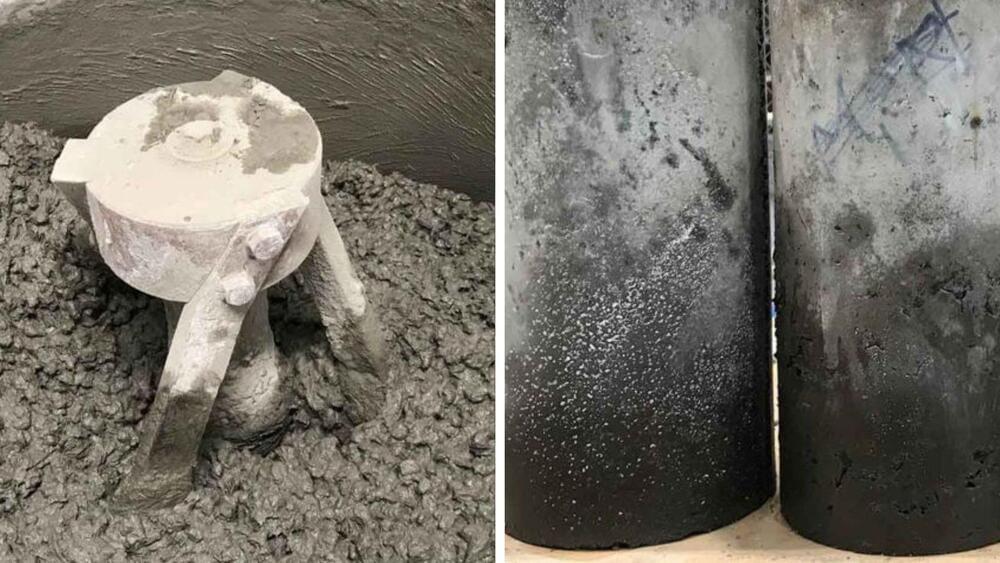
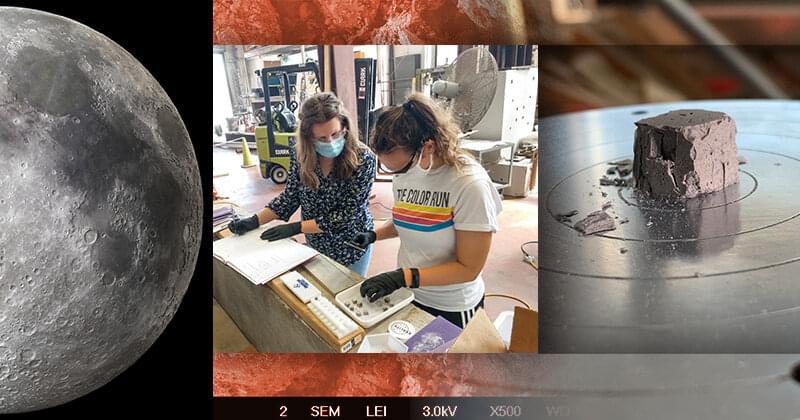
The new concrete made of tyres will be eco-friendly and cheaper. Engineers from RMIT succeeded in producing concrete from materials such as gravel, tyre, rubber, and crushed rock. It is believed that this innovation will be cheaper and eco-friendly. The team is now looking into reinforcing the concrete to see how it can work in structural elements. A group of researchers from the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology (RMIT), has succeeded in replacing the classic method of making concrete, which is made of gravel and crushed rock, with rubber from discarded tyres that are suitable for building codes.
According to the press release that has been published by the university, new greener and lighter concrete also promises to reduce manufacturing and transportation costs significantly. Small amounts of rubber particles from tyres are already used to replace these concrete aggregates. However, the previous process of replacing all concrete with aggregates had not been successful.
The study published in the Resources, Conservation & Recycling journal showed the tyres’ manufacturing process.
Continue reading “Australian engineers produce concrete from tyre, rubber, and rocks” »