Unfortunately, these precise cell arrangements are also why artificial muscles are difficult to recreate in the lab. Despite being soft, squishy, and easily damaged, our muscles can perform incredible feats—adapt to heavy loads, sense the outside world, and rebuild after injury. A main reason for these superpowers is alignment—that is, how muscle cells orient to form stretchy fibers.
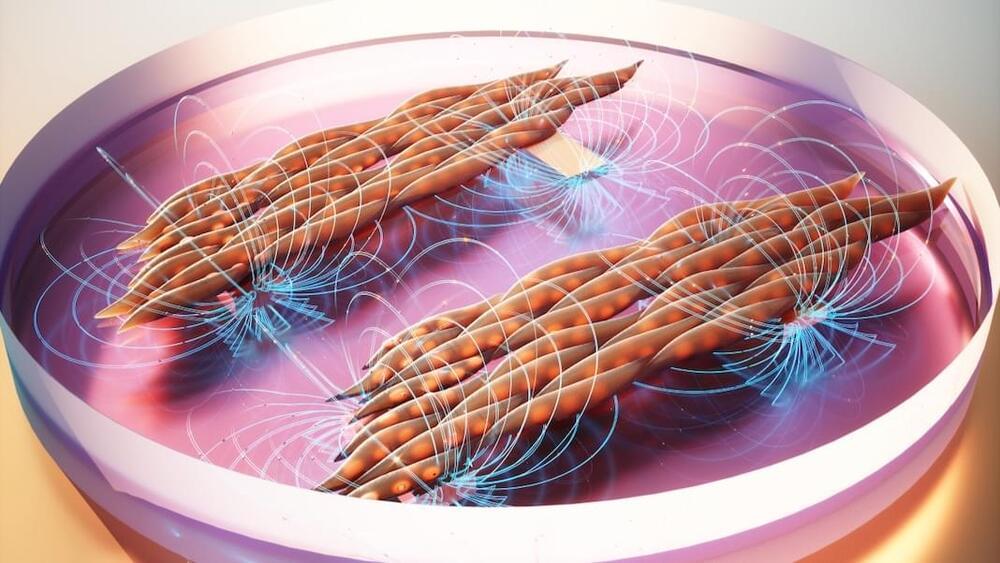
Now, a new study suggests that the solution to growing better lab-grown muscles may be magnets. Led by Dr. Ritu Raman at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), scientists developed a magnetic hydrogel “sandwich” that controls muscle cell orientation in a lab dish. By changing the position of the magnets, the muscle cells aligned into fibers that contracted in synchrony as if they were inside a body.
The whole endeavor sounds rather Frankenstein. But lab-grown tissues could one day be grafted into people with heavily damaged muscles—either from inherited diseases or traumatic injuries—and restore their ability to navigate the world freely. Synthetic muscles could also coat robots, providing them with human-like senses, flexible motor control, and the ability to heal after inevitable scratches and scrapes.