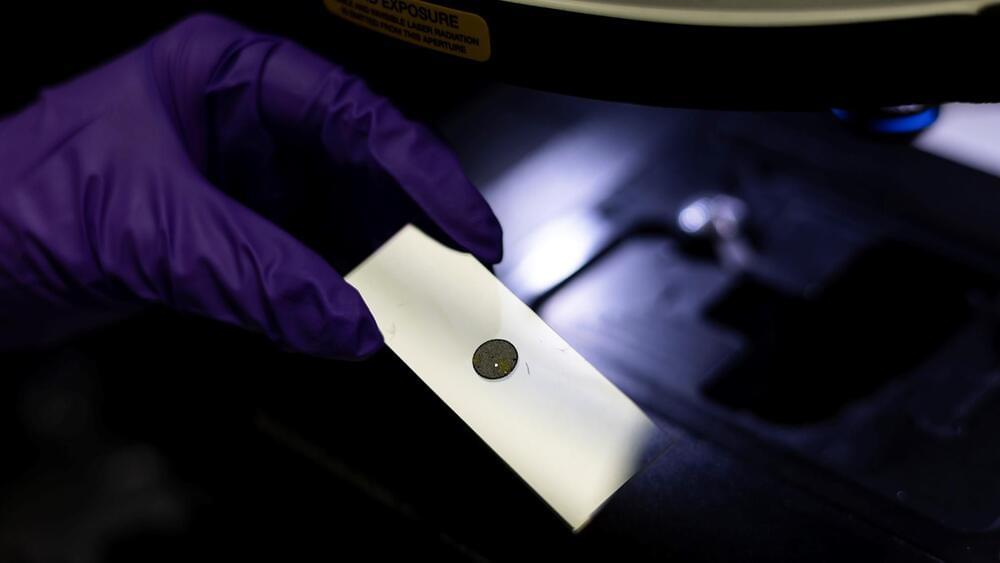
Nuclear nonproliferation scientists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have published the Compendium of Uranium Raman and Infrared Experimental Spectra, or CURIES, a public database and analysis of structure-spectral relationships for uranium minerals. This first-of-its-kind dataset and corresponding analysis fill a key gap in the existing body of knowledge for mineralogists and actinide scientists.
Laser based vibrational spectroscopy methods such as Raman and IR are frequently employed by nonproliferation materials scientists because they are rapid, nominally non-destructive, and can give direct insight to what a material contains. Where spectral assignments may be difficult, the CURIES database uses structural information, subject matter expertise and statistical analysis to determine key features of Raman spectra based on their structural origins.
“When I was in grad school studying uranium mineralogy, there was no single repository to look up a feature of a sample and compare it for identification,” said ORNL’s Tyler Spano, lead author on the CURIES article in American Minerologist. “What we did was bring together data from many different sources including structural information and spectroscopy to understand spectral features and similarities as they relate to chemical, structural and other properties.” The ORNL team hopes that CURIES will support researchers who are looking for new relationships among various types of uranium materials and foster development of rapid characterization and analysis of spectra collected on new materials.