Sep 29, 2016
Nanosensors help understand how tumors will respond to therapies
Posted by Karen Hurst in categories: biotech/medical, computing, engineering, health
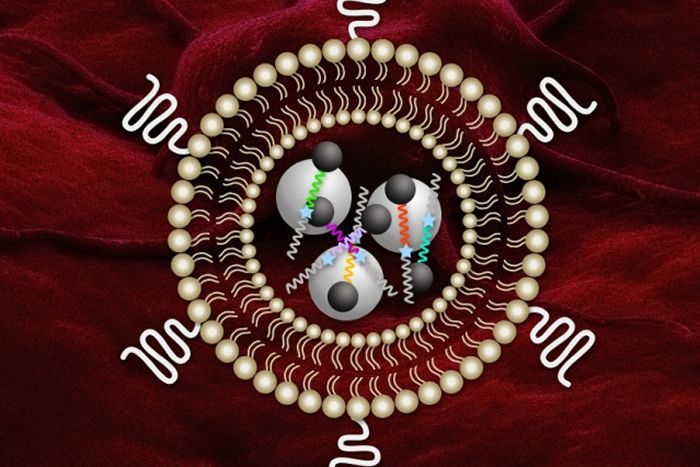
MIT researchers have designed nanosensors that can profile tumors and may yield insight into how they will respond to certain therapies. The system is based on levels of enzymes called proteases, which cancer cells use to remodel their surroundings.
Once adapted for humans, this type of sensor could be used to determine how aggressive a tumor is and help doctors choose the best treatment, says Sangeeta Bhatia, the John and Dorothy Wilson Professor of Health Sciences and Technology and Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and a member of MIT’s Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research.
“This approach is exciting because people are developing therapies that are protease-activated,” Bhatia says. “Ideally you’d like to be able to stratify patients based on their protease activity and identify which ones would be good candidates for these therapies.”
Continue reading “Nanosensors help understand how tumors will respond to therapies” »