Mar 15, 2024
APOE from patient-derived astrocytic extracellular vesicles alleviates neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in a mouse model
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, neuroscience
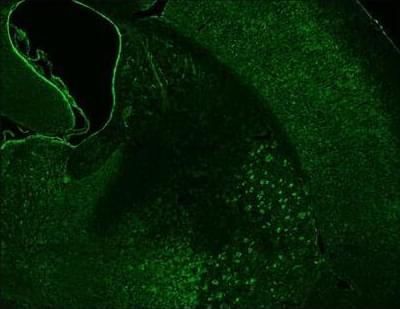
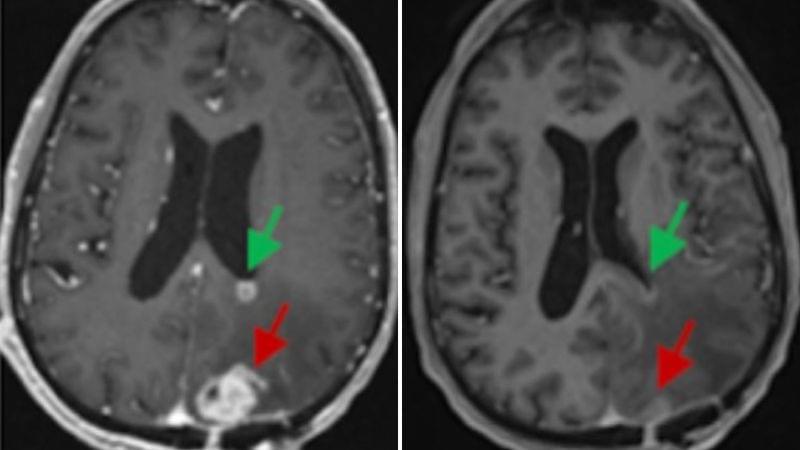
Analyzing cells from patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder, researchers show transfers of patient-derived extracellular vesicles rich in the apolipoprotein APOE alleviate neuroinflammation and slow astrocyte loss in a mouse model of this severe autoimmune disease.
📄 :
APOE was augmented in astrocytic extracellular vesicles from patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and decreased brain lesions in a mouse model.