Archive for the ‘neuroscience’ category: Page 128
Apr 29, 2024
Resurrection through simulation: questions of feasibility, desirability and some implications
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: computing, cryonics, information science, life extension, neuroscience
Could a future superintelligence bring back the already dead? This discussion has come up a while back (and see the somewhat related); I’d like to resurrect the topic because … it’s potentially quite important.
Algorithmic resurrection is a possibility if we accept the same computational patternist view of identity that suggests cryonics and uploading will work. I see this as the only consistent view of my observations, but if you don’t buy this argument/belief set then the rest may not be relevant.
The general implementation idea is to run a forward simulation over some portion of earth’s history, constrained to enforce compliance with all recovered historical evidence. The historical evidence would consist mainly of all the scanned brains and the future internet.
Apr 29, 2024
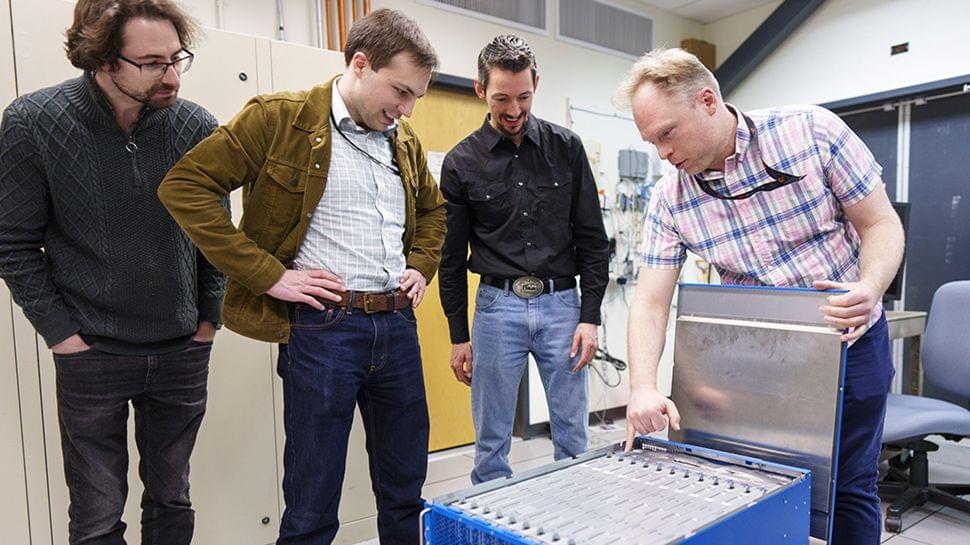
‘Inspired by the human brain’: Intel debuts neuromorphic system that aims to mimic grey matter with a clear aim — making the machine exponentially faster and much more power efficient, just like us
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: computing, neuroscience
Neuromorphic computing is about mimicking the human brain’s structure to deliver more efficient data processing, including faster speeds and higher accuracy, and it’s a hot topic right now. A lot of universities and tech firms are working on it, including scientists at Intel who have built the world’s largest “brain-based” computing system for Sandia National Laboratories in New Mexico.
Intel’s creation, called Hala Point, is only the size of a microwave, but boasts 1.15 billion artificial neurons. That’s a massive step up from the 50 million neuron capacity of its predecessor, Pohoiki Springs, which debuted four years ago. There’s a theme with Intel’s naming in case you were wondering – they’re locations in Hawaii.
Apr 29, 2024
China Shows Off Monkey With Brain Chip Allowing It to Control Robotic Arm
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: Elon Musk, government, neuroscience, robotics/AI
A Chinese company says it’s successfully developed a brain chip and implanted it into a monkey — who can now remotely control a robot arm with the device.
That’s according to state-run news media outfit Xinhua, putting Elon Musk’s startup Neuralink on notice that there will be international as well as domestic competition for his brain-computer interface venture.
The company, Beijing Xinzhida Neurotechnology, which is backed by the Chinese government, unveiled its device, the NeuCyber Array BMI (brain-machine interface) System at a technology convention in Beijing on Thursday, according to Reuters.
Apr 29, 2024
Russellian Monism (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: information science, neuroscience, physics

Russellian monism is a theory in the metaphysics of mind, on which a single set of properties underlies both consciousness and the most basic entities posited by physics. The theory is named for Bertrand Russell, whose views about consciousness and its place in nature were informed by a structuralist conception of theoretical physics. On such a structuralist conception, physics describes the world in terms of its spatiotemporal structure and dynamics (changes within that structure) and says nothing about what, if anything, underlies that structure and dynamics. For example, as it is sometimes put, physics describes what mass and charge do, e.g., how they dispose objects to move toward or away from each other, but not what mass and charge are. Thus, Russell writes the following about the events physics describes:
All that physics gives us is certain equations giving abstract properties of their changes. But as to what it is that changes, and what it changes from and to—as to this, physics is silent. (Russell 1959: 18)
Continue reading “Russellian Monism (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)” »
Apr 29, 2024
Scientists Have Created a Functional Brain Cell Based on a Mix of Salt And Water
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: biological, neuroscience, particle physics
For the first time, researchers have simulated neurological junctions called synapses using the same water and salt ingredients the brain uses, contributing to an emerging field that combines biology with electronics called iontronics.
