Aug 11, 2018
High thermal conductivity in cubic boron arsenide crystals
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: computing, engineering
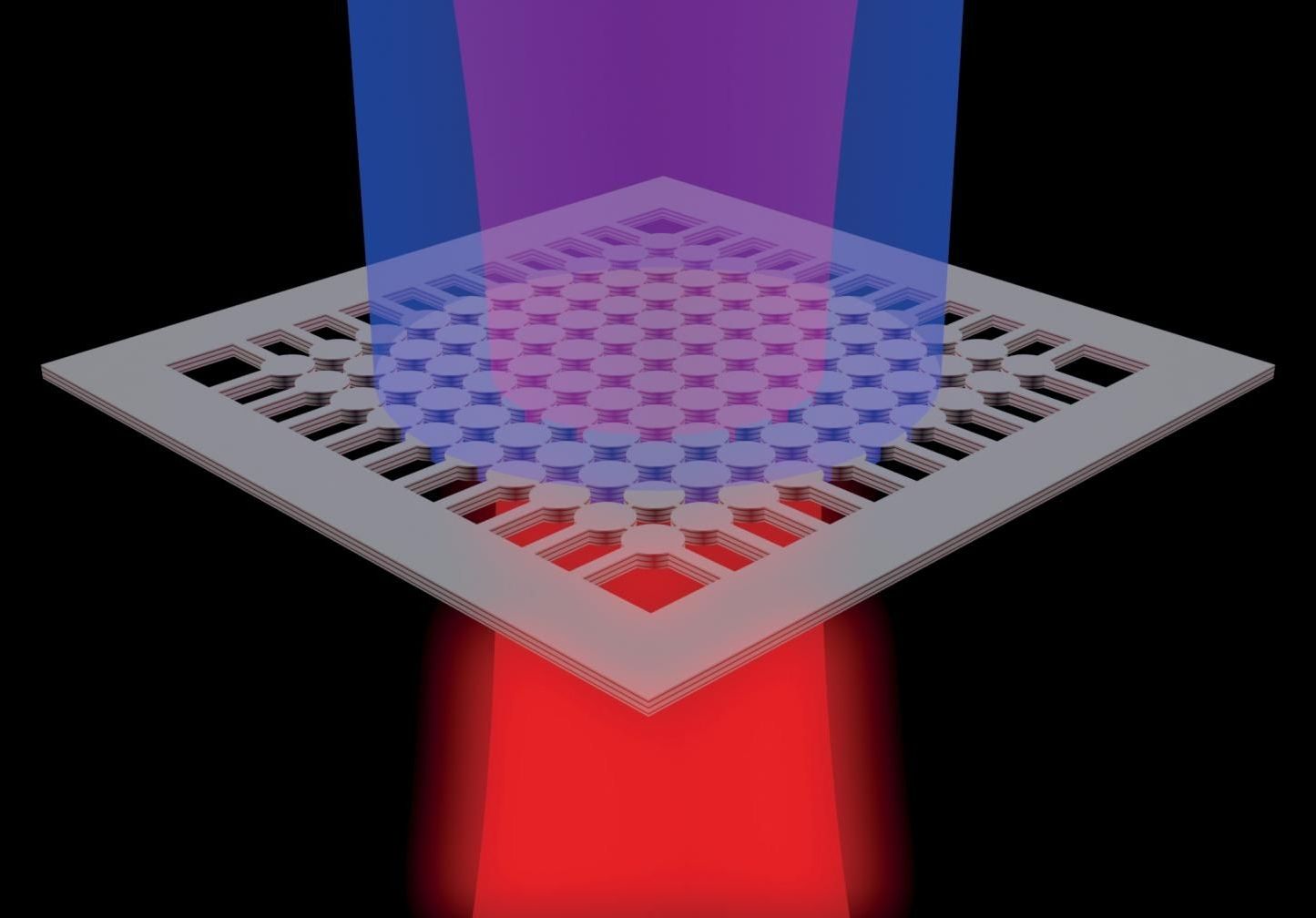
Thermal management becomes increasingly important as we decrease device size and increase computing power. Engineering materials with high thermal conductivity, such as boron arsenide (BAs), is hard because it is essential to avoid defects and impurities during synthesis, which would stop heat flow. Three different research groups have synthesized BAs with a thermal conductivity around 1000 watts per meter-kelvin: Kang et al., Li et al., and Tian et al. succeeded in synthesizing high-purity BAs with conductivities half that of diamond but more than double that of conventional metals (see the Perspective by Dames). The advance validates the search for high-thermal-conductivity materials and provides a new material that may be more easily integrated into semiconducting devices.