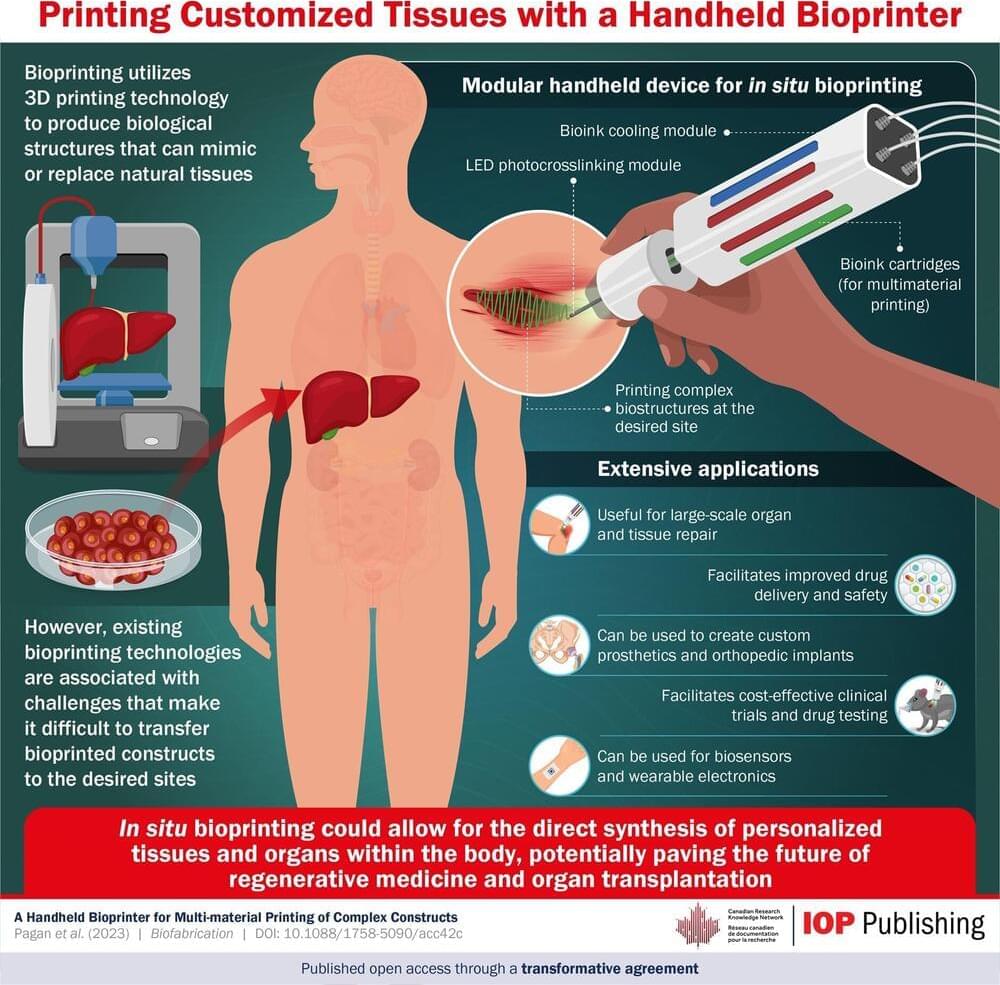
In situ bioprinting, which involves 3D printing biocompatible structures and tissues directly within the body, has seen steady progress over the past few years. In a recent study, a team of researchers developed a handheld bioprinter that addresses key limitations of previous designs, i.e., the ability to print multiple materials and control the physicochemical properties of printed tissues. This device will pave the way for a wide variety of applications in regenerative medicine, drug development and testing, and custom orthotics and prosthetics.
The emergence of regenerative medicine has resulted in substantial improvements in the lives of patients worldwide through the replacement, repair, or regeneration of damaged tissues and organs. It is a promising solution to challenges such as the lack of organ donors or transplantation-associated risks. One of the major advancements in regenerative medicine is on-site (or “in situ”) bioprinting, an extension of 3D printing technology, which is used to directly synthesize tissues and organs within the human body. It shows great potential in facilitating the repair and regeneration of defective tissues and organs.
Although significant progress has been made in this field, currently used in situ bioprinting technologies are not devoid of limitations. For instance, certain devices are only compatible with specific types of bioink, while others can only create small patches of tissue at a time. Moreover, their designs are usually complex, making them unaffordable and restricting their applications.