Archive for the ‘futurism’ category: Page 88
Jun 9, 2024
Tony Seba’s Prediction: Nuclear Obsolete by 2030 — Wind, Solar, and Battery Storage the Future
Posted by Chris Smedley in categories: futurism, nuclear energy

Small modular nuclear reactors are too expensive, too slow, and too risky, and the focus should be on wind, solar, and battery storage for energy needs Questions to inspire discussion What did Tony Seba predict about nuclear power in 2014? —Tony Seba predicted in 2014 that nuclear power would be obsolete by 2030, and recent research has shown that his predictions about the cost blowouts and inefficiency of small modular nuclear reactors were accurate.
Jun 9, 2024
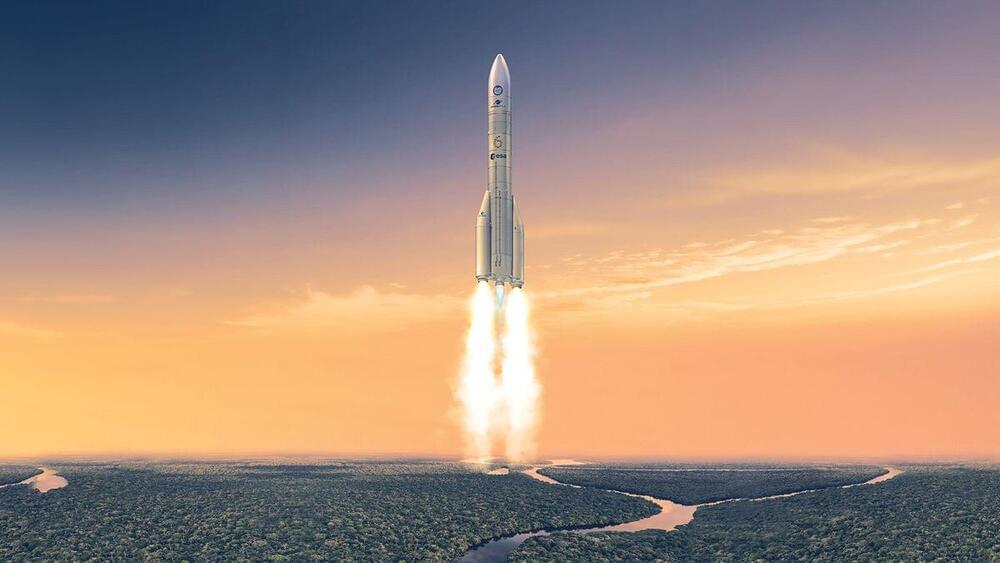
At long last: Europe’s new Ariane 6 rocket set to debut on July 9
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: futurism
Jun 9, 2024
San Francisco police to start using non-lethal BolaWrap restraint tool
Posted by Raphael Ramos in category: futurism
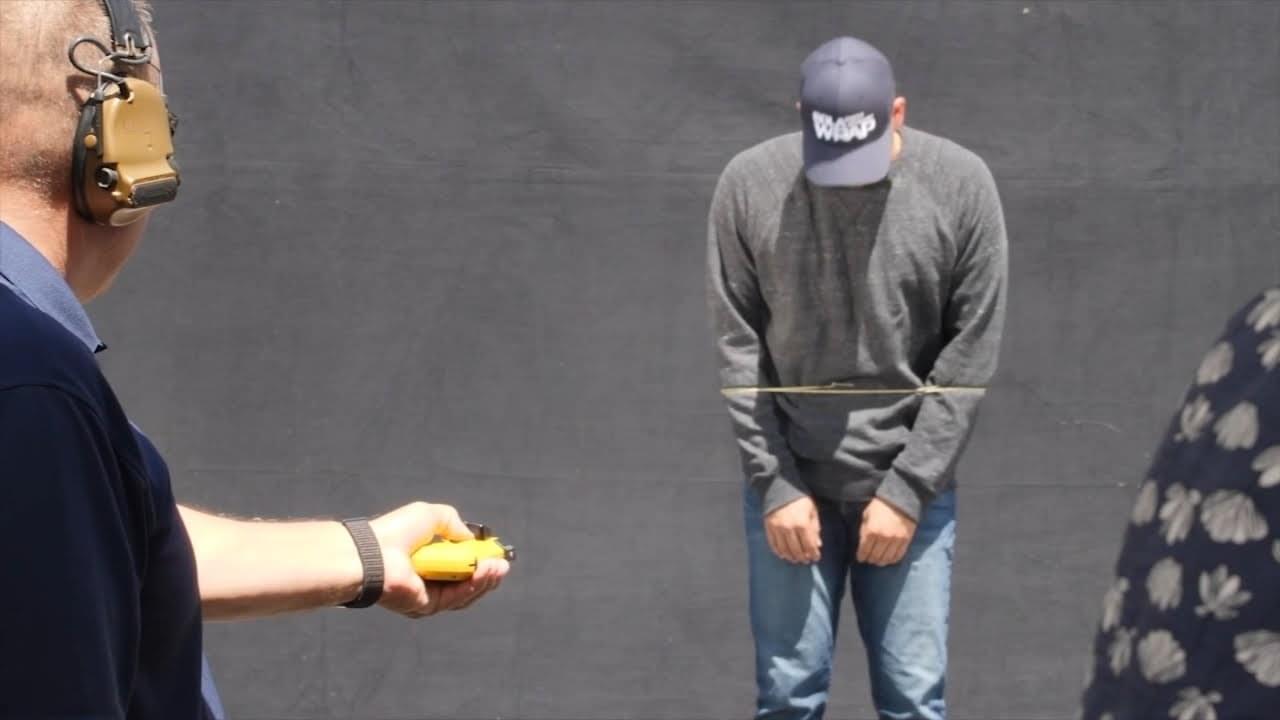

A new tool, described as “flying handcuffs,” will soon be used by San Francisco police. https://abc7ne.ws/3x2ZZVJ#restraint #police #handcuffs #crime #lasso #…
Jun 8, 2024
The Order of Time: Carlo Rovelli explains that time doesn’t really exist
