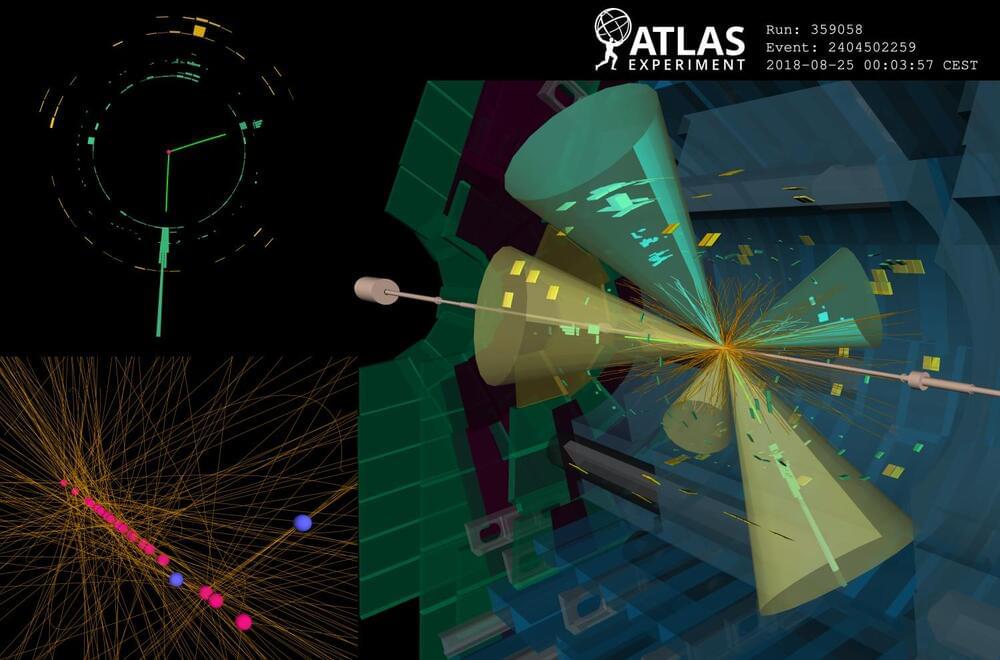
The Higgs boson has an extremely short lifespan, living for about 10–22 seconds before quickly decaying into other particles. For comparison, in that brief time, light can only travel about the width of a small atomic nucleus. Scientists study the Higgs boson by detecting its decay products in particle collisions at the Large Hadron Collider. But what if the Higgs boson could also decay into unexpected new particles that are long-lived? What if these particles can travel a few centimeters through the detector before they decay? These long-lived particles (LLPs) could shed light on some of the universe’s biggest mysteries, such as the reason matter prevailed over antimatter in the early universe and the nature of dark matter. Searching for LLPs is extremely challenging because they rarely interact with matter, making them difficult to observe in a particle detector. However, their unusual signatures provide exciting prospects for discovery. Unlike particles that leave a continuous track, LLPs result in noticeable displacements between their production and decay points within the detector. Identifying such a signature requires dedicated algorithms. In a new study submitted to Physical Review Letters, ATLAS scientists used a new algorithm to search for LLPs produced in the decay of Higgs bosons. Boosting sensitivity with a new algorithm Figure 1: A comparison of the radial distributions of reconstructed displaced vertices in a simulated long-lived particle (LLP) sample using the legacy and new (updated) track reconstruction configurations. The circular markers represent reconstructed vertices that are matched to LLP decay vertices and the dashed lines represent reconstructed vertices from background decay vertices (non-LLP). (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) Despite being critical to the LLP searches, dedicated reconstruction algorithms were previously so resource intensive that they could only be applied to less than 10% of all recorded ATLAS data. Recently, however, ATLAS scientists implemented a new “Large-Radius Tracking” algorithm (LRT), which significantly speeds up the reconstruction of charged particle trajectories in the ATLAS Inner Detector that do not point back to the primary proton-proton collision point, while drastically reducing backgrounds and random combinations of detector signals. The LRT algorithm is executed after the primary tracking iteration using exclusively the detector hits (energy deposits from charged particles recorded in individual detector elements) not already assigned to primary tracks. As a result, ATLAS saw an enormous increase in the efficiency of identifying LLP decays (see Figure 1). The new algorithm also improved CPU processing time more than tenfold compared to the legacy implementation, and the disk space usage per event was reduced by more than a factor of 50. These improvements enabled physicists to fully integrate the LRT algorithm into the standard ATLAS event reconstruction chain. Now, every recorded collision event can be scrutinized for the presence of new LLPs, greatly enhancing the discovery potential of such signatures. Physicists are searching for Higgs bosons decaying into new long-lived particles, which may leave a ‘displaced’ signature in the ATLAS detector. Exploring the dark with the Higgs boson Figure 2: Observed 95% confidence-limit on the decay of the Higgs boson to a pair of long-lived s particles that decay back to Standard-Model particles shown as a function of the mean proper decay length ( of the long-lived particle. The observed limits for the Higgs Portal model from the previous ATLAS search are shown with the dotted lines. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) In their new result, ATLAS scientists employed the LRT algorithm to search for LLPs that decay hadronically, leaving a distinct signature of one or more hadronic “jets” of particles originating at a significantly displaced position from the proton–proton collision point (a displaced vertex). Physicists also focused on the Higgs “portal” model, in which the Higgs boson mediates interactions with dark-matter particles through its coupling to a neutral boson s, resulting in exotic decays of the Higgs boson to a pair of long-lived s particles that decay into Standard-Model particles. The ATLAS team studied collision events with unique characteristics consistent with the production of the Higgs boson. The background processes that mimic the LLP signature are complex and challenging to model. To achieve good discrimination between signal and background processes, ATLAS physicists used a machine learning algorithm trained to isolate events with jets arising from LLP decays. Complementary to this, a dedicated displaced vertex reconstruction algorithm was used to pinpoint the origin of hadronic jets originating from the decay of LLPs. This new search did not uncover any events featuring Higgs-boson decays to LLPs. It improves bounds on Higgs-boson decays to LLPs by a factor of 10 to 40 times compared to the previous search using the exact same dataset (see Figure 2)! For the first time at the LHC, bounds on exotic decays of the Higgs boson for low LLP masses (less than 16 GeV) have surpassed results for direct searches of exotic Higgs-boson decays to undetected states. About the event display: A 13 TeV collision event recorded by the ATLAS experiment containing two displaced decay vertices (blue circles) significantly displaced from the beam line showing “prompt” non displaced decay vertices (pink circles). The event characteristics are compatible with what would be expected if a Higgs boson is produced in association with a Z boson (decaying to two electrons indicated by green towers), and decayed into two LLPs (decaying into two b-quarks each). Tracks shown in yellow and jets are indicated by cones. The green and yellow blocks correspond to energy deposition in the electromagnetic and hadronic calorimeters, respectively. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) Learn more Search for light long-lived particles in proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV using displaced vertices in the ATLAS inner detector (Submitted to PRL, arXiv:2403.15332, see figures) Performance of the reconstruction of large impact parameter tracks in the inner detector of ATLAS (Eur. Phys. J. C 83 (2023) 1,081, arXiv:2304.12867, see figures) Search for exotic decays of the Higgs boson into long-lived particles in proton-proton collisions at 13 TeV using displaced vertices in the ATLAS inner detector (JHEP 11 (2021) 229, arXiv:2107.06092, see figures)

















