May 10, 2024
Neuralink Admits That Implant’s Threads Have Retracted From First Patient’s Brain, Possibly Due to Air in Skull
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, computing, Elon Musk, neuroscience
Not ideal!
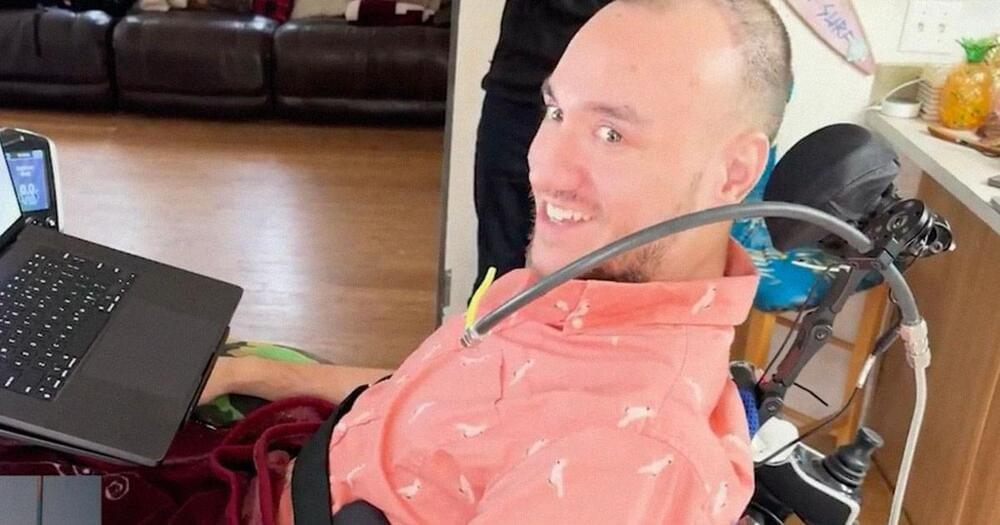
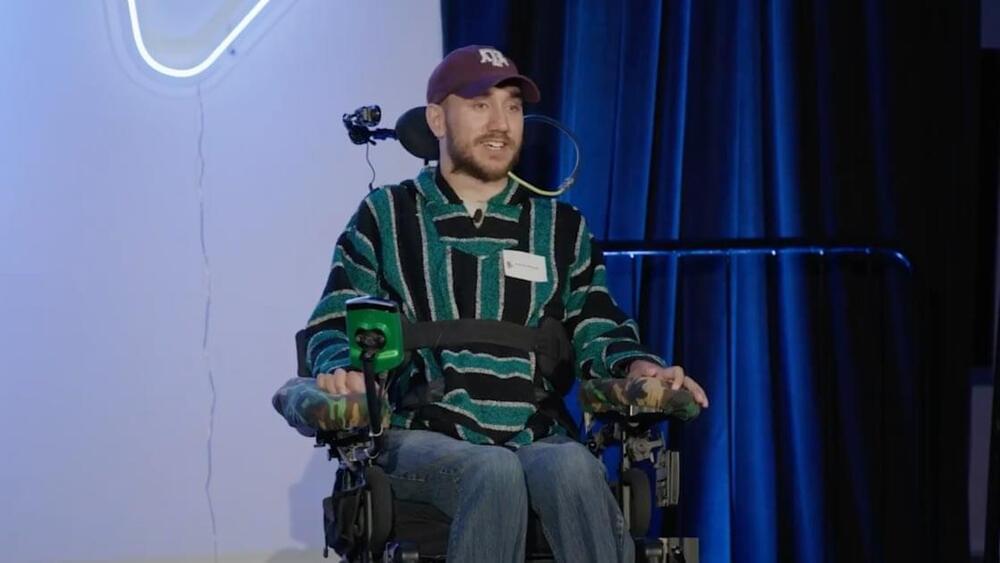
In January, multi-hyphenate billionaire Elon Musk announced that his brain-computer interface startup Neuralink had successfully implanted a wireless brain chip into a human subject for the first time.
Over the next couple of months, 29-year-old Noland Arbaugh was shown moving a cursor with his mind, playing Civilization VI and even a fast-paced round of Mario Kart.