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: futurism, quantum physics

The bestselling author of Seven Brief Lessons on Physics introduces the mysteries of time, further explored in his new book, The Order of Time.
Time is a mystery that does not cease to puzzle us. Philosophers, artists and poets have long explored its meaning while scientists have found that its structure is different from the simple idea we have of it. From Einstein to quantum theory and beyond, our understanding of time has been undergoing radical transformations. Time flows at a different speed in different places, the past and the future differ far less than we might think, and the very notion of the present evaporates in the vast universe.
Continue reading “The Order of Time: Carlo Rovelli explains that time doesn’t really exist” »
Jun 8, 2024
Noetic Aether Part One; Cutting the Einsteinian Knot
Posted by Dan Breeden in category: futurism

Related channels worth checking out; https://youtu.be/SBx1_V8n-Dg?si=rY8mz2tFxM5V8BkG https://youtu.be/0CSL702JSdY?si=uHv-hc2OSJmpLjlJ
Jun 7, 2024
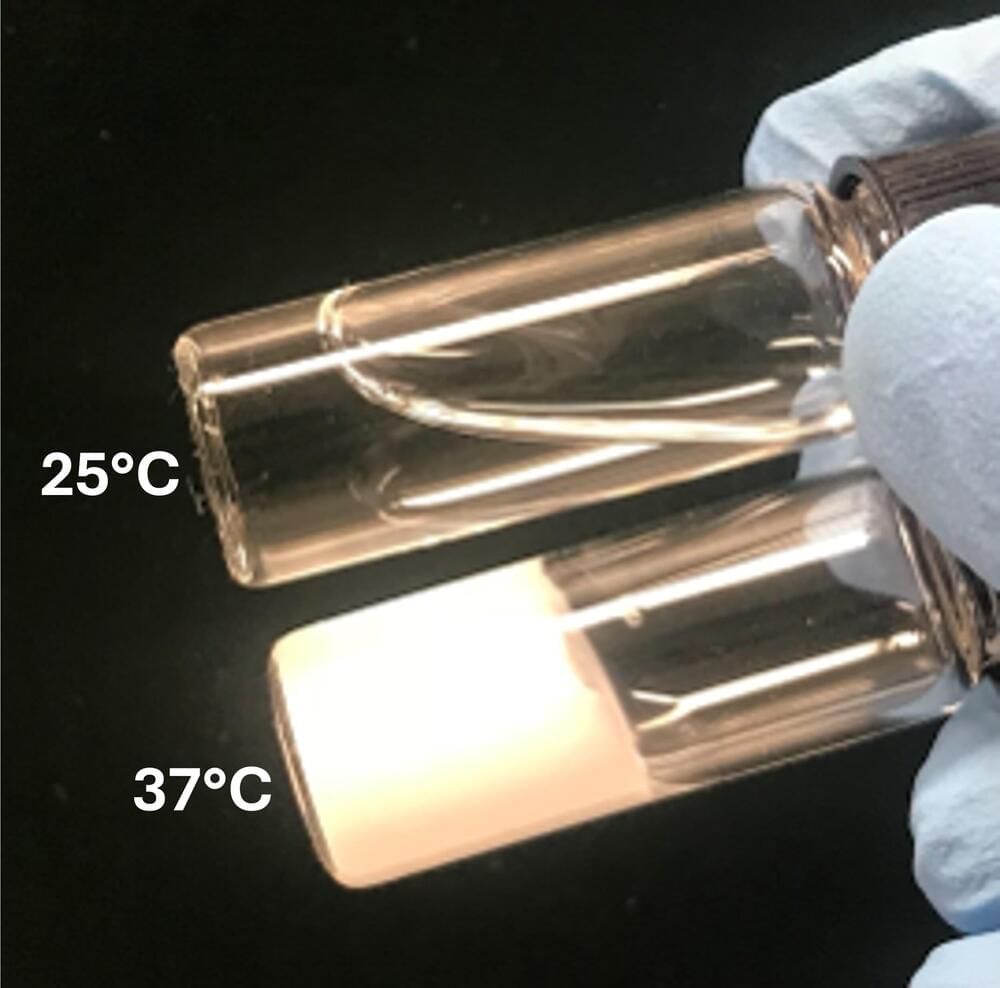
Antioxidant gel preserves islet function after pancreas removal
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in category: futurism
\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t\t.