The team from Utrecht University in the Netherlands and Sogang University in South Korea claim to have been inspired by the functioning of the human brain, which also uses charged particles called ions dissolved in water to transmit signals within neurons.
An important feature of the brain’s ability to process information is synaptic plasticity, which allows neurons to adjust the strength of connections between them in response to input history.
Apr 29, 2024
Research uncovers Differences between Men and Women in Sleep, Circadian Rhythms and Metabolism
Posted by Natalie Chan in category: neuroscience
A new review of research evidence has explored the key differences in how women and men sleep, variations in their body clocks, and how this affects their metabolism.
Apr 28, 2024
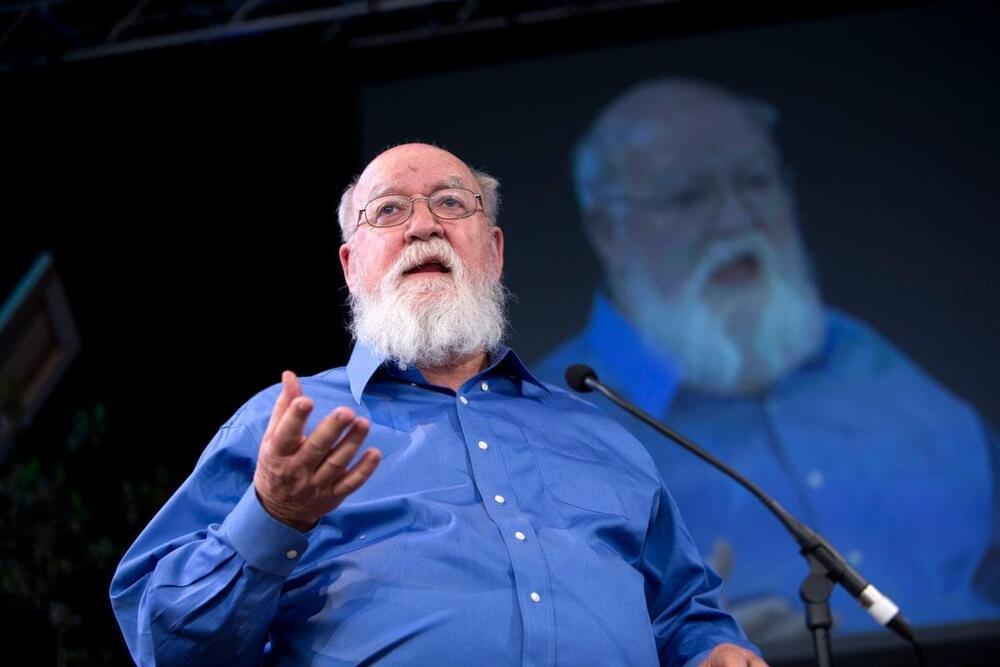
An Epitaph for Daniel Dennett, Philosopher of Consciousness
Posted by Dan Breeden in category: neuroscience
Is consciousness nothing more than an illusion? That idea defined the work of Daniel Dennett (1942–2024)
By John Horgan
Philosopher Daniel Dennett died a few days ago, on April 19. When he argued that we overrate consciousness, he demonstrated, paradoxically, how conscious he was, and he made his audience more conscious.
Apr 28, 2024
Boost Your Brain: Scientists Develop New Method To Improve Your Reading Efficiency
Posted by Dan Breeden in category: neuroscience
Researchers from the University of Cologne and the University of Würzburg have discovered through training studies that individuals can improve their ability to distinguish between familiar and unfamiliar words, enhancing reading efficiency. Recognizing words is necessary to understand the meaning of a text. When we read, we move our eyes very efficiently and quickly from word to word. This reading flow is interrupted when we encounter a word we do not know, a situation common when learning a new language.
The words of the new language might have yet to be comprehended in their entirety, and language-specific peculiarities in spelling still need to be internalized. The team of psychologists led by junior professor Dr. Benjamin Gagl from the University of Cologne’s Faculty of Human Sciences has now found a method to optimize this process.
The current research results were published in npj Science of Learning under the title ‘Investigating lexical categorization in reading based on joint diagnostic and training approaches for language learners’. Starting in May, follow-up studies extending the training program will be carried out within a project funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG).