Page 11663
Sep 24, 2015
Banks Embrace Bitcoin’s Heart but Not Its Soul — By Tim Simonite | MIT Technology Review
Posted by Odette Bohr Dienel in category: bitcoin
“Major financial institutions like some technical features of Bitcoin but are building their own versions that leave out the digital cash and built-in economics.”
Tags: banks, blockchain
Sep 24, 2015
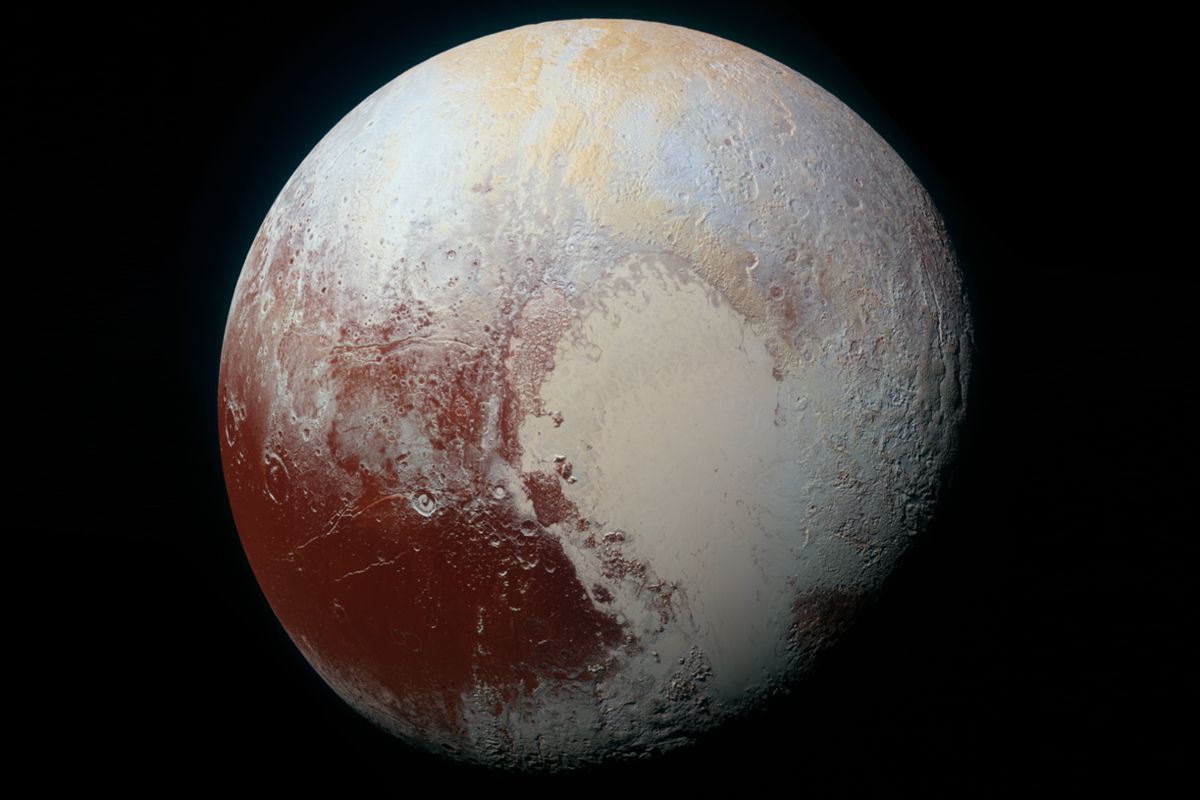
A colorful and dazzling view of Pluto
Posted by Philip Raymond in categories: astronomy, science, space
[From Engadget]…
While NASA has already shown us Pluto’s best images yet, the administration is anything but done blowing our minds. What you see above is an enhanced high-resolution color view of Pluto, created with a combination of blue, red and infrared images. NASA says this photo, taken by New Horizons spacecraft, highlights Pluto’s diverse landforms and shows us its complex geological and climatological story — as much as scientists have been able to figure out, anyway. Over the past few months, NASA’s shared many things related to Pluto, including a closer look at its desolate surface and icy mountain range.
Tags: New Horizons, Pluto, Solar system, space
Sep 24, 2015
Brain-computer link enables paralyzed California man to walk
Posted by Sean Brazell in categories: biotech/medical, computing, engineering, information science, neuroscience, robotics/AI
By Steve Gorman LOS ANGELES (Reuters) — A brain-to-computer technology that can translate thoughts into leg movements has enabled a man paralyzed from the waist down by a spinal cord injury to become the first such patient to walk without the use of robotics, doctors in Southern California reported on Wednesday. The slow, halting first steps of the 28-year-old paraplegic were documented in a preliminary study published in the British-based Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, along with a YouTube video. The feat was accomplished using a system allowing the brain to bypass the injured spinal cord and instead send messages through a computer algorithm to electrodes placed around the patient’s knees to trigger controlled leg muscle movements.
Sep 24, 2015
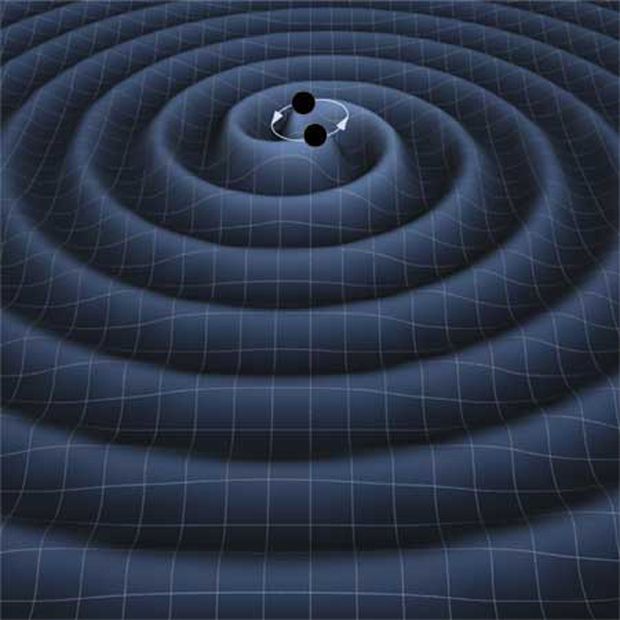
Double Black Holes May Warp Spacetime — But Quietly
Posted by Sean Brazell in category: cosmology
Two black holes, circling one another on their way to merging together, can create ripples in spacetime, but the waves are weaker than previously thought.
Sep 24, 2015
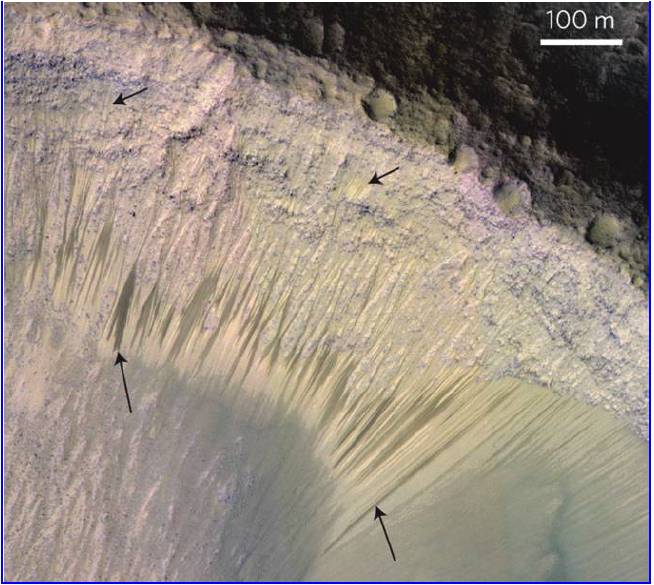
Mars‘ Mysterious Dark Streaks Spur Exploration Debate
Posted by Sean Brazell in category: space
The dark, fingerlike features that creep down steep Martian slopes in warm weather continue to puzzle scientists.
