May 8, 2024
New Evidence for Our Solar System’s Ghost: Planet Nine
Posted by Dan Breeden in category: space
New simulations support the existence of Planet Nine. We won’t have to wait long before they can be tested with the Vera Rubin Observatory.
New simulations support the existence of Planet Nine. We won’t have to wait long before they can be tested with the Vera Rubin Observatory.
A research team led by Dr. Serge Krasnokutski from the Astrophysics Laboratory at the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy at the University of Jena had already demonstrated that simple peptides can form on cosmic dust particles. However, it was previously assumed that this would not be possible if molecular ice, which covers the dust particle, contains water—which is usually the case.
Now the team, in collaboration with the University of Poitiers, France, has discovered that the presence of water molecules is not a major obstacle for the formation of peptides on such dust particles. The researchers report on their finding in the journal Science Advances.
Chemistry in the icy vacuum “We have replicated conditions similar to those in outer space in a vacuum chamber, also adding substances that occur in so-called molecular clouds,” explains Krasnokutski. These substances include ammonia, atomic carbon, and carbon monoxide. “Thus, all the chemical elements needed for simple peptides are present,” adds the physicist.
Earth’s magnetic field plays a key role in making our planet habitable. The protective bubble over the atmosphere shields the planet from solar radiation, winds, cosmic rays and wild swings in temperature.
However, Earth’s magnetic field almost collapsed 591 million years ago, and this change, paradoxically, may have played a pivotal role in the blossoming of complex life, new research has found.
“In general, the field is protective. If we had not had a field early in Earth history water would have been stripped from the planet by the solar wind (a stream of energized particles flowing from the sun toward Earth),” said John Tarduno, a professor of geophysics at the University of Rochester in New York and senior author of the new study.
Superradiant atoms offer a groundbreaking method for measuring time with an unprecedented level of precision. In a recent study published by the scientific journal Nature Communications, researchers from the University of Copenhagen present a new method for measuring the time interval, seconds, that overcomes some of the limitations that even today’s most advanced atomic clocks encounter. This advancement could have broad implications in areas such as space exploration, volcanic monitoring, and GPS systems.
The second, which is the most precisely defined unit of measurement, is currently measured by atomic clocks in different places around the world that together tell us what time it is. Using radio waves, atomic clocks continuously send signals that synchronize our computers, phones, and watches.
Oscillations are the key to keeping time. In a grandfather clock, these oscillations are from a pendulum’s swinging from side to side every second, while in an atomic clock, it is a laser beam that corresponds to an energy transition in strontium and oscillates about a million billion times per second.
Here is a panel between David Chalmers and Scott Aaronson at Mindfest 2024. This discussion covers the philosophical implications of the simulation hypothesis, exploring whether our reality might be a simulation and engaging with various perspectives on the topic. This presentation was recorded at MindFest, held at Florida Atlantic University, CENTER FOR THE FUTURE MIND, spearheaded by Susan Schneider. YouTube: https://youtu.be/7PlmOXQ18jk Please consider signing up for TOEmail at https://www.curtjaimungal.org.
Support TOE: — Patreon: https://patreon.com/curtjaimungal (early access to ad-free audio episodes!) — Crypto: https://tinyurl.com/cryptoTOE — PayPal: https://tinyurl.com/paypalTOE — TOE Merch: https://tinyurl.com/TOEmerch … see more.
Using new observations from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), astronomers have discovered methane emission on a brown dwarf, an unexpected finding for such a cold and isolated world. Published in the journal Nature, the findings suggest that this brown dwarf might generate aurorae similar to those seen on our own planet as well as on Jupiter and Saturn.
More massive than planets but lighter than stars, brown dwarfs are ubiquitous in our solar neighborhood, with thousands identified. Last year, Jackie Faherty, a senior research scientist and senior education manager at the American Museum of Natural History, led a team of researchers who were awarded time on JWST to investigate 12 brown dwarfs.
Among those was CWISEP J193518.59–154620.3 (or W1935 for short)—a cold brown dwarf 47 light years away that was co-discovered by Backyard Worlds: Planet9, citizen science volunteer Dan Caselden and the NASA CatWISE team. W1935 is a cold brown dwarf with a surface temperature of about 400° Fahrenheit. The mass for W1935 isn’t well known but it likely ranges between six-to 35-times the mass of Jupiter.
Astronomers still don’t know what causes fast radio bursts, but they’re starting to use them to illuminate the space between galaxies.