Northwestern University researchers have developed a new antioxidant biomaterial that someday could provide much-needed relief to people living with chronic pancreatitis.
Jun 7, 2024
A Researcher’s Model Suggests We’re Connected to an Anti-Universe
Posted by Paul Battista in category: futurism
Jun 6, 2024
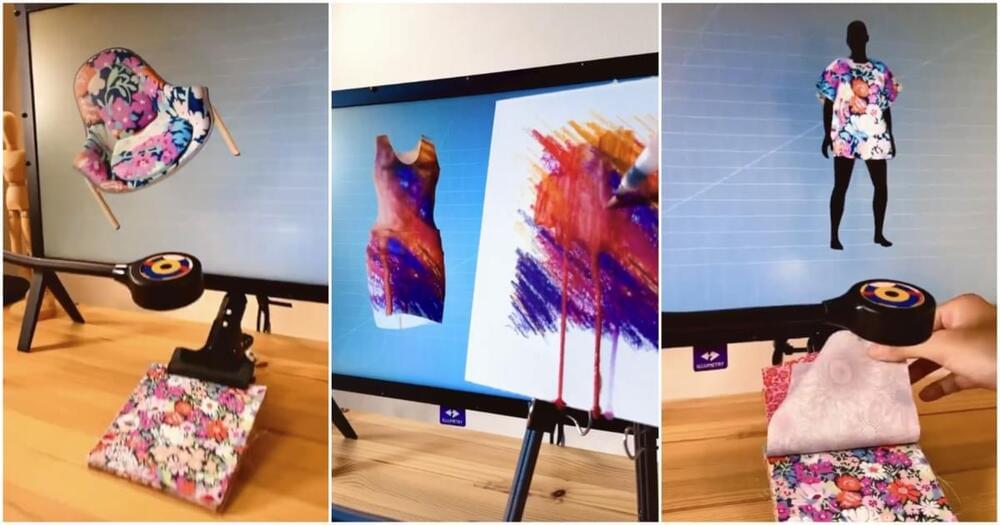
Shopping Made Magical with Holographic Projection
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in category: futurism
Jun 6, 2024
People Aren’t Happy With Adobe’s Spyware-Like Terms of Service Update
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in category: futurism
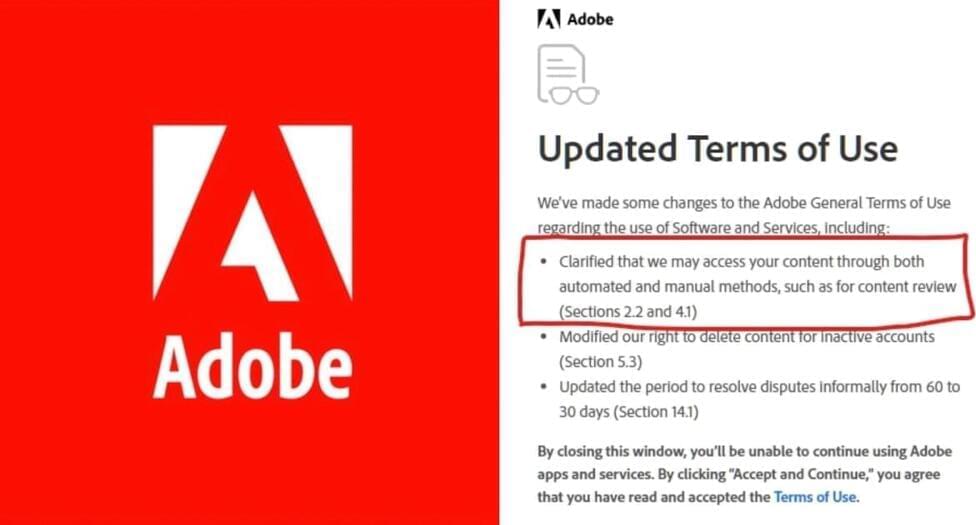
Users of Photoshop, Substance 3D, and other Adobe products are now required to provide the company with unlimited access to their creations.