Aug 20, 2023
New Discovery Could Revolutionize Sustainable Chemical Synthesis
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, food
A new discovery by the Polytechnic University of Milan opens up new perspectives in the field of sustainable chemical synthesis, promoting innovative solutions that allow chemicals to be created in a more efficient and environmentally friendly way. The findings were recently published in the journal Nature Synthesis.
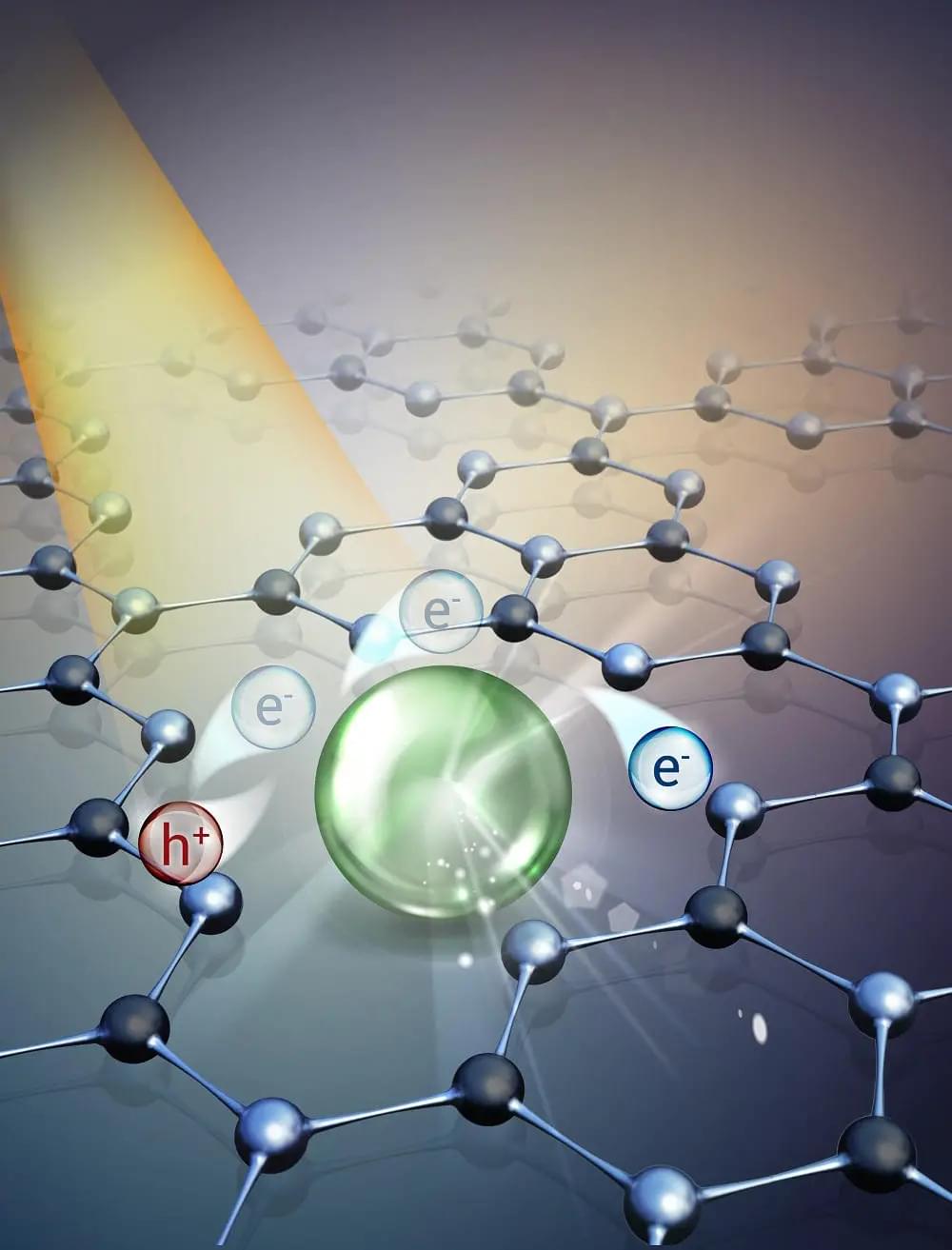
Using the innovative technique of dispersing isolated atoms on carbon nitride supports, the team developed a catalyst that is more active and selective in esterification reactions. This is an important reaction in which carboxylic acids and bromides are combined to form products used in the manufacture of medicines, food additives, and polymers.
The revolutionary feature of this new catalyst is that it reduces the use of rare metals, a significant step towards conserving critical resources and making processes more sustainable. In addition, the catalyst can be activated by sunlight, eliminating the need for energy-intensive methods. This discovery holds enormous potential in reducing dependence on finite resources and lowering the environmental impact of catalytic processes.