Sep 16, 2016
Reinforcement Learning for Torch: Introducing torch-twrl
Posted by Bruno Henrique de Souza in categories: information science, robotics/AI
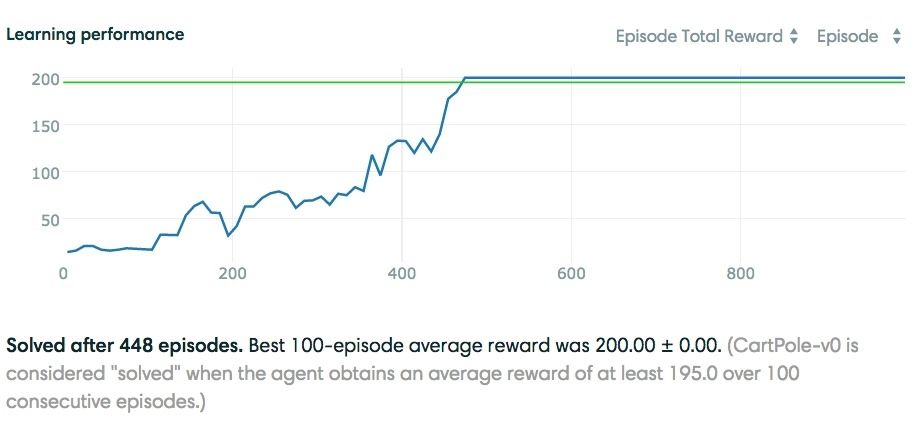
Advances in machine learning have been driven by innovations and ideas from many fields. Inspired by the way that humans learn, Reinforcement Learning (RL) is concerned with algorithms which improve with trial-and-error feedback to optimize future performance.
Board games and video games often have well-defined reward functions which allow for straightforward optimization with RL algorithms. Algorithmic advances have allowed for RL to be in real-world problems, such as high degree-of-freedom robotic manipulation and large-scale recommendation tasks, with more complex goals.
Twitter Cortex invests in novel state-of-the-art machine learning methods to improve the quality of our products. We are exploring RL as a learning paradigm, and to that end, Twitter Cortex built a framework for RL development. Today, Twitter is open sourcing torch-twrl to the world.
Continue reading “Reinforcement Learning for Torch: Introducing torch-twrl” »