Oct 2, 2024
Filament structure found to activate and regulate CRISPR-Cas ‘protein scissors’
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
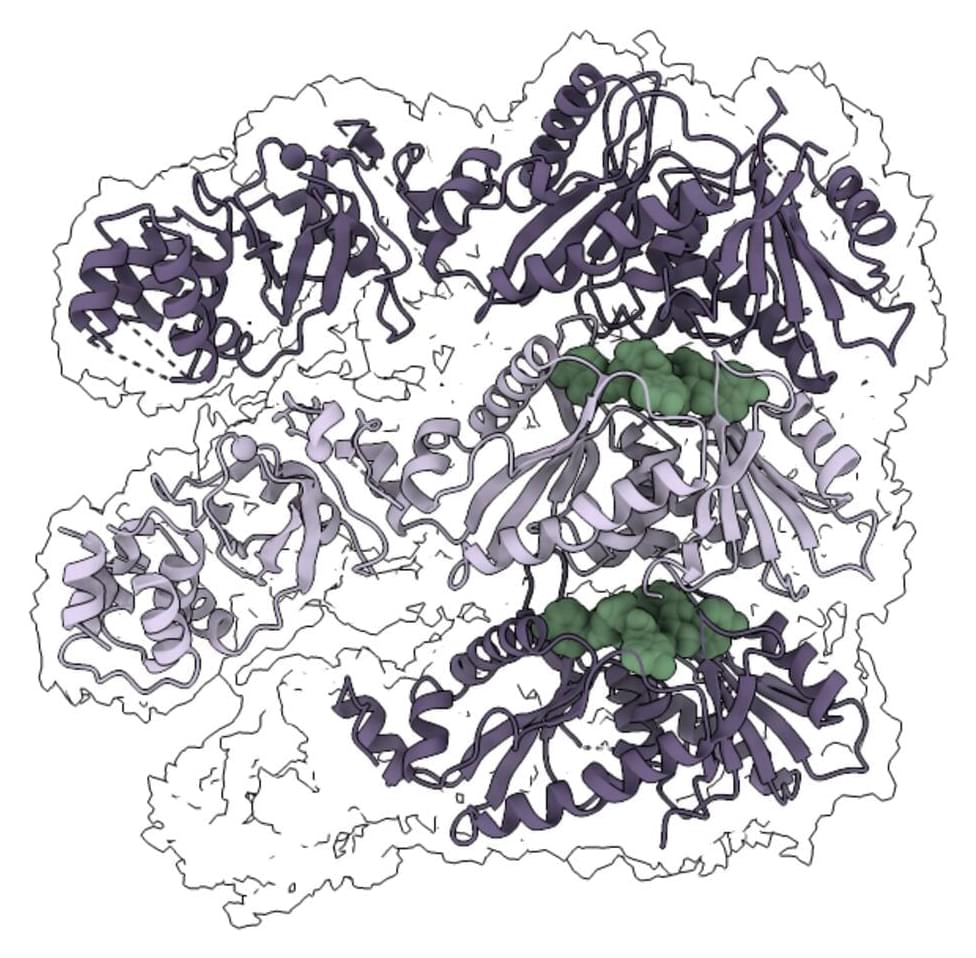
CRISPR-Cas systems help to protect bacteria from viruses. Several different types of CRISPR-Cas defense systems are found in bacteria, which differ in their composition and functions. Among them, the most studied proteins today are Cas9 and Cas12, also known as DNA or “gene scissors,” which have revolutionized the field of genome editing, enabling scientists to edit genomes and correct disease-causing mutations precisely.