May 11, 2024
Combination of Genetics and Nanotechnology for Down Syndrome Modification: A Potential Hypothesis and Review of the Literature
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, genetics, nanotechnology, neuroscience
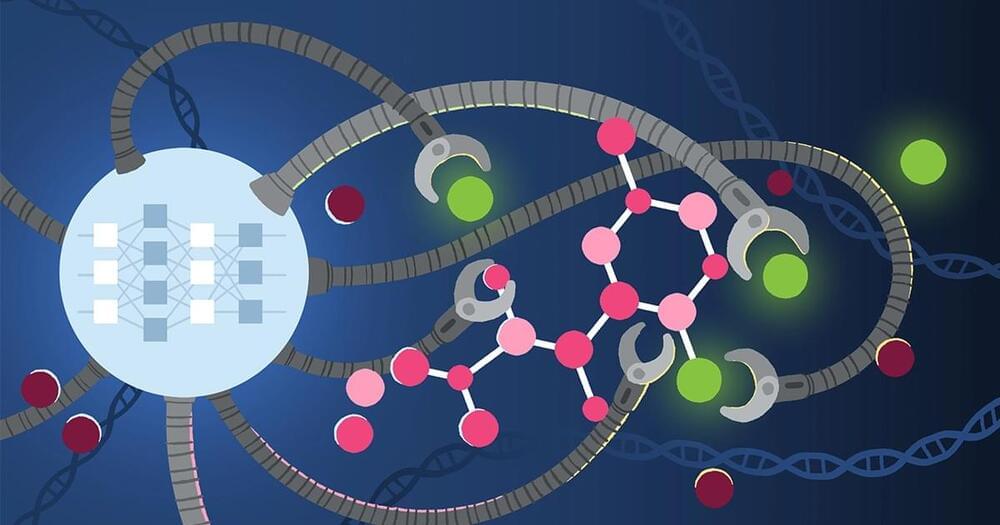
Down syndrome (DS) is one of the most prevalent genetic disorders in humans. The use of new approaches in genetic engineering and nanotechnology methods in combination with natural cellular phenomenon can modify the disease in affected people. We consider two CRISPR/Cas9 systems to cut a specific region from short arm of the chromosome 21 (Chr21) and replace it with a novel designed DNA construct, containing the essential genes in chromatin remodeling for inactivating of an extra Chr21. This requires mimicking of the natural cellular pattern for inactivation of the extra X chromosome in females. By means of controlled dosage of an appropriate Nano-carrier (a surface engineered Poly D, L-lactide-co-glycolide (PLGA) for integrating the relevant construct in Trisomy21 brain cell culture media and then in DS mouse model, we would be able to evaluate the modification and the reduction of the active extra Chr21 and in turn reduce substantial adverse effects of the disease, like intellectual disabilities. The hypothesis and study seek new insights in Down syndrome modification.
Keywords: Down syndrome, CRISPR/Cas9, Designed DNA construct, Poly D L-lactide-co-glycolide (PLGA), Nano-carrier, Chromosome 21 inactivation.