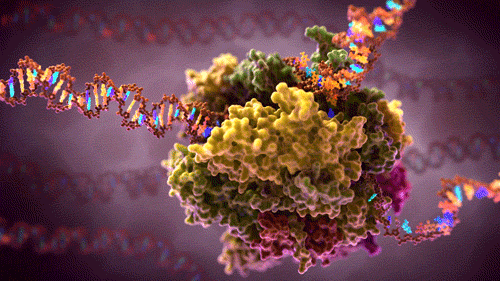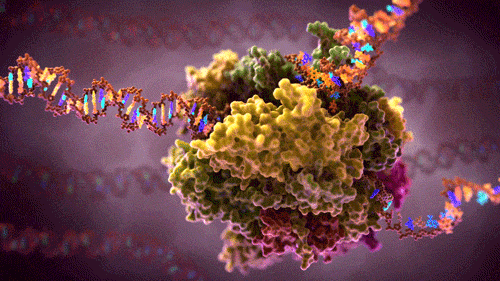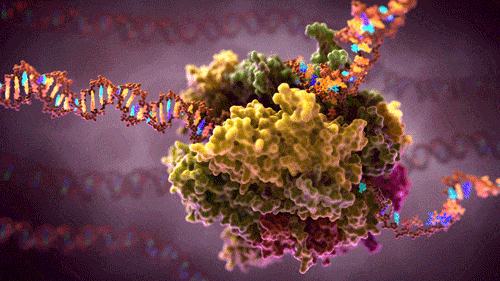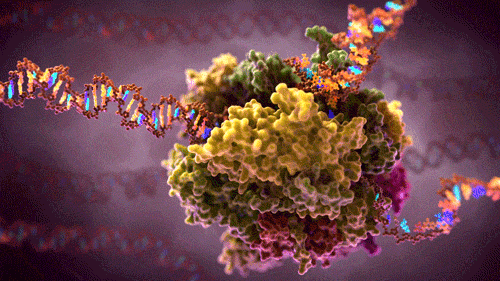
How does the human brain collect, process and store the flow of data which it constantly encounters? How does it manage cognitive tasks, which require complex interaction between various areas of the brain and overload high performance computers that work much more quickly? Why can the brain cope with all of this using much less energy? It is the aim of the research team from Kiel led by Professor Hermann Kohlstedt, Head of the Nanoelectronics Department at Kiel University (CAU) and spokesman of the national collaborative research project “Memristive devices for neural systems” (FOR 2093) funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) to track this impressive efficiency of the human brain using technology and to implement its method of operation in artificial neural networks. The scientists from Kiel have now succeeded in electronically reproducing two fundamental principles of operation of the human brain, memory and synchronisation. They recently published their results in Applied Physics Letters.
The human brain is a master of energy efficiency. It has approximately 100 billion nerve cells, also known as neurons, which manage with power of only about 20 Watt. Modern high performance computers would require many thousands of times more energy to perform similarly complex calculations as the brain manages. The neurons in the brain are linked to each other with synapses and form a highly complex network. The term “learning” in the neurological sense means that the synaptic connections in the brain are not determined statically. Instead they are continually readjusting on the basis of environmental influences, for example sensations. This makes it possible to store new memory content locally, known as the neurological plasticity of the brain.
In addition to the spatial ability of the neural connections to adjust, there is another important building block to process information in the brain: the synchronisation of neural groups. Electrical impulses, so-called action potentials, form the basic unit of information processing in the brain. These impulses permanently transmit information between the neurons and in doing so they cross and influence the synaptic connections in the brain. “In the case of conscious sensory perceptions the spatial irregular occurrence of neural impulses changes into ordered structures suddenly and for a limited time,” says Professor Thorsten Bartsch, a neurologist at Kiel University and member of the research group. The previously independent impulses of the neurons synchronise themselves in this case even over areas of the brain that are not close together. Evidence of this synchronised “firing” in humans can also be shown by measuring brain waves (electroencephalography, EEG).
Continue reading “Research team reproduces major functional principles of the brain using technology” »