Sep 5, 2024
DARPA Robotic Satellite Servicing
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: climatology, robotics/AI, satellites
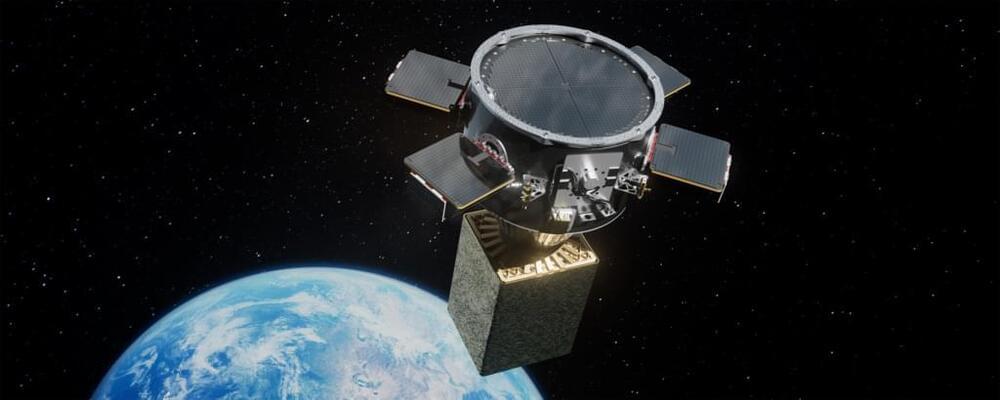
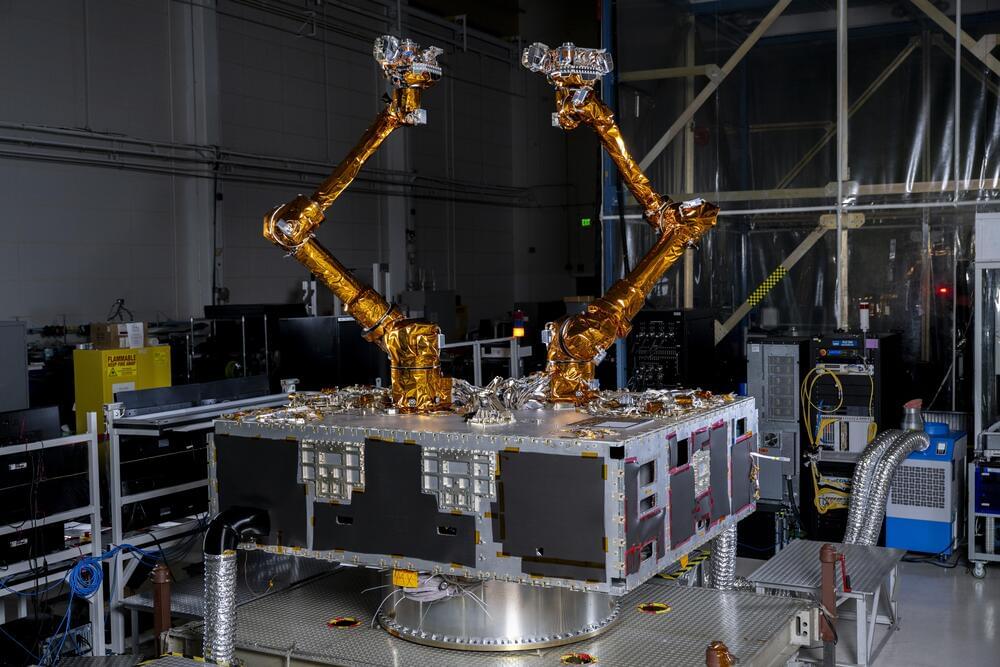
NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) have signed an interagency agreement to collaborate on a satellite servicing demonstration in geosynchronous Earth orbit, where hundreds of satellites provide communications, meteorological, national security, and other vital functions.
Under this agreement, NASA will provide subject matter expertise to DARPA’s Robotic Servicing of Geosynchronous Satellites (RSGS) program to help complete the technology development, integration, testing, and demonstration. The RSGS servicing spacecraft will advance in-orbit satellite inspection, repair, and upgrade capabilities.