For decades, neuroscientists have been trying to understand how we manage to make the best possible decisions. Due to technical limitations, researchers have so far had to rely on experiments in which monkeys perform tasks on computer screens while the activity of their brain cells is measured.
The animals are trained to sit still in a chair and are therefore restricted in their natural freedom of movement. Since it is now possible to wirelessly record the activity of several individual nerve cells, decision-making in scenarios with natural movement sequences can be investigated.
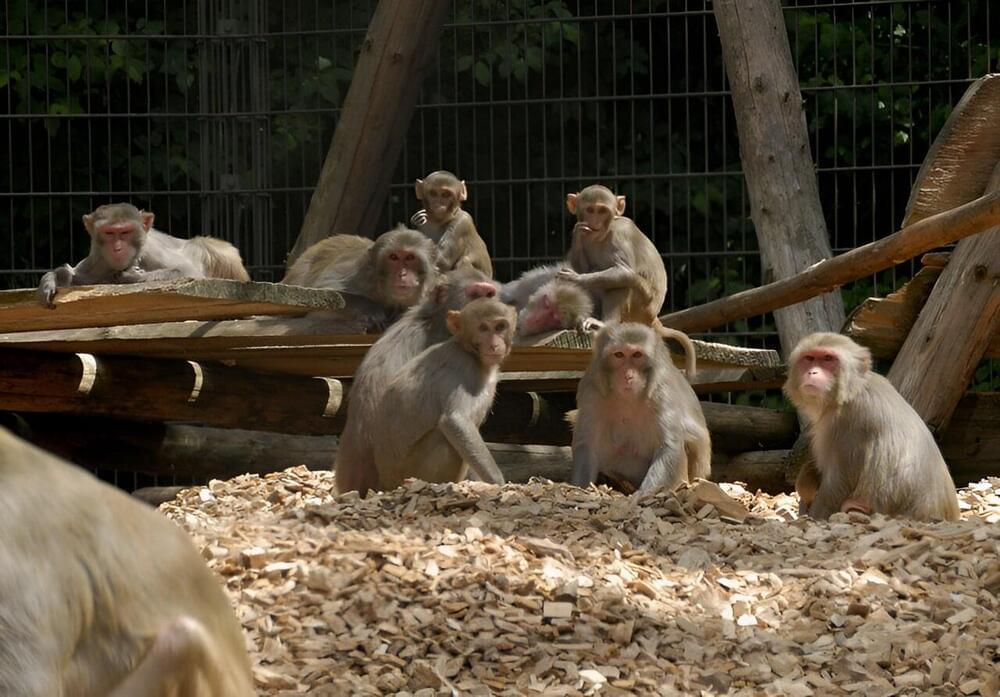
For the study, a team of researchers from Germany and the U.S. trained two rhesus monkeys to explore an experimental room with two button-controlled food boxes. Each time the monkeys pressed a button on one of the boxes, they had the chance to receive food pellets.