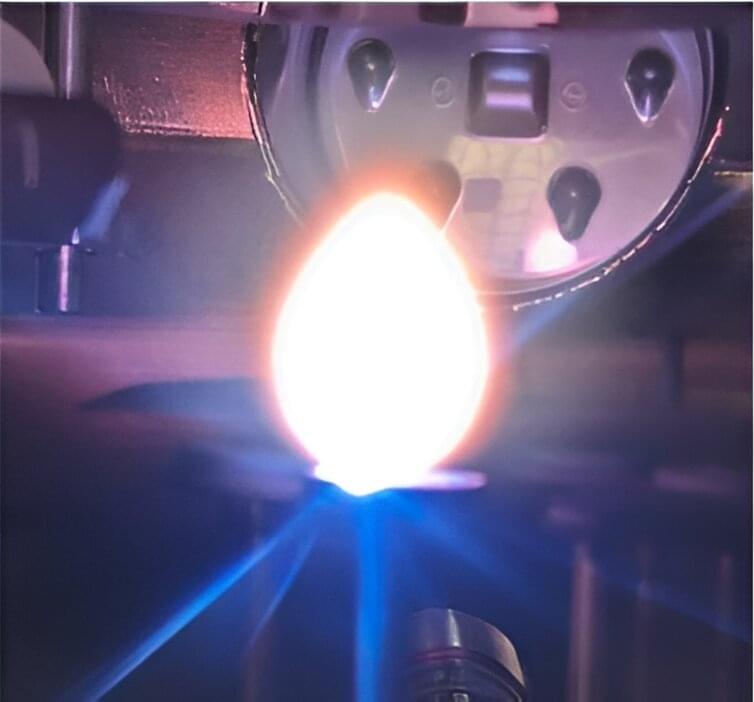
Some experts believe that the future of fusion in the U.S. may be found in compact, spherical fusion vessels. A smaller tokamak is seen as a potentially more economical solution for fusion energy. The challenge lies in fitting all necessary components into a limited space. Recent research indicates that removing one key component used to heat the plasma could create the additional space required.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), the private company Tokamak Energy, and Kyushu University in Japan have proposed a design for a compact, spherical fusion pilot plant that heats the plasma using only microwaves. Typically, spherical tokamaks also use a massive coil of copper wire called a solenoid, located near the center of the vessel, to heat the plasma. Neutral beam injection, which involves applying beams of uncharged particles to the plasma, is often used as well. But much like a tiny kitchen is easier to design if it has fewer appliances, it would be simpler and more economical to make a compact tokamak if it has fewer heating systems.
The new approach eliminates ohmic heating, which is the same heating that happens in a toaster and is standard in tokamaks. “A compact, spherical tokamak plasma looks like a cored apple with a relatively small core, so one does not have the space for an ohmic heating coil,” said Masayuki Ono, a principal research physicist at PPPL and lead author of the paper detailing the new research. “If we don’t have to include an ohmic heating coil, we can probably design a machine that is easier and cheaper to build.”