Yes this says a 3 year epigenetic clock reversal in just 8 weeks thanks to diet and lifestyle changes. There is a list of supplements too:
Alpha ketoglutarate, vitamin C and vitamin A curcumin, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), rosmarinic acid, quercetin, luteolin.
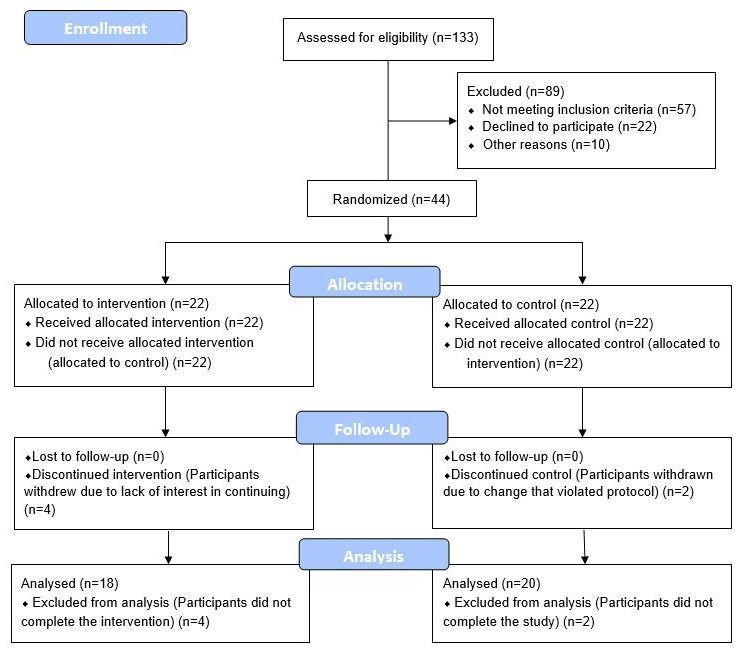
Manipulations to slow biological aging and extend healthspan are of interest given the societal and healthcare costs of our aging population. Herein we report on a randomized controlled clinical trial conducted among 43 healthy adult males between the ages of 50–72. The 8-week treatment program included diet, sleep, exercise and relaxation guidance, and supplemental probiotics and phytonutrients. The control group received no intervention. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis was conducted on saliva samples using the Illumina Methylation Epic Array and DNAmAge was calculated using the online Horvath DNAmAge clock (2013). The diet and lifestyle treatment was associated with a 3.23 years decrease in DNAmAge compared with controls (p=0.018). DNAmAge of those in the treatment group decreased by an average 1.96 years by the end of the program compared to the same individuals at the beginning with a strong trend towards significance (p=0.066). Changes in blood biomarkers were significant for mean serum 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (+15%, p=0.004) and mean triglycerides (−25%, p=0.009). To our knowledge, this is the first randomized controlled study to suggest that specific diet and lifestyle interventions may reverse Horvath DNAmAge (2013) epigenetic aging in healthy adult males. Larger-scale and longer duration clinical trials are needed to confirm these findings, as well as investigation in other human populations.
Continue reading “Potential reversal of epigenetic age using a diet and lifestyle intervention: a pilot randomized clinical trial” »