The past few decades have seen astonishing advances in imaging technology, from high-speed optical sensors that process over two million frames per second to tiny lensless cameras that record images using a single pixel.
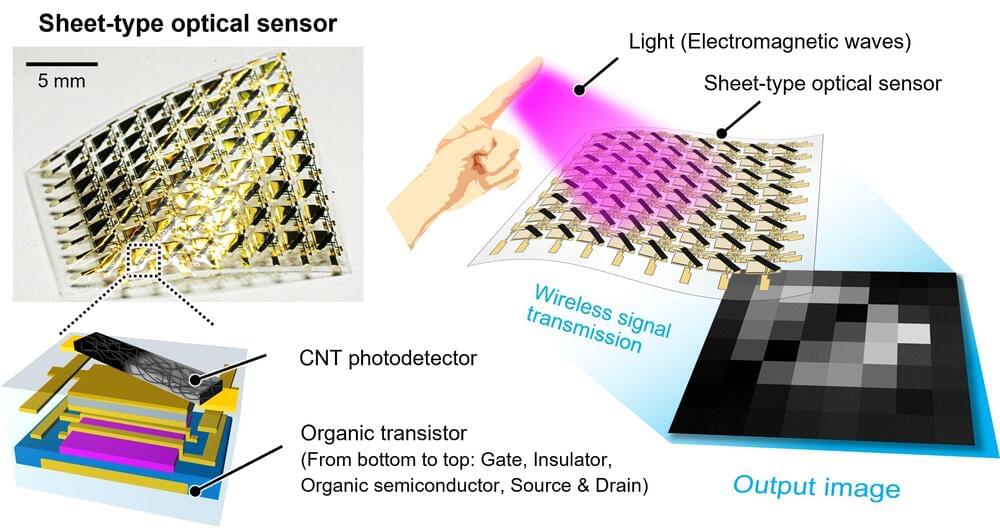
In a study published in Advanced Materials, researchers from SANKEN (The Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research), at Osaka University have developed an optical sensor on an ultrathin, flexible sheet that can be bent without breaking. In fact, this sensor is so flexible, it will work even after it has been crumpled into a ball.
In a camera, the optical sensor is the device that senses the light that has passed through a lens, similar to the retina inside a human eye.