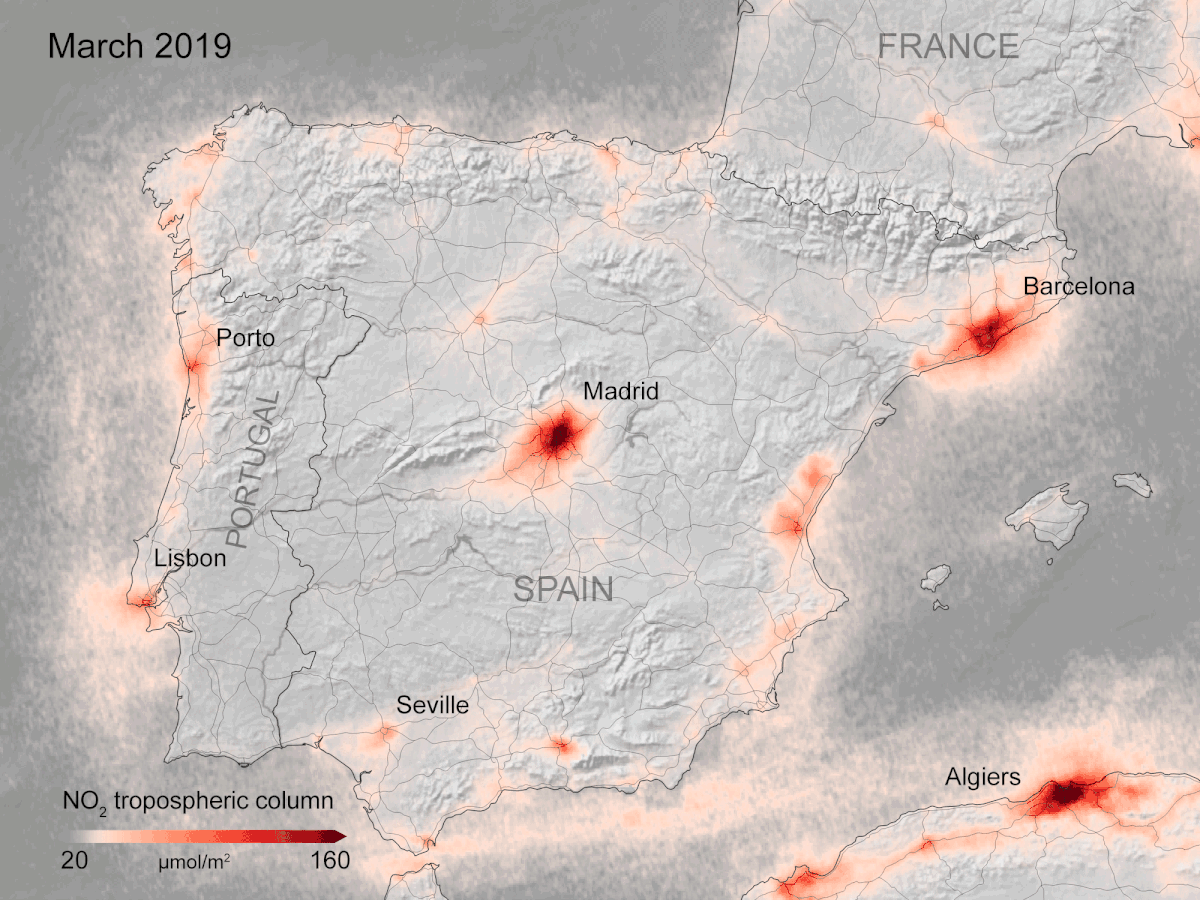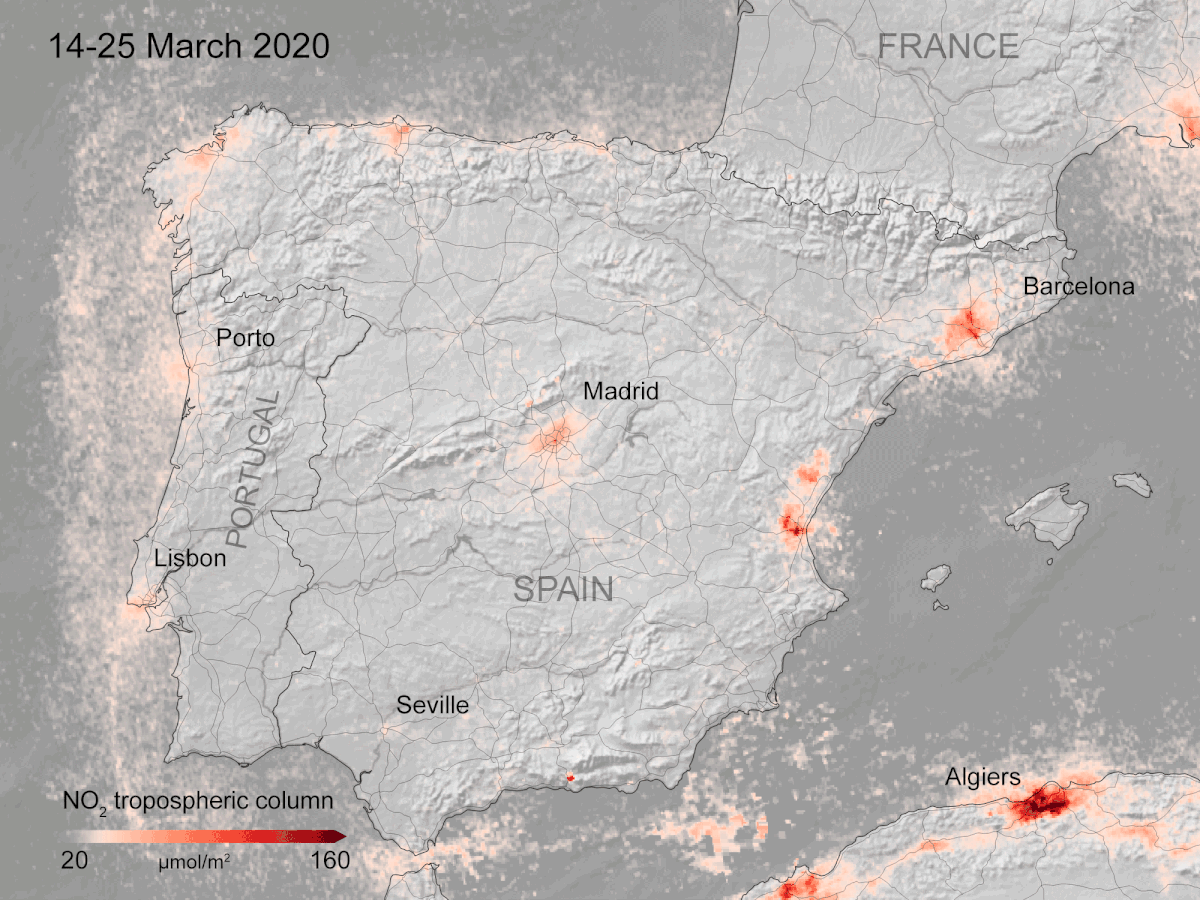
Mar 30, 2020
Stars and Starlink
Posted by Roderick Reilly in categories: biotech/medical, finance, satellites
Astronomers may have one less (satellite) constellation to worry about.
Late Friday, OneWeb announced it had filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in a New York court. In a statement, the company said it had been in “advanced negotiations” since the beginning of the year to raise a new round of funding needed to complete its broadband satellite constellation. The company said it was close to completing that deal, but “the financial impact and market turbulence related to the spread of COVID-19” kept it from closing the deal.
OneWeb had just started large-scale deployment of its constellation, with Soyuz launches in early February and again March 21 each placing 34 satellites into orbit. Future launches are now on hold—launch services provider Arianespace was the largest single unsecured creditor identified in OneWeb’s bankruptcy, at $238 million—and may never resume, depending on who buys the company’s assets in a planned sale and their intentions for them.