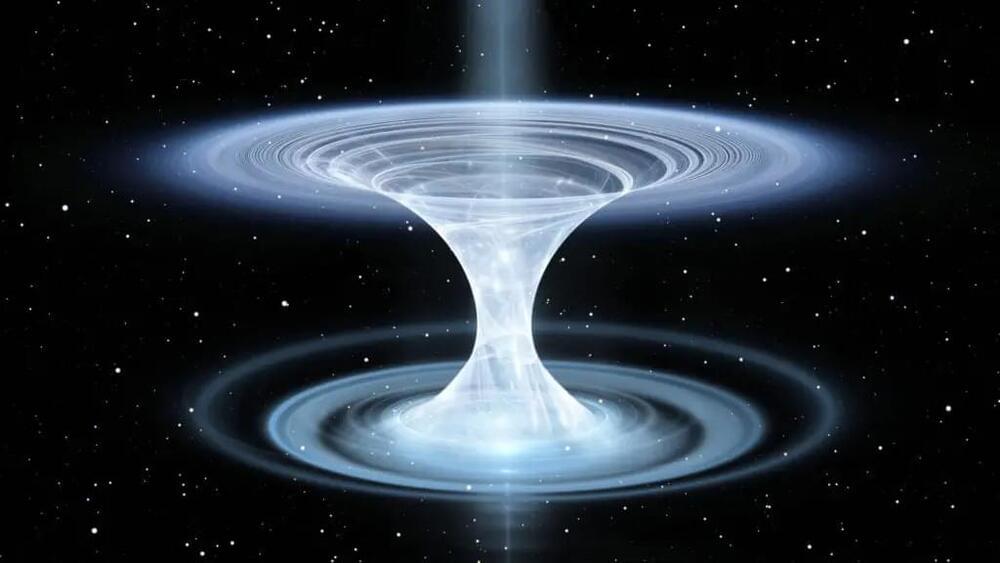
Black holes have long fascinated scientists, known for their ability to trap anything that crosses their event horizon. But what if there were a counterpart to black holes? Enter the white hole—a theoretical singularity where nothing can enter, but energy and matter are expelled with immense force.
First proposed in the 1970s, white holes are essentially black holes in reverse. They rely on the same equations of general relativity but with time flowing in the opposite direction. While a black hole pulls matter in and lets nothing escape, a white hole would repel matter, releasing high-energy radiation and light.
Despite their intriguing properties, white holes face significant scientific challenges. The laws of thermodynamics, particularly entropy, make it improbable for matter to move backward in time, as white holes would require. Additionally, introducing a singularity into the Universe without a preceding collapse defies current understanding of cosmic evolution.