Page 11046
Jul 6, 2016
Paralyzed chimp walks, courtesy touch screen tech
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, computing
In a first, Japanese scientists have used a computer programme and a touch screen device to encourage a paralysed chimpanzee to walk again, showing that euthanasia need not be the only option for animals injured in captivity.
Jul 6, 2016
A Section of Route 66 Will Become America’s First Public Solar Road
Posted by Montie Adkins in category: solar power

I’ve seen people try and shoot this down, but it’s on its way.
Missouri will line a swath of the iconic highway with special energy-generating photovoltaic pavers.
Continue reading “A Section of Route 66 Will Become America’s First Public Solar Road” »
Jul 6, 2016
The World’s Largest Vertical Farm Is Being Built in New Jersey
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: food, sustainability
A huge vertical farm—where crops are planted, grown, and harvested all with neither sun nor soil—is being built in New Jersey. When it’s finished, it will be the largest one in the world.
You can see one of the (smaller) existing factories from AeroFarm, on which the new one will be modeled, above in this video from Seeker Stories. Nothing they are doing or planning is really new—people have been growing vegetables indoors under LED lights, minus the soil, for a very long time now. Even the factory spin is nothing new. Japan’s Mirai factory has been doing something similar on a slightly smaller scale for years now. What is interesting here, though, is just how big this place is.
Jul 5, 2016
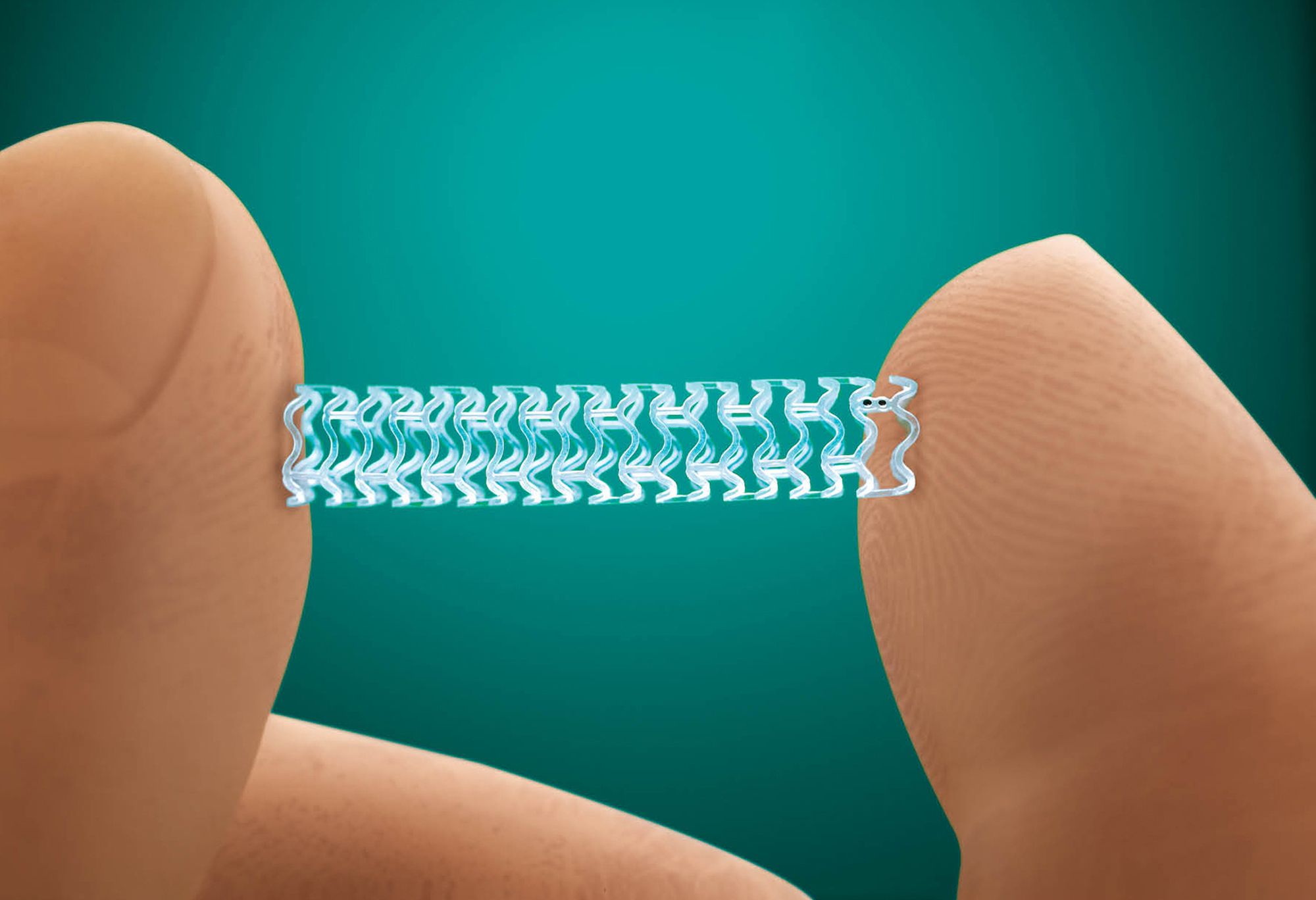
FDA approves first dissolving stent for US patients
Posted by Karen Hurst in category: biotech/medical
Glad it has been approved. This would have been great for BMI technology as well; however, FDA limits it to only treat clogged arteries.
WASHINGTON (AP) — A medical implant that slowly dissolves into the body could be the answer to long-standing safety concerns with devices used to treat clogged arteries.
But not so fast, say experts.
Continue reading “FDA approves first dissolving stent for US patients” »
Jul 5, 2016
DARPA’s Hacking Contest Will Pit Machines Against Each Other
Posted by Karen Hurst in category: cybercrime/malcode
Battle of the Machines.
