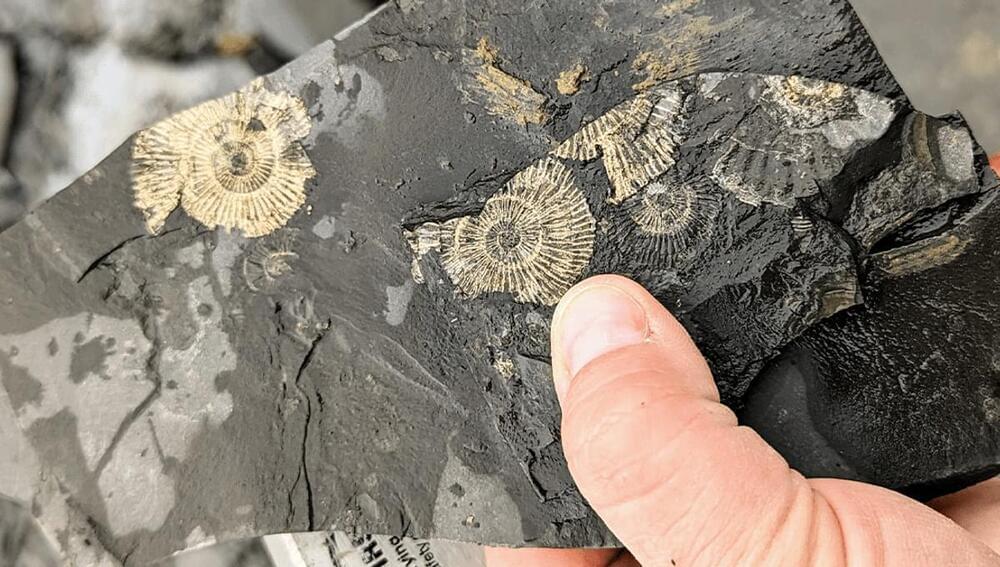
All that glitters isn’t usually gold, and the same is true for 183 million-year-old fossils found in the Posidonia Shale. Moreover, while the researchers used to think the shiny gold coating on the fossils was fool’s gold, new research has revealed a more surprising answer.
The Posidonia Shale in southwest Germany is the source of many of these golden-hued fossils, particularly those of soft-bodied sea life such as squid and ichthyosaur embryos that were around in the early Jurassic. These geological deposits containing soft-bodied preserves are known as Konservat-Lagerstätten and are extremely rare.
Previously it was thought that anoxic conditions helped to fossilize these specimens. While pyrite, also known as fool’s gold, was thought to be the source of this shine, a closer inspection has revealed more about the conditions in which these fossils were formed.