These “recurring slope lineae” (RSL), which have been spotted by NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) at low and middle latitudes on the Red Planet, fade during cooler months but come back again annually at nearly the same locations over multiple Martian years.
Scientists continue to debate the true nature of the RSL phenomenon; no guess as to what they are and why they occur yet satisfies all observations. And just how RSL sites should be explored generates spirited debate, as evidenced by the discussions that emerged during the second Mars 2020 Landing Site Workshop, which was held last month in Monrovia, California. [Photos: The Search for Water on Mars].
Sep 24, 2015
Losing Your Mind? Great Thinkers on the Brain
Posted by Johnny Boston in categories: biological, biotech/medical, cryonics, neuroscience, philosophy, science, theory

Aristotle is frequently regarded as one of the greatest thinkers of antiquity. So why didn’t he think much of his brain?
In this brief history of the brain, the GPA explores what the great minds of the past thought about thought. And we discover that questions that seem to have obvious answers today were anything but self-evident for the individuals that first tackled them. And that conversely, sometimes the facts which we simply accept to be true can be blinding, preventing us from making deeper discoveries about our our world and ourselves.
Tags: aristotle, Brain, debate, hippocrates, history, mind, Neurology, neuron, philosophers, philosophy of mind, scientists
Sep 24, 2015
Hooked-up human brains play telepathic ‘20 Questions’
Posted by Amnon H. Eden in categories: entertainment, neuroscience

“For the experiment, pairs of people played the well-known question-and-answer game “20 Questions”, but were located in two rooms a mile apart and hooked up to a brain-reading system. The person answering “yes” or “no” was connected to an ECG machine, which records electrical brain activity. The person guessing had a transcranial magnetic stimulation coil behind their head — a non-invasive tool that stimulates small areas of the brain”
Two human brains have successfully played “20 Questions”, showing for the first time that it is possible for two brains to share thoughts.
Continue reading “Hooked-up human brains play telepathic ‘20 Questions’” »
Sep 23, 2015
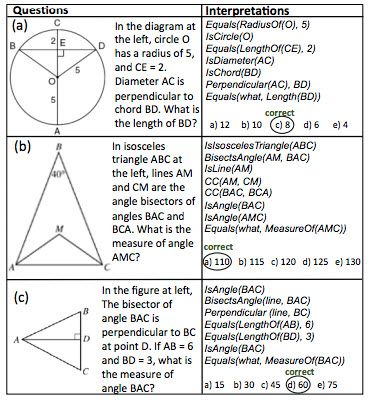
AI system solves SAT geometry questions as well as average American 11th-grade student
Posted by Sean Brazell in category: robotics/AI
Examples of questions (left column) and interpretations (right column) derived by GEOS (credit: Minjoon Seo et al./Proceedings of EMNLP)
An AI system that can solve SAT geometry questions as well as the average American 11th-grade student has been developed by researchers at the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence (AI2) and University of Washington.
Sep 23, 2015
DNA-guided 3-D printing of human tissue
Posted by Sean Brazell in categories: 3D printing, biotech/medical
Reconstituting epithelial (skin) microtissues with programmed size, shape, composition, spatial heterogeneity, and embedding extracellular matrix. Scheme and images of fully embedded aggregates of human luminal and myoepithelial cells. (credit: Michael E Todhunter et al./Nature Methods)
A new technique developed by UCSF scientists for building organoids (tiny models of human tissues) more precisely turns human cells into the biological equivalent of LEGO bricks. Called DNA Programmed Assembly of Cells (DPAC), it allows researchers in hours to create arrays of thousands of custom-designed organoids, such as models of human mammary glands containing several hundred cells each.