The United States is transitioning from a primary reliance on fossil fuels to greater use of sustainable natural and nuclear energy sources. There are two reasons for this transition. The first reason is that the abnormally high and increasing level of atmospheric carbon dioxide has created scientific uncertainty and concern as to the detrimental impact this may have on the environment and, consequentially, human civilization. Almost certainly, this abnormal level is due to anthropogenic causes linked to the tremendous expansion in the human population since the early 1700s, the growth of human civilization (e.g., agriculture and industrialization), and the increasing use of fossil fuels. Although fossil fuels have enabled worldwide progress in elevating the standard of living, most of the world’s nations have reached the conclusion that the world should transition entirely to sustainable energy by 2100 (see “The Paris climate agreement and space solar power”, The Space Review, February 29, 2016). It is, however, very important to manage this transition carefully to avoid economic hardship or energy deprivation.
While the United States has large remaining fossil fuel resources, only some are technically recoverable with current safe, legal, and profitable extraction methods. The remaining known and yet-to-be-discovered domestic technically recoverable fossil fuels are inadequate to sustain US fossil fuel energy needs to the end of this century, especially given likely continued immigration-driven US population growth (see “US fossil fuel energy insecurity and space solar power”, The Space Review, March 7, 2016). While the United States has an ethical environmental obligation to end its use of fossil fuels by the end of the century, the reality of having inadequate oil and natural gas resources makes the urgency of transitioning successfully to new sustainable energy sources a clear matter of national energy security. This warrants federal government leadership and strong American private sector engagement.
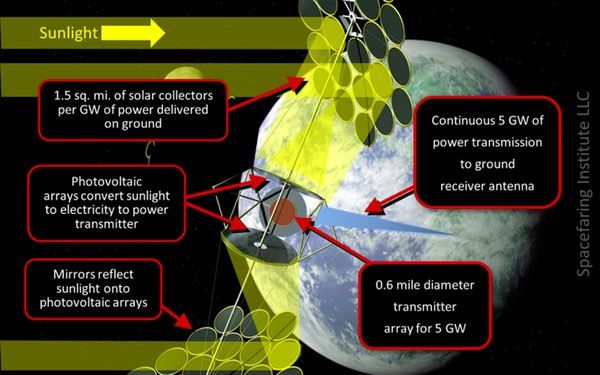
Unfortunately, due to its large and growing population and per capita energy needs, the United States lacks sufficient suitable land to utilize terrestrial renewable energy to replace fossil fuels. (see “US terrestrial non-fossil fuel energy vs. space solar power”, The Space Review, March 14, 2016). While the United States will utilize terrestrial domestic renewable energy to the extent it is politically acceptable, many factors will likely limit their scale-up. The expansion of nuclear fission energy is also not a satisfactory approach, given the large number of reactors needed. These factors lead to the conclusion that only space-based sustainable energy, such as space solar power, will enable the United States to practically transition away from fossil fuels.
Read more