An X-ray burst (XRB) is a violent explosion that occurs on the surface of a neutron star as it absorbs material from a companion star. During this absorption, increasing temperatures and densities on the surface of the neutron star ignite a cascade of thermonuclear reactions.
The original version of this story appeared in Quanta Magazine.
In October, a Falcon Heavy rocket is scheduled to launch from Cape Canaveral in Florida, carrying NASA’s Europa Clipper mission. The $5 billion mission is designed to find out if Europa, Jupiter’s fourth-largest moon, can support life. But because Europa is constantly bombarded by intense radiation created by Jupiter’s magnetic field, the Clipper spacecraft can’t orbit the moon itself. Instead, it will slide into an eccentric orbit around Jupiter and gather data by repeatedly swinging by Europa—53 times in total—before retreating from the worst of the radiation. Every time the spacecraft rounds Jupiter, its path will be slightly different, ensuring that it can take pictures and gather data from Europa’s poles to its equator.
To plan convoluted tours like this one, trajectory planners use computer models that meticulously calculate the trajectory one step at a time. The planning takes hundreds of mission requirements into account, and it’s bolstered by decades of mathematical research into orbits and how to join them into complicated tours. Mathematicians are now developing tools which they hope can be used to create a more systematic understanding of how orbits relate to one another.
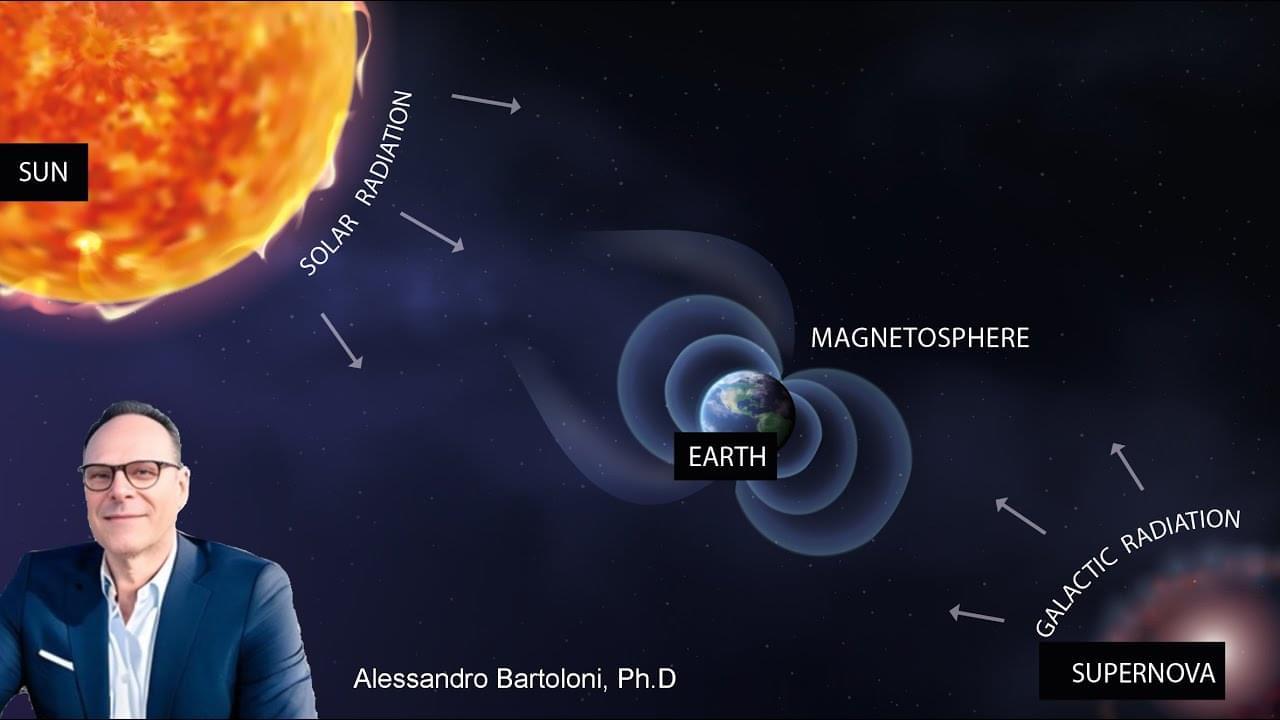
AbstractThis talk will delve into the intricate web of space radiation, focusing on its three primary components – galactic cosmic rays, solar energetic part…