Page 10825
Oct 5, 2016
Google $80 Daydream VR headset is soft and self-contained
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: virtual reality
Oct 5, 2016
Google’s Pixel phones make their debut
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: mobile phones, virtual reality
The first ‘Made by Google’ phones are here, meet the Pixel.
It has Google Assistant built-in, the “best smartphone camera,” unlimited photo storage and is Daydream VR compatible. The price starts at $649.
Oct 5, 2016
Hacking Our Senses Will Transform How We Experience the World
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: neuroscience
For millennia the human experience has been governed by five senses, but advances in neuroscience and technology may soon give us a far broader perspective.
What counts as a sense in the first place is not clear cut. Sight, hearing, taste, smell, and touch make up the traditional five senses, but our sense of balance and the ability to track the movement of our own body (proprioception) are both key sensory inputs. While often lumped in with touch, our temperature and pain monitoring systems could potentially qualify as independent senses.
These senses are also not as concrete as we probably believe. Roughly 4.4% of the population experiences synesthesia — where the stimulation of one sense simultaneously produces sensations in another. This can result in people perceiving colors when they hear sounds or associating shapes with certain tastes, demonstrating the potential fluidity of our senses.
Continue reading “Hacking Our Senses Will Transform How We Experience the World” »
Oct 5, 2016
Driverless Electric Minibuses Have Hit the Roads in France
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: robotics/AI, transportation
A driverless, electric public transport service is now making its way onto the streets of Lyon, France. Unveiled in an announcement made earlier this month, two Navya ARMA minibuses have embarked on a year-long trial. The purely battery-powered vehicles travel at an average speed of 10 kph (6 mph) and are able to carry 15 passengers at a time.
The ARMA shuttles along a circular route 1,350 meters (0.8 miles) long in the Confluence district of Lyon’s 2nd borough. Unlike other roads, this route does not have crosswalks, stoplights, or intersections. Though pretty advanced, the minibuses are not able to weave in and out of traffic due to restrictions based on the current level of technology, as well as legislative issues.
According to Navya chief executive Christophe Sapet in an interview with The Telegraph, the buses are “equipped with a range of detectors that allow them to know exactly where they are and to detect everything happening around them and to manage it intelligently to avoid collisions.” Human operators are present within the vehicle at all times as an added precaution.
Continue reading “Driverless Electric Minibuses Have Hit the Roads in France” »
Oct 5, 2016
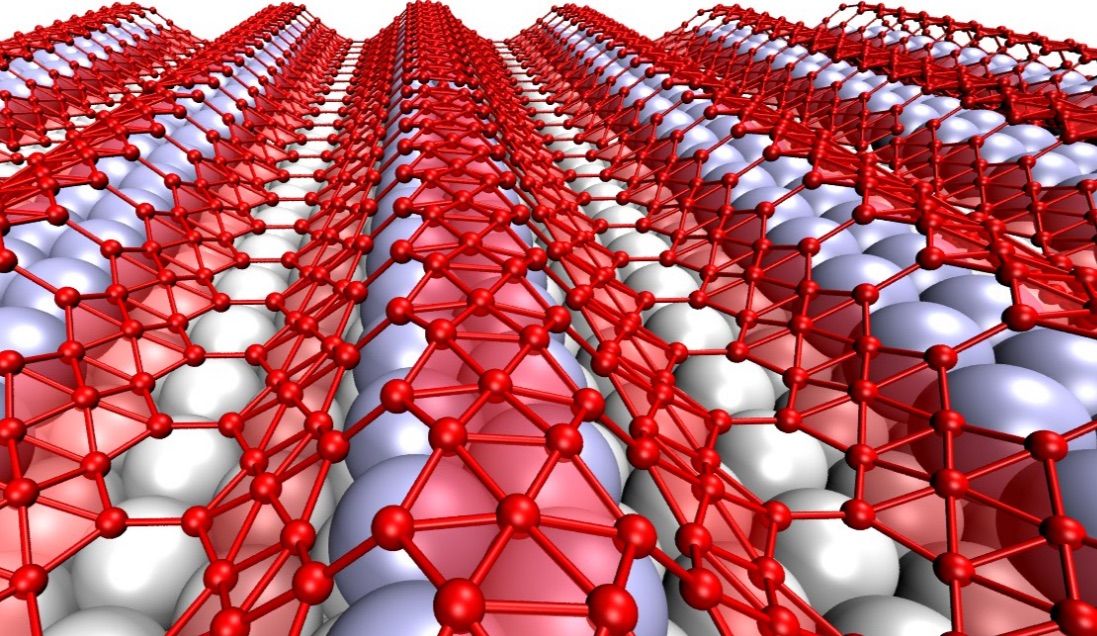
Researchers say 2-D boron may be best for flexible electronics
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: nanotechnology, particle physics, wearables
Though they’re touted as ideal for electronics, two-dimensional materials like graphene may be too flat and hard to stretch to serve in flexible, wearable devices. “Wavy” borophene might be better, according to Rice University scientists.
The Rice lab of theoretical physicist Boris Yakobson and experimental collaborators observed examples of naturally undulating, metallic borophene, an atom-thick layer of boron, and suggested that transferring it onto an elastic surface would preserve the material’s stretchability along with its useful electronic properties.
Highly conductive graphene has promise for flexible electronics, Yakobson said, but it is too stiff for devices that also need to stretch, compress or even twist. But borophene deposited on a silver substrate develops nanoscale corrugations. Weakly bound to the silver, it could be moved to a flexible surface for use.
Oct 5, 2016
New “Interscatter Communication” Could Let Your Implants Talk via Wi-Fi
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: internet, mobile phones, neuroscience, wearables
In Brief.
Interscatter communication has enabled the first Wi-Fi communication between implanted devices, wearables, and smart devices.
Researchers from the University of Washington have created a new form of communication that allows devices like credit cards, smart contact lenses, brain implants, and smaller wearable electronics to use Wi-Fi to talk to everyday devices like watches and smartphones. It’s called “interscatter communication,” and it works by using reflections to convert Bluetooth signals into Wi-Fi transmissions in the air that can be picked up by smart devices.
Continue reading “New ‘Interscatter Communication’ Could Let Your Implants Talk via Wi-Fi” »
Oct 4, 2016
Legally Blind Man Sees Clearly For The First Time Ever, Thanks to Virtual Reality
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: virtual reality
In Brief.
- Jamie Soar suffers from retinitis pigmentosa, a condition that has rendered him legally blind and which affects some 100,000 people in the U.S. alone.
- Because of the dual-screen projection method used in virtual reality, Soar was able to see normally for the first time in his life.
With the rise of specialized hardware such as the HTC Vive, Oculus Rift, and Samsung Gear VR, virtual reality (VR) is at its most accessible point ever. It provides an immersive and realistic simulation of an environment, one which is created entirely through software and hardware. And notably, this environment can be experienced or controlled by the movements of your body. To this end, VR opens up an entirely new world (literally) of possibilities.