DARPA is hosting a competition, the Cyber Grand Challenge, to find ways to solve cybersecurity vulnerabilities automatically.
Jul 5, 2016
Amazon moves one step closer toward army of warehouse robots
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: 3D printing, 4D printing, robotics/AI

I told folks just the other day; US Manufacturing in the next 3 to 5 years will primarily be robots, 3-/4-D printers, other AI systems, and a couple of line managers to spot check quality of the operation. Just surprised Amazon wasn’t already fully robotic.
Amazon’s progress toward an army of helpful robots is one step closer: a prize for the best warehouse-working “picker” machine has gone to a robot designed by a team from TU Delft Robotics Institute and Delft Robotics, both based in the Netherlands.
Continue reading “Amazon moves one step closer toward army of warehouse robots” »
Jul 5, 2016
A little impurity makes nanolasers shine
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: mobile phones, particle physics
Nice.
Researcher Tim Burgess added atoms of zinc to lasers one hundredth the diameter of a human hair and made of gallium arsenide — a material used extensively in smartphones and other electronic devices.
The impurities led to a 100 times improvement in the amount of light from the lasers.
Continue reading “A little impurity makes nanolasers shine” »
Jul 5, 2016
Engineers Design Programmable RNA Vaccines That Protext Against Ebola and H1N1 Influenza
Posted by Phillipe Bojorquez in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, genetics
A newly published study details how engineers developed programmable RNA vaccines that work against Ebola, H1N1 influenza, and a common parasites in mice.
MIT engineers have developed a new type of easily customizable vaccine that can be manufactured in one week, allowing it to be rapidly deployed in response to disease outbreaks. So far, they have designed vaccines against Ebola, H1N1 influenza, and Toxoplasma gondii (a relative of the parasite that causes malaria), which were 100 percent effective in tests in mice.
The vaccine consists of strands of genetic material known as messenger RNA, which can be designed to code for any viral, bacterial, or parasitic protein. These molecules are then packaged into a molecule that delivers the RNA into cells, where it is translated into proteins that provoke an immune response from the host.