed.