Aug 24, 2023
SpaceX Introduces Third-Generation Starlink Wi-Fi Router, Only Available to Select Early Customers
Posted by Kelvin Dafiaghor in categories: internet, satellites
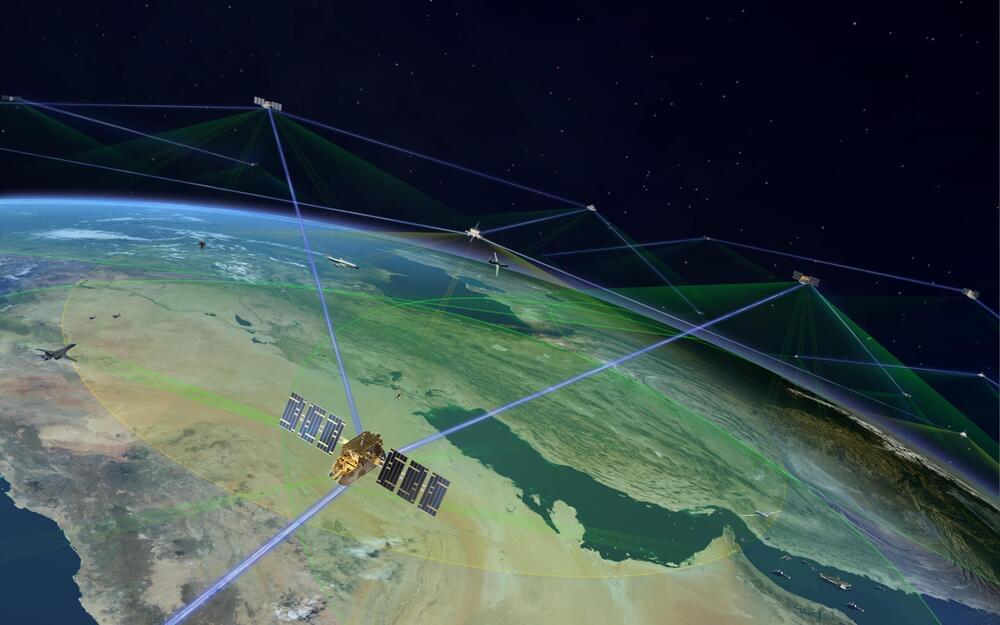
SpaceX has taken a step further in its mission to enhance global internet connectivity with the unveiling of its third-generation (Gen 3) Wi-Fi for the Starlink satellite internet service. This announcement comes as a select group of customers have been invited via email to test the new at a cost of $200 USD, according to multiple individuals who received the invite.
“You’re Invited: New Starlink,” says the email, “As an early Starlink customer, you’re invited to a limited launch of our next generation WiFi We would love to hear about your experience, including setup, performance, or any other recommendations you may have, as these will be the firsts produced. […] You may order up to 3s per account. This offer applies only to your Starlink account. What’s improved? The new Gen 3 introduces WiFi 6 and tri-band radios to Starlink. With improved range, performance, and device support, the Starlink Gen 3 will extend your WiFi network throughout your home to provide a more consistent and reliable connection with faster speeds,” the company states. “The Gen 3 can replace your current, and multiple Gen 3s can be meshed together to extend the range of your WiFi network.”