Single neutral atoms trapped individually in optical microtraps are incredibly useful tools for studying quantum physics, as the atoms then exist in complete isolation from the environment. Arrays of optical microtraps containing single atoms could enable quantum logic devices, quantum information processing, and quantum simulation.
While single atom trapping has already been achieved, there are still many challenges to overcome. One such challenge is making sure each trap holds no more than one atom at a time, and also keeping it there so it won’t escape. This requires uniform optical microtraps, which have yet been fully realized.
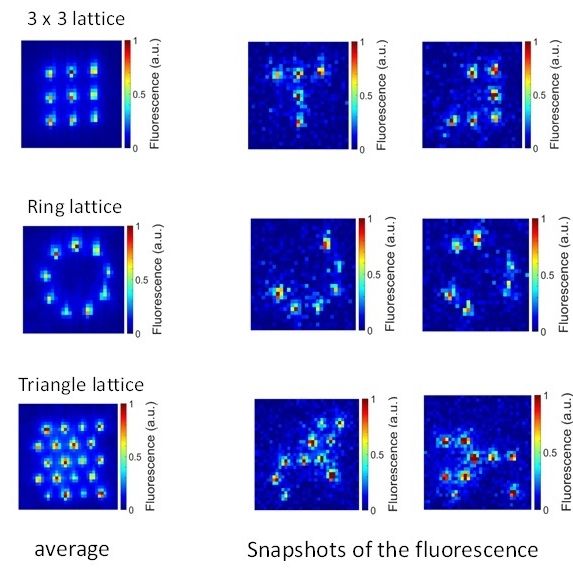
Now, Ken’ichi Nakagawa and co‐workers at the University of Electro‐Communications, Tokyo, Japan, together with scientists across Japan and China, have successfully demonstrated an optimization method for ensuring the creation of uniform holographic microtrap arrays to capture single rubidium (87Rb) atoms.








Comments